編輯:關於Android編程
其實這個安卓計算機,所有的後台思想與《C#計算器編寫代碼》是一模一樣的。Win窗體程序移植到安卓,從C#到Java其實很簡單的,因為兩者的基本語法都很相像,唯一的難點是安卓的xml布局部分,不像C#窗體能夠直接拖。
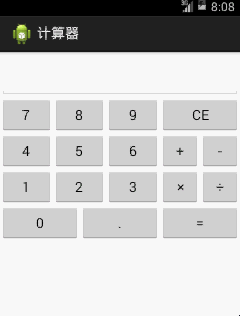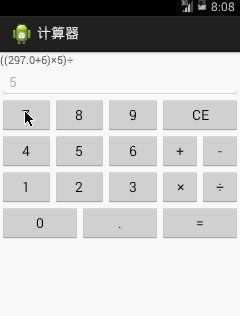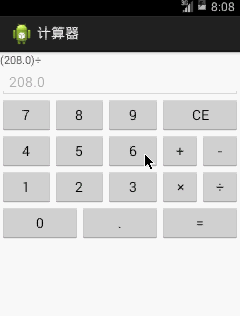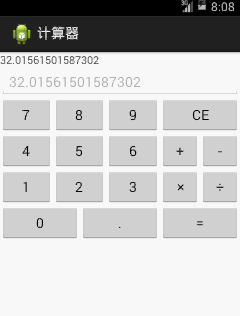
還是如下圖一個能夠完成基本四則運算的計算器:
先在res\values\strings.xml設置按鈕相應的字體,以免布局文件警告滿天飛:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="app_name">計算器</string> <string name="bt_1">1</string> <string name="bt_2">2</string> <string name="bt_3">3</string> <string name="bt_4">4</string> <string name="bt_5">5</string> <string name="bt_6">6</string> <string name="bt_7">7</string> <string name="bt_8">8</string> <string name="bt_9">9</string> <string name="bt_0">0</string> <string name="bt_point">.</string> <string name="bt_ce">CE</string> <string name="bt_plus">+</string> <string name="bt_minus">-</string> <string name="bt_multi">×</string> <string name="bt_div">÷</string> <string name="bt_result">=</string> </resources>
之後,布局部分采用了《【Android】關於百分比布局多個LinearLayout嵌套時出現的問題與解決方案》(點擊打開鏈接)的思想,具體如下圖,一個TextView、一個EditText,皆直接用match_parent占據整行的寬度,之後利用LinearLayout與TableLayout作橫向比例的劃分。
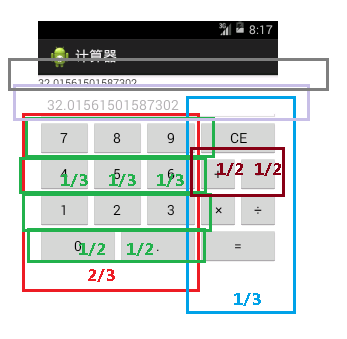
因此,res\layout\activity_main.xml具體代碼如下,之後的操作要操作的組件加上Id,這裡加上《【Android】內存卡圖片讀取器,圖庫app》(點擊打開鏈接)的ScrollView是防止某些手機屏幕過少,加上垂直滾動條:
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:enabled="false"
android:inputType="none"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_7"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_7" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_8"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_8" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_9"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_9" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_4"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_4" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_5"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_6"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_6" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_3"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_3" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_0"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_point"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_point" />
</LinearLayout>
</TableLayout>
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_ce"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/bt_ce" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_plus"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_plus" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_minus"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_minus" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_multi"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_multi" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_div"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="@string/bt_div" />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_result"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/bt_result" />
</TableLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
之後是MainActivity.java沒什麼好說的,基本與直接Win窗體的《C#計算器編寫代碼》,將C#改成java是一個很簡單的事情。唯一注意的是,這裡的按鈕比較多,因此不建議像《【Android】利用Java代碼布局,按鈕添加點擊事件》(點擊打開鏈接)一樣,使用內部匿名類實現按鈕的點擊事件,應該讓MainActivity實現OnClickListener接口,之後在繼承下來的onClick方法,根據傳遞過來的View v中的id,利用switch-case結構來搞,這樣清晰明了。
package com.calculator;
import java.util.*;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.app.Activity;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private List<Double> value_list = new ArrayList<Double>();// 存用戶輸入的數字
private List<Integer> operator_list = new ArrayList<Integer>();// 存用戶輸入的運算符,定義+為0,-為1,×為2,÷為3
// 狀態記錄
private boolean add_flag = false;// +按下
private boolean minus_flag = false;// -按下
private boolean multi_flag = false;// ×按下
private boolean div_flag = false;// ÷按下
private boolean result_flag = false;// =按下
private boolean can_operate_flag = false;// 按下=是否響應
private TextView textView1;
private EditText editText1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.bt_0).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_1).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_2).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_3).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_4).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_5).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_6).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_7).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_8).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_9).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_point).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_ce).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_plus).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_minus).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_multi).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_div).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.bt_result).setOnClickListener(this);
textView1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
editText1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText1);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.bt_0:
num_down("0");
break;
case R.id.bt_1:
num_down("1");
break;
case R.id.bt_2:
num_down("2");
break;
case R.id.bt_3:
num_down("3");
break;
case R.id.bt_4:
num_down("4");
break;
case R.id.bt_5:
num_down("5");
break;
case R.id.bt_6:
num_down("6");
break;
case R.id.bt_7:
num_down("7");
break;
case R.id.bt_8:
num_down("8");
break;
case R.id.bt_9:
num_down("9");
break;
case R.id.bt_point:
num_down(".");
break;
case R.id.bt_plus:
if (!add_flag)// 防止用戶多次輸入一個符號鍵,符號鍵只允許輸入一次
{
result_flag = false;
value_list.add(Double.parseDouble(editText1.getText()
.toString()));// 將當前已輸入的數字放入value_list
operator_list.add(0);
textView1.setText(textView1.getText() + "+");
add_flag = true;
can_operate_flag = false;// 剛剛輸入完符號,不能構成一條正常的表達式,如111+,設置為不可運行狀態
}
break;
case R.id.bt_minus:
if (!minus_flag) {
result_flag = false;
value_list.add(Double.parseDouble(editText1.getText()
.toString()));
operator_list.add(1);
textView1.setText(textView1.getText() + "-");
minus_flag = true;
can_operate_flag = false;
}
break;
case R.id.bt_multi:
if (!multi_flag) {
result_flag = false;
value_list.add(Double.parseDouble(editText1.getText()
.toString()));
operator_list.add(2);
textView1.setText("(" + textView1.getText() + ")×");// 給前面的已經輸入的東西加個括號。(運算符棧問題是一個很復雜的數據結構問題,這裡不做,:P)
multi_flag = true;
can_operate_flag = false;
}
break;
case R.id.bt_div:
if (!div_flag) {
result_flag = false;
value_list.add(Double.parseDouble(editText1.getText()
.toString()));
operator_list.add(3);
textView1.setText("(" + textView1.getText() + ")÷");
div_flag = true;
can_operate_flag = false;
}
break;
case R.id.bt_result:
if (value_list.size() > 0 && operator_list.size() > 0
&& can_operate_flag) {// 需要防止用戶沒輸入數字,或者只輸入了一個數,就按=。
value_list.add(Double.parseDouble(editText1.getText()
.toString()));
double total = value_list.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < operator_list.size(); i++) {
int _operator = operator_list.get(i);// operator是C#的運算符重載的關鍵字,前面加個_來區別
switch (_operator) {
case 0:
total += value_list.get(i + 1);
break;
case 1:
total -= value_list.get(i + 1);
break;
case 2:
total *= value_list.get(i + 1);
break;
case 3:
total /= value_list.get(i + 1);
break;
}
}
editText1.setText(total + "");
textView1.setText(total + "");
operator_list.clear();// 算完,就清空累積數字與運算數組
value_list.clear();
result_flag = true;// 表示=按下
}
break;
case R.id.bt_ce:
operator_list.clear();
value_list.clear();
add_flag = false;
minus_flag = false;
multi_flag = false;
div_flag = false;
result_flag = false;
can_operate_flag = false;
editText1.setText("");
textView1.setText("");
break;
}
}
// 數字鍵按下,含0與.,類似000001223這類情況這裡允許,因為java可以講000001223自己轉化為1223
private void num_down(String num) {
if (add_flag || minus_flag || multi_flag || div_flag || result_flag) {
if (result_flag)// 按下等號,剛剛算完一個運算的狀態
{
textView1.setText("");
}
editText1.setText("");// 如果用戶剛剛輸入完一個運算符
add_flag = false;
minus_flag = false;
multi_flag = false;
div_flag = false;
result_flag = false;
}
if ((num.equals(".") && editText1.getText().toString().indexOf(".") < 0)
|| !num.equals(".")) {
// 如果用戶輸入的是小數點.,則要判斷當前已輸入的數字中是否含有小數點.才允許輸入
editText1.setText(editText1.getText() + num);
textView1.setText(textView1.getText() + num);
can_operate_flag = true;
}
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
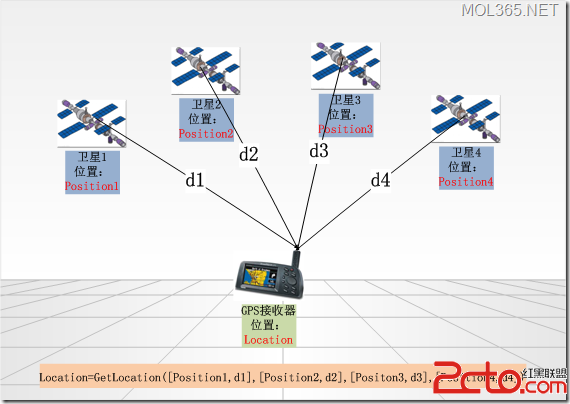 android GPS應用程序設計
android GPS應用程序設計
GPS簡介 GPS是英文Global Positioning System(全球定位系統)的簡稱。GPS是20世紀70年代由美國陸海空三軍聯合研制的 新一代空間衛星導航定
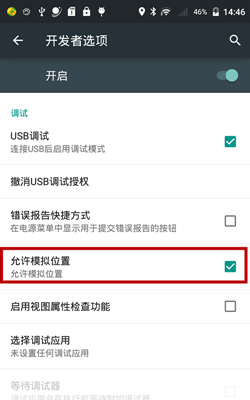 Android 使用模擬位置(支持Android 6.0)
Android 使用模擬位置(支持Android 6.0)
開啟系統設置中的模擬位置Android 6.0 以下:【開發者選項 -> 允許模擬位置】Android 6.0 及以上:【開發者選項 -> 選擇模擬位置信息應
 Android通過JNI實現守護進程
Android通過JNI實現守護進程
開發一個需要常住後台的App其實是一件非常頭疼的事情,不僅要應對國內各大廠商的ROM,還需要應對各類的安全管家...雖然不斷的研究各式各樣的方法,但是效果並不好,比如任務
 Android開發之自定義控件用法詳解
Android開發之自定義控件用法詳解
本文實例講述了Android開發之自定義控件用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:今天和大家分享下組合控件的使用。很多時候android自定義控件並不能滿足需求,如何做呢