編輯:關於Android編程
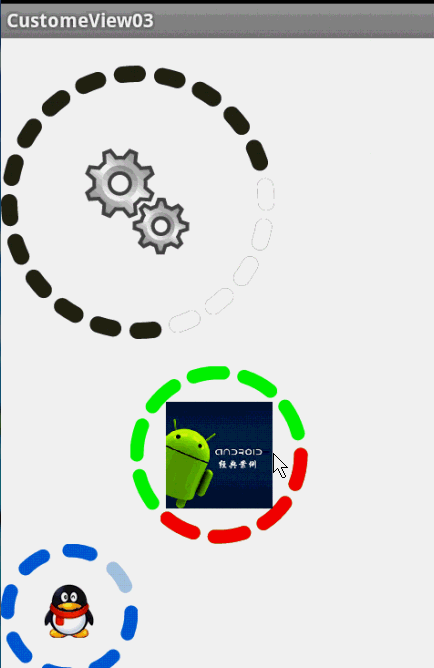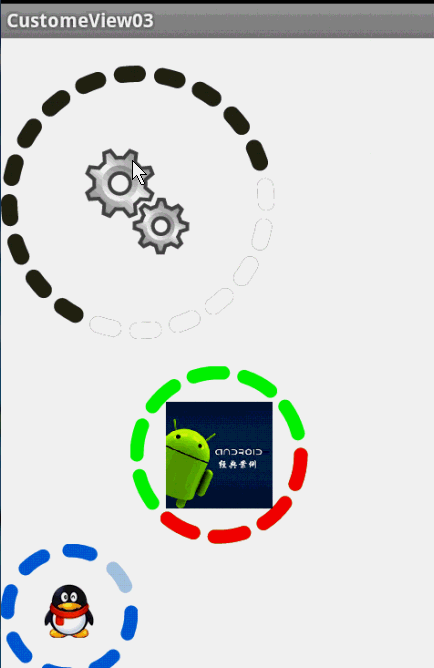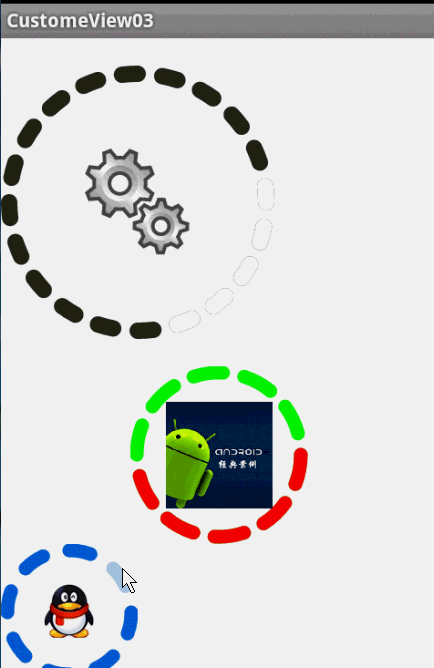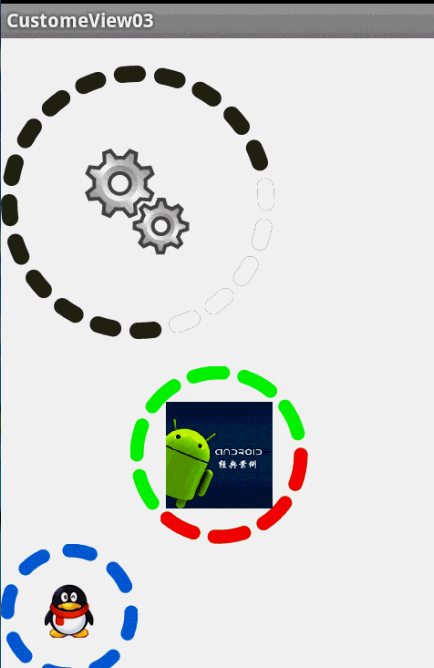
圓環交替、等待效果

效果就這樣,分析了一下,大概有這幾個屬性,兩個顏色,一個速度,一個圓環的寬度。
自定View的幾個步驟:
1、自定義View的屬性
2、在View的構造方法中獲得我們自定義的屬性
3、重寫onMesure
4、重寫onDraw
1、自定義屬性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<attr name="firstColor" format="color" />
<attr name="secondColor" format="color" />
<attr name="circleWidth" format="dimension" />
<attr name="speed" format="integer" />
<declare-styleable name="CustomProgressBar">
<attr name="firstColor" />
<attr name="secondColor" />
<attr name="circleWidth" />
<attr name="speed" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
2、在View的構造方法中獲得我們自定義的屬性
/**
* 第一圈的顏色
*/
private int mFirstColor;
/**
* 第二圈的顏色
*/
private int mSecondColor;
/**
* 圈的寬度
*/
private int mCircleWidth;
/**
* 畫筆
*/
private Paint mPaint;
/**
* 當前進度
*/
private int mProgress;
/**
* 速度
*/
private int mSpeed;
/**
* 是否應該開始下一個
*/
private boolean isNext = false;
public CustomProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomProgressBar(Context context)
{
this(context, null);
}
/**
* 必要的初始化,獲得一些自定義的值
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyle
*/
public CustomProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomProgressBar, defStyle, 0);
int n = a.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr)
{
case R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_firstColor:
mFirstColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.GREEN);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_secondColor:
mSecondColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.RED);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_circleWidth:
mCircleWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(
TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX, 20, getResources().getDisplayMetrics()));
break;
case R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_speed:
mSpeed = a.getInt(attr, 20);// 默認20
break;
}
}
a.recycle();
mPaint = new Paint();
// 繪圖線程
new Thread()
{
public void run()
{
while (true)
{
mProgress++;
if (mProgress == 360)
{
mProgress = 0;
if (!isNext)
isNext = true;
else
isNext = false;
}
postInvalidate();
try
{
Thread.sleep(mSpeed);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}.start();
}
3、直接重寫onDraw,這不需要重寫onMeasure
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
int centre = getWidth() / 2; // 獲取圓心的x坐標
int radius = centre - mCircleWidth / 2;// 半徑
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mCircleWidth); // 設置圓環的寬度
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // 消除鋸齒
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); // 設置空心
RectF oval = new RectF(centre - radius, centre - radius, centre + radius, centre + radius); // 用於定義的圓弧的形狀和大小的界限
if (!isNext)
{// 第一顏色的圈完整,第二顏色跑
mPaint.setColor(mFirstColor); // 設置圓環的顏色
canvas.drawCircle(centre, centre, radius, mPaint); // 畫出圓環
mPaint.setColor(mSecondColor); // 設置圓環的顏色
canvas.drawArc(oval, -90, mProgress, false, mPaint); // 根據進度畫圓弧
} else
{
mPaint.setColor(mSecondColor); // 設置圓環的顏色
canvas.drawCircle(centre, centre, radius, mPaint); // 畫出圓環
mPaint.setColor(mFirstColor); // 設置圓環的顏色
canvas.drawArc(oval, -90, mProgress, false, mPaint); // 根據進度畫圓弧
}
}
大功完成了,當然了,唯一比較糾結的地方就是兩個顏色何時切換,如何切換,我采用上面的辦法,你也可以自己想想怎麼實現。
視頻音量調控

這樣一個效果使用自定義View來實現的話和圓環的思路差不多,所以我們一起來看:
1、先分許需要的屬性,兩個小塊的顏色、一張中間的圖片、間隙大小、一個多少個塊塊。分析完畢,開始寫attr.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<attr name="firstColor" format="color" />
<attr name="secondColor" format="color" />
<attr name="circleWidth" format="dimension" />
<attr name="dotCount" format="integer" />
<attr name="splitSize" format="integer" />
<attr name="bg" format="reference"></attr>
<declare-styleable name="CustomVolumControlBar">
<attr name="firstColor" />
<attr name="secondColor" />
<attr name="circleWidth" />
<attr name="dotCount" />
<attr name="splitSize" />
<attr name="bg" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
2、在構造中獲取這些屬性:
/**
* 第一圈的顏色
*/
private int mFirstColor;
/**
* 第二圈的顏色
*/
private int mSecondColor;
/**
* 圈的寬度
*/
private int mCircleWidth;
/**
* 畫筆
*/
private Paint mPaint;
/**
* 當前進度
*/
private int mCurrentCount = 3;
/**
* 中間的圖片
*/
private Bitmap mImage;
/**
* 每個塊塊間的間隙
*/
private int mSplitSize;
/**
* 個數
*/
private int mCount;
private Rect mRect;
public CustomVolumControlBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomVolumControlBar(Context context)
{
this(context, null);
}
/**
* 必要的初始化,獲得一些自定義的值
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyle
*/
public CustomVolumControlBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar, defStyle, 0);
int n = a.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr)
{
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_firstColor:
mFirstColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.GREEN);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_secondColor:
mSecondColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.CYAN);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_bg:
mImage = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), a.getResourceId(attr, 0));
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_circleWidth:
mCircleWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(
TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX, 20, getResources().getDisplayMetrics()));
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_dotCount:
mCount = a.getInt(attr, 20);// 默認20
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_splitSize:
mSplitSize = a.getInt(attr, 20);
break;
}
}
a.recycle();
mPaint = new Paint();
mRect = new Rect();
}
3、重寫onDraw
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // 消除鋸齒
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mCircleWidth); // 設置圓環的寬度
mPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND); // 定義線段斷電形狀為圓頭
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // 消除鋸齒
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); // 設置空心
int centre = getWidth() / 2; // 獲取圓心的x坐標
int radius = centre - mCircleWidth / 2;// 半徑
/**
* 畫塊塊去
*/
drawOval(canvas, centre, radius);
/**
* 計算內切正方形的位置
*/
int relRadius = radius - mCircleWidth / 2;// 獲得內圓的半徑
/**
* 內切正方形的距離頂部 = mCircleWidth + relRadius - √2 / 2
*/
mRect.left = (int) (relRadius - Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * relRadius) + mCircleWidth;
/**
* 內切正方形的距離左邊 = mCircleWidth + relRadius - √2 / 2
*/
mRect.top = (int) (relRadius - Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * relRadius) + mCircleWidth;
mRect.bottom = (int) (mRect.left + Math.sqrt(2) * relRadius);
mRect.right = (int) (mRect.left + Math.sqrt(2) * relRadius);
/**
* 如果圖片比較小,那麼根據圖片的尺寸放置到正中心
*/
if (mImage.getWidth() < Math.sqrt(2) * relRadius)
{
mRect.left = (int) (mRect.left + Math.sqrt(2) * relRadius * 1.0f / 2 - mImage.getWidth() * 1.0f / 2);
mRect.top = (int) (mRect.top + Math.sqrt(2) * relRadius * 1.0f / 2 - mImage.getHeight() * 1.0f / 2);
mRect.right = (int) (mRect.left + mImage.getWidth());
mRect.bottom = (int) (mRect.top + mImage.getHeight());
}
// 繪圖
canvas.drawBitmap(mImage, null, mRect, mPaint);
}
/**
* 根據參數畫出每個小塊
*
* @param canvas
* @param centre
* @param radius
*/
private void drawOval(Canvas canvas, int centre, int radius)
{
/**
* 根據需要畫的個數以及間隙計算每個塊塊所占的比例*360
*/
float itemSize = (360 * 1.0f - mCount * mSplitSize) / mCount;
RectF oval = new RectF(centre - radius, centre - radius, centre + radius, centre + radius); // 用於定義的圓弧的形狀和大小的界限
mPaint.setColor(mFirstColor); // 設置圓環的顏色
for (int i = 0; i < mCount; i++)
{
canvas.drawArc(oval, i * (itemSize + mSplitSize), itemSize, false, mPaint); // 根據進度畫圓弧
}
mPaint.setColor(mSecondColor); // 設置圓環的顏色
for (int i = 0; i < mCurrentCount; i++)
{
canvas.drawArc(oval, i * (itemSize + mSplitSize), itemSize, false, mPaint); // 根據進度畫圓弧
}
}
這裡需要注意下:
畫塊:首先根據塊數量和間隙計算,每個塊所占的比例。
畫圖:當圖比較大時,直接使用該環內切正方形大小進行約束,當圖片比較小時,在正中心的位置繪制。有些數學運算過程,樓主在草稿上畫了一會,不復雜,大家自己畫畫,我就不貼草稿了。
4、添加觸摸監聽:
/**
* 當前數量+1
*/
public void up()
{
mCurrentCount++;
postInvalidate();
}
/**
* 當前數量-1
*/
public void down()
{
mCurrentCount--;
postInvalidate();
}
private int xDown, xUp;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
xDown = (int) event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
xUp = (int) event.getY();
if (xUp > xDown)// 下滑
{
down();
} else
{
up();
}
break;
}
return true;
}
觸摸監聽也得很簡單哈,基本能實現,大家也可以加個最小距離加速度什麼的,都行。
最後,效果圖:
 Android直播推流學習
Android直播推流學習
第一部本文也主要是一步步分析spydroid源碼。 首先spydroid的采用的協議是RTSP,目前我知道支持RTSP協議的服務器是Darwin,但是Darwin比較復雜
 android中Handler的初步認識(三)
android中Handler的初步認識(三)
在上一個例子中,最終我們發現,其實用到的線程只有一個,那就是程序的主線程(UI線程)。那麼怎麼把那個例子改成用新建的線程來實現呢,今天我嘗試了一下,寫了下面這個小程序。
 Android 史上最強多語言國際化,不僅第一次會跟隨系統,而且會保存用戶的語言設置
Android 史上最強多語言國際化,不僅第一次會跟隨系統,而且會保存用戶的語言設置
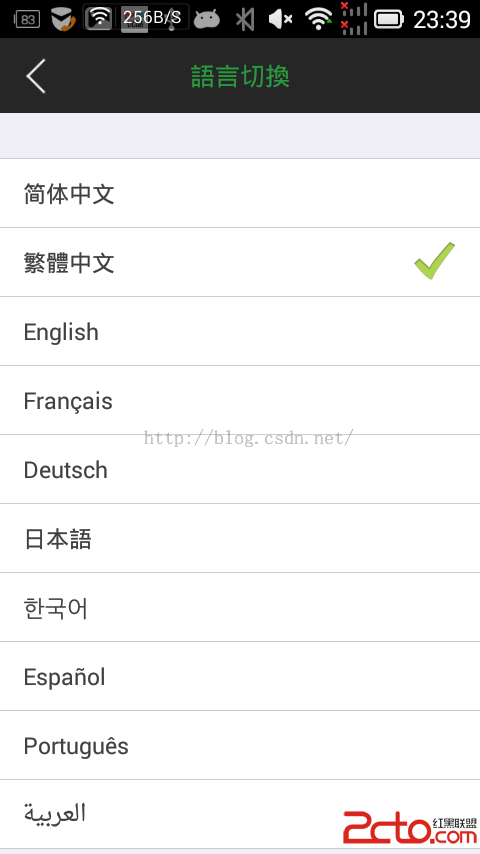
1.我等屌絲喜歡簡單粗暴,首先來一幅圖哥們我是大陸人,當然默認語言是 中文簡體,但是我剛剛切換成了繁體了 2.看下配置文件,按照這個格式 ,看圖吧,簡單粗暴,別
 Android Studio使用Lint進行代碼檢查
Android Studio使用Lint進行代碼檢查
Android Studio目前已經更新到1.4版本,它作為Google官方推薦的IDE,功能非常強大,其中提供了一套靜態代碼分析工具,它可以幫助我們檢查項目中存在的問題