編輯:關於Android編程
public BitmapShader(Bitmap bitmap,Shader.TileMode tileX,Shader.TileMode tileY)
調用這個類來產生一個畫有一個位圖的渲染器(Shader)。
bitmap:在渲染器內使用的位圖
(1)tileX:The tiling mode for x to draw the bitmap in. 在位圖上X方向花磚模式
(2)tileY:The tiling mode for y to draw the bitmap in. 在位圖上Y方向花磚模式
TileMode:(一共有三種)
(1)CLAMP:如果渲染器超出原始邊界范圍,會復制范圍內邊緣染色。
(2)REPEAT:橫向和縱向的重復渲染器圖片,平鋪。
(3)MIRROR:橫向和縱向的重復渲染器圖片,這個和REPEAT 重復方式不一樣,他是以鏡像方式平鋪。
還是不太明白?那看一下效果圖吧!


對於我們的圓角,以及圓形,我們設置的模式都是CLAMP ,但是你會不會會有一個疑問:
view的寬或者高大於我們的bitmap寬或者高豈不是會拉伸?
嗯,我們會為BitmapShader設置一個matrix,去適當的放大或者縮小圖片,不會讓“ view的寬或者高大於我們的bitmap寬或者高 ”此條件成立的。
到此我們的原理基本介紹完畢了,拿到drawable轉化為bitmap,然後直接初始化BitmapShader,畫筆設置Shader,最後在onDraw裡面進行畫圓就行了。
基本用法及實例
首先就來看看利用BitmapShader實現的圓形或者圓角。
我們這裡直接繼承ImageView,這樣大家設置圖片的代碼會比較熟悉;但是我們需要支持兩種模式,那麼就需要自定義屬性了:
1、自定義屬性
values/attr.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <attr name="borderRadius" format="dimension" /> <attr name="type"> <enum name="circle" value="0" /> <enum name="round" value="1" /> </attr> <declare-styleable name="RoundImageView"> <attr name="borderRadius" /> <attr name="type" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
我們定義了一個枚舉和一個圓角的大小borderRadius。
2、獲取自定義屬性
public class RoundImageView extends ImageView
{
/**
* 圖片的類型,圓形or圓角
*/
private int type;
private static final int TYPE_CIRCLE = 0;
private static final int TYPE_ROUND = 1;
/**
* 圓角大小的默認值
*/
private static final int BODER_RADIUS_DEFAULT = 10;
/**
* 圓角的大小
*/
private int mBorderRadius;
/**
* 繪圖的Paint
*/
private Paint mBitmapPaint;
/**
* 圓角的半徑
*/
private int mRadius;
/**
* 3x3 矩陣,主要用於縮小放大
*/
private Matrix mMatrix;
/**
* 渲染圖像,使用圖像為繪制圖形著色
*/
private BitmapShader mBitmapShader;
/**
* view的寬度
*/
private int mWidth;
private RectF mRoundRect;
public RoundImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
mMatrix = new Matrix();
mBitmapPaint = new Paint();
mBitmapPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.RoundImageView);
mBorderRadius = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.RoundImageView_borderRadius, (int) TypedValue
.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP,
BODER_RADIUS_DEFAULT, getResources()
.getDisplayMetrics()));// 默認為10dp
type = a.getInt(R.styleable.RoundImageView_type, TYPE_CIRCLE);// 默認為Circle
a.recycle();
}
可以看到我們的一些成員變量,基本都加了注釋;然後在構造方法中獲取了我們的自定義屬性,以及部分變量的初始化。
3、onMeasure
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
Log.e("TAG", "onMeasure");
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/**
* 如果類型是圓形,則強制改變view的寬高一致,以小值為准
*/
if (type == TYPE_CIRCLE)
{
mWidth = Math.min(getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight());
mRadius = mWidth / 2;
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mWidth);
}
}
我們復寫了onMeasure方法,主要用於當設置類型為圓形時,我們強制讓view的寬和高一致。
接下來只剩下設置BitmapShader和繪制了
4、設置BitmapShader
/**
* 初始化BitmapShader
*/
private void setUpShader()
{
Drawable drawable = getDrawable();
if (drawable == null)
{
return;
}
Bitmap bmp = drawableToBitamp(drawable);
// 將bmp作為著色器,就是在指定區域內繪制bmp
mBitmapShader = new BitmapShader(bmp, TileMode.CLAMP, TileMode.CLAMP);
float scale = 1.0f;
if (type == TYPE_CIRCLE)
{
// 拿到bitmap寬或高的小值
int bSize = Math.min(bmp.getWidth(), bmp.getHeight());
scale = mWidth * 1.0f / bSize;
} else if (type == TYPE_ROUND)
{
// 如果圖片的寬或者高與view的寬高不匹配,計算出需要縮放的比例;縮放後的圖片的寬高,一定要大於我們view的寬高;所以我們這裡取大值;
scale = Math.max(getWidth() * 1.0f / bmp.getWidth(), getHeight()
* 1.0f / bmp.getHeight());
}
// shader的變換矩陣,我們這裡主要用於放大或者縮小
mMatrix.setScale(scale, scale);
// 設置變換矩陣
mBitmapShader.setLocalMatrix(mMatrix);
// 設置shader
mBitmapPaint.setShader(mBitmapShader);
}
在setUpShader中,首先對drawable轉化為我們的bitmap;
然後初始化
mBitmapShader = new BitmapShader(bmp, TileMode.CLAMP, TileMode.CLAMP);
接下來,根據類型以及bitmap和view的寬高,計算scale;
關於scale的計算:
(1)圓形時:取bitmap的寬或者高的小值作為基准,如果采用大值,縮放後肯定不能填滿我們的圓形區域。然後,view的mWidth/bSize ; 得到的就是scale。
(2)圓角時:因為設計到寬/高比例,我們分別getWidth() * 1.0f / bmp.getWidth() 和 getHeight() * 1.0f / bmp.getHeight() ;最終取大值,因為我們要讓最終縮放完成的圖片一定要大於我們的view的區域,有點類似centerCrop;
(3)比如:view的寬高為10*20;圖片的寬高為5*100 ; 最終我們應該按照寬的比例放大,而不是按照高的比例縮小;因為我們需要讓縮放後的圖片,自定大於我們的view寬高,並保證原圖比例。
有了scale,就可以設置給我們的matrix;
然後使用mBitmapShader.setLocalMatrix(mMatrix);
最後將bitmapShader設置給paint。
關於drawable轉bitmap的代碼:
/**
* drawable轉bitmap
*
* @param drawable
* @return
*/
private Bitmap drawableToBitamp(Drawable drawable)
{
if (drawable instanceof BitmapDrawable)
{
BitmapDrawable bd = (BitmapDrawable) drawable;
return bd.getBitmap();
}
int w = drawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
int h = drawable.getIntrinsicHeight();
Bitmap bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(w, h, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmap);
drawable.setBounds(0, 0, w, h);
drawable.draw(canvas);
return bitmap;
}
最後我們會在onDraw裡面調用setUpShader(),然後進行繪制。
5、繪制
到此,就剩下最後一步繪制了,因為我們的范圍,以及縮放都完成了,所以真的只剩下繪制了。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
if (getDrawable() == null)
{
return;
}
setUpShader();
if (type == TYPE_ROUND)
{
canvas.drawRoundRect(mRoundRect, mBorderRadius, mBorderRadius,
mBitmapPaint);
} else
{
canvas.drawCircle(mRadius, mRadius, mRadius, mBitmapPaint);
// drawSomeThing(canvas);
}
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh)
{
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
// 圓角圖片的范圍
if (type == TYPE_ROUND)
mRoundRect = new RectF(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
繪制就很簡單了,畫個圓,圓角矩形什麼的。圓角矩形的限定范圍mRoundRect在onSizeChanged裡面進行了初始化。
6、狀態的存儲與恢復
當然了,如果內存不足,而恰好我們的Activity置於後台,不幸被重啟,或者用戶旋轉屏幕造成Activity重啟,我們的View應該也能盡可能的去保存自己的屬性。
狀態保存什麼用處呢?比如,現在一個的圓角大小是10dp,用戶點擊後變成50dp;當用戶旋轉以後,或者長時間置於後台以後,返回我們的Activity應該還是50dp;
我們簡單的存儲一下,當前的type以及mBorderRadius
private static final String STATE_INSTANCE = "state_instance";
private static final String STATE_TYPE = "state_type";
private static final String STATE_BORDER_RADIUS = "state_border_radius";
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState()
{
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable(STATE_INSTANCE, super.onSaveInstanceState());
bundle.putInt(STATE_TYPE, type);
bundle.putInt(STATE_BORDER_RADIUS, mBorderRadius);
return bundle;
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state)
{
if (state instanceof Bundle)
{
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) state;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(((Bundle) state)
.getParcelable(STATE_INSTANCE));
this.type = bundle.getInt(STATE_TYPE);
this.mBorderRadius = bundle.getInt(STATE_BORDER_RADIUS);
} else
{
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
}
代碼比較簡單。我們文章中的demo中,第一個,第四個是可以點擊的,點擊後會發生變化,你可以點擊後,然後旋轉屏幕進行測試。
同時我們也對外公布了兩個方法,用於動態修改圓角大小和type
public void setBorderRadius(int borderRadius)
{
int pxVal = dp2px(borderRadius);
if (this.mBorderRadius != pxVal)
{
this.mBorderRadius = pxVal;
invalidate();
}
}
public void setType(int type)
{
if (this.type != type)
{
this.type = type;
if (this.type != TYPE_ROUND && this.type != TYPE_CIRCLE)
{
this.type = TYPE_CIRCLE;
}
requestLayout();
}
}
public int dp2px(int dpVal)
{
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP,
dpVal, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
最後貼一下我們的布局文件和MainActivity。
6、調用
布局文件:
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:zhy="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.zhy.variousshapeimageview" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.zhy.view.RoundImageView android:id="@+id/id_qiqiu" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/qiqiu" > </com.zhy.view.RoundImageView> <com.zhy.view.RoundImageView android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/aa" > </com.zhy.view.RoundImageView> <com.zhy.view.RoundImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/icon" > </com.zhy.view.RoundImageView> <com.zhy.view.RoundImageView android:id="@+id/id_meinv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/aa" zhy:borderRadius="20dp" zhy:type="round" > </com.zhy.view.RoundImageView> <com.zhy.view.RoundImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/icon" zhy:borderRadius="40dp" zhy:type="round" > </com.zhy.view.RoundImageView> <com.zhy.view.RoundImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/qiqiu" zhy:borderRadius="60dp" zhy:type="round" > </com.zhy.view.RoundImageView> </LinearLayout> </ScrollView>
沒撒,ScrollView裡面一個線性布局,裡面一堆RoundImageView。
MainActivity
package com.zhy.variousshapeimageview;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import com.zhy.view.RoundImageView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private RoundImageView mQiQiu;
private RoundImageView mMeiNv ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mQiQiu = (RoundImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_qiqiu);
mMeiNv = (RoundImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_meinv);
mQiQiu.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
mQiQiu.setType(RoundImageView.TYPE_ROUND);
}
});
mMeiNv.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
mMeiNv.setBorderRadius(90);
}
});
}
}
最後的效果圖:

 Android-PullToRefresh下拉刷新庫基本用法
Android-PullToRefresh下拉刷新庫基本用法
PullToRefresh是一套實現非常好的下拉刷新庫,它支持: ListView ExpandableListView GridView WebView ScrollV
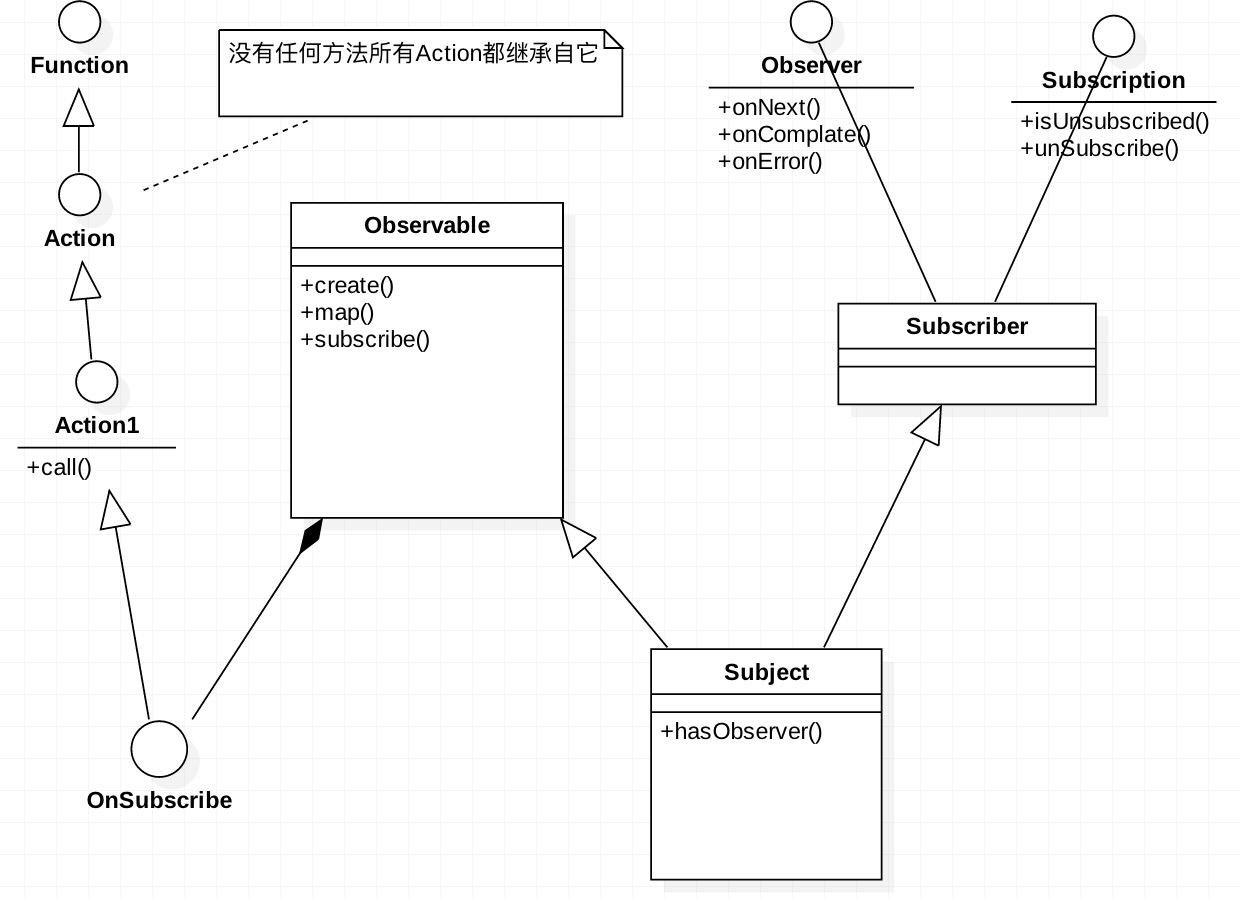 RxJava(RxAndroid)線程切換機制
RxJava(RxAndroid)線程切換機制
自從項目中使用RxJava以來,可以很方便的切換線程。至於是怎麼實現的,一直沒有深入的研究過!本篇文章就是分析RxJava的線程模型。 RxJava基本使用 先上一個
 【Android】掌握自定義LayoutManager(一) 系列開篇 常見誤區、問題、注意事項,常用API。
【Android】掌握自定義LayoutManager(一) 系列開篇 常見誤區、問題、注意事項,常用API。
概述這篇文章是深入掌握自定義LayoutManager系列的開篇,是一份總結報告。部分內容不屬於引言、過於深入,用作系列後續文章的參考,以及浏覽完後的復習之用。本文內容涉
 Android Mediaplayer本地音樂播放器(綁定服務)
Android Mediaplayer本地音樂播放器(綁定服務)
本文章介紹MediaPlayer本地音樂播放器,而當應用程序不再位於前台且沒有正在使用它的活動時,為了確保音頻繼續播放,我們需要建立一個服務Service。 Activi