編輯:關於Android編程
轉載請標明出處:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/24252901
很多的Android入門程序猿來說對於Android自定義View,可能都是比較恐懼的,但是這又是高手進階的必經之路,所有准備在自定義View上面花一些功夫,多寫一些文章。先總結下自定義View的步驟:
1、自定義View的屬性
2、在View的構造方法中獲得我們自定義的屬性
[ 3、重寫onMesure ]
4、重寫onDraw
我把3用[]標出了,所以說3不一定是必須的,當然了大部分情況下還是需要重寫的。
1、自定義View的屬性,首先在res/values/ 下建立一個attrs.xml , 在裡面定義我們的屬性和聲明我們的整個樣式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <attr name="titleText" format="string" /> <attr name="titleTextColor" format="color" /> <attr name="titleTextSize" format="dimension" /> <declare-styleable name="CustomTitleView"> <attr name="titleText" /> <attr name="titleTextColor" /> <attr name="titleTextSize" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
我們定義了字體,字體顏色,字體大小3個屬性,format是值該屬性的取值類型:
一共有:string,color,demension,integer,enum,reference,float,boolean,fraction,flag;不清楚的可以google一把。
然後在布局中聲明我們的自定義View
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.customview01" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.example.customview01.view.CustomTitleView android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="100dp" custom:titleText="3712" custom:titleTextColor="#ff0000" custom:titleTextSize="40sp" /> </RelativeLayout>
一定要引入 xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.customview01"我們的命名空間,後面的包路徑指的是項目的package
2、在View的構造方法中,獲得我們的自定義的樣式
/**
* 文本
*/
private String mTitleText;
/**
* 文本的顏色
*/
private int mTitleTextColor;
/**
* 文本的大小
*/
private int mTitleTextSize;
/**
* 繪制時控制文本繪制的范圍
*/
private Rect mBound;
private Paint mPaint;
public CustomTitleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomTitleView(Context context)
{
this(context, null);
}
/**
* 獲得我自定義的樣式屬性
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyle
*/
public CustomTitleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
/**
* 獲得我們所定義的自定義樣式屬性
*/
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomTitleView, defStyle, 0);
int n = a.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr)
{
case R.styleable.CustomTitleView_titleText:
mTitleText = a.getString(attr);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomTitleView_titleTextColor:
// 默認顏色設置為黑色
mTitleTextColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.BLACK);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomTitleView_titleTextSize:
// 默認設置為16sp,TypeValue也可以把sp轉化為px
mTitleTextSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(
TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 16, getResources().getDisplayMetrics()));
break;
}
}
a.recycle();
/**
* 獲得繪制文本的寬和高
*/
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setTextSize(mTitleTextSize);
// mPaint.setColor(mTitleTextColor);
mBound = new Rect();
mPaint.getTextBounds(mTitleText, 0, mTitleText.length(), mBound);
}
我們重寫了3個構造方法,默認的布局文件調用的是兩個參數的構造方法,所以記得讓所有的構造調用我們的三個參數的構造,我們在三個參數的構造中獲得自定義屬性。
3、我們重寫onDraw,onMesure調用系統提供的:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
mPaint.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
canvas.drawRect(0, 0, getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight(), mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(mTitleTextColor);
canvas.drawText(mTitleText, getWidth() / 2 - mBound.width() / 2, getHeight() / 2 + mBound.height() / 2, mPaint);
}
此時的效果是:
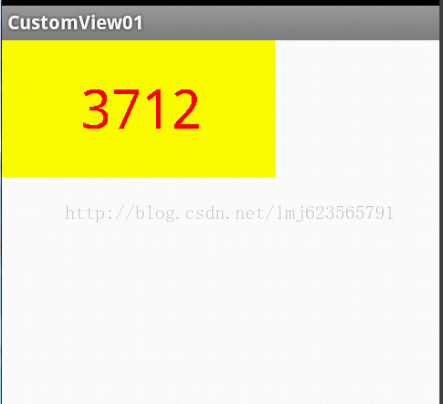
是不是覺得還不錯,基本已經實現了自定義View。但是此時如果我們把布局文件的寬和高寫成wrap_content,會發現效果並不是我們的預期:

系統幫我們測量的高度和寬度都是MATCH_PARNET,當我們設置明確的寬度和高度時,系統幫我們測量的結果就是我們設置的結果,當我們設置為WRAP_CONTENT,或者MATCH_PARENT系統幫我們測量的結果就是MATCH_PARENT的長度。
所以,當設置了WRAP_CONTENT時,我們需要自己進行測量,即重寫onMesure方法”:
重寫之前先了解MeasureSpec的specMode,一共三種類型:
EXACTLY:一般是設置了明確的值或者是MATCH_PARENT
AT_MOST:表示子布局限制在一個最大值內,一般為WARP_CONTENT
UNSPECIFIED:表示子布局想要多大就多大,很少使用
下面是我們重寫onMeasure代碼:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int width;
int height ;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
{
width = widthSize;
} else
{
mPaint.setTextSize(mTitleTextSize);
mPaint.getTextBounds(mTitle, 0, mTitle.length(), mBounds);
float textWidth = mBounds.width();
int desired = (int) (getPaddingLeft() + textWidth + getPaddingRight());
width = desired;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
{
height = heightSize;
} else
{
mPaint.setTextSize(mTitleTextSize);
mPaint.getTextBounds(mTitle, 0, mTitle.length(), mBounds);
float textHeight = mBounds.height();
int desired = (int) (getPaddingTop() + textHeight + getPaddingBottom());
height = desired;
}
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
現在我們修改下布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.customview01" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.example.customview01.view.CustomTitleView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" custom:titleText="3712" android:padding="10dp" custom:titleTextColor="#ff0000" android:layout_centerInParent="true" custom:titleTextSize="40sp" /> </RelativeLayout>
現在的效果是:

完全復合我們的預期,現在我們可以對高度、寬度進行隨便的設置了,基本可以滿足我們的需求。
當然了,這樣下來我們這個自定義View與TextView相比豈不是沒什麼優勢,所有我們覺得給自定義View添加一個事件:
在構造中添加:
this.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
mTitleText = randomText();
postInvalidate();
}
});
private String randomText()
{
Random random = new Random();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
while (set.size() < 4)
{
int randomInt = random.nextInt(10);
set.add(randomInt);
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (Integer i : set)
{
sb.append("" + i);
}
return sb.toString();
}
下面再來運行:

我們添加了一個點擊事件,每次讓它隨機生成一個4位的隨機數,有興趣的可以在onDraw中添加一點噪點,然後改寫為驗證碼,是不是感覺很不錯。
源碼下載: Android自定義View
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 如何使用Fiddler對Android應用進行抓包
如何使用Fiddler對Android應用進行抓包
1.場景還原之FliddlerFiddler是一款抓包神器,近日,由於項目中要嵌入H5頁面,公司又沒專門的UI設計師,所以你懂得,這個任務就要給我喽!可憐的我並沒有藝術細
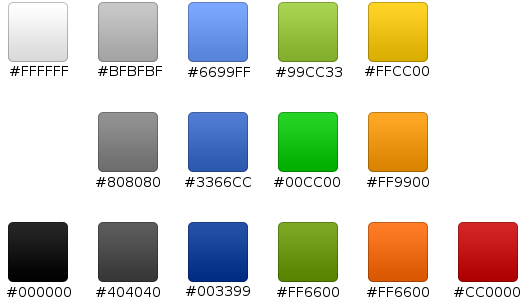 Android 界面開發顏色整理
Android 界面開發顏色整理
下圖是幫助文檔中的關於界面開發的推薦色值,大家可以參考一下: 補充一些常用的顏色值: <color name=white>#f
 Android中的腦殘設計總結
Android中的腦殘設計總結
Trackball軌跡球 這有點類似於PC上面的鼠標,可以用於導航,為此便有了Focus,但是這實際操作意義並不大,因為整個屏幕都是觸控的,還用導航干什麼,先把Focus
 Android源碼系列之深入理解ImageView的ScaleType屬性
Android源碼系列之深入理解ImageView的ScaleType屬性
做Android開發的童靴們肯定對系統自帶的控件使用的都非常熟悉,比如Button、TextView、ImageView等。如果你問我具體使用,我會給說:拿ImageVi