編輯:關於Android編程
Tab與TabHost:

這就是Tab,而盛放Tab的容器就是TabHost 。
如何實現??
每一個Tab還對應了一個布局,這個就有點好玩了。一個Activity,對應了多個功能布局。
新建一個Tab項目,注意,不要生成main Activity 。
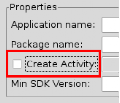
注意IDE,這裡不要選...
在包裡面新建一個類MyTab,繼承於TabActivity。
其實,TabActivity是Activity的子類
package zyf.tab.test;
import android.app.TabActivity;
public class MyTab extends TabActivity {
}
從父類繼承OnCreate()入口方法
package zyf.tab.test;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MyTab extends TabActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
}
在Manifest.xml文件中注冊一下MyTab類(Activity)
<activity android:name=".MyTab">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"></action>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"></category>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
這時候,需要設計一下標簽頁對應的布局,一般采用FrameLayout作為根布局,每個標簽頁面對應一個子節點的Layout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 這裡是根節點布局 -- >
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<!-- 第一個Tab 對應的布局 -- >
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/widget_layout_Blue"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
androidrientation="vertical" >
<EditText android:id="@+id/widget34" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="EditText"
android:textSize="18sp">
</EditText>
<Button android:id="@+id/widget30" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button">
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 第二個Tab 對應的布局 -- >
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/widget_layout_red"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
androidrientation="vertical" >
<AnalogClock android:id="@+id/widget36"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</AnalogClock>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 第三個Tab 對應的布局 -- >
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/widget_layout_green"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
androidrientation="vertical">
<RadioGroup android:id="@+id/widget43"
android:layout_width="166px" android:layout_height="98px"
androidrientation="vertical">
<RadioButton android:id="@+id/widget44"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="RadioButton">
</RadioButton>
<RadioButton android:id="@+id/widget45"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="RadioButton">
</RadioButton>
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</FrameLayout>
首先,應該聲明TabHost,然後用LayoutInflater過濾出布局來,給TabHost加上含有Tab頁面的FrameLayout
private TabHost myTabhost; myTabhost=this.getTabHost();//從TabActivity上面獲取放置Tab的TabHost LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.main, myTabhost.getTabContentView(), true); //from(this)從這個TabActivity獲取LayoutInflater //R.layout.main 存放Tab布局 //通過TabHost獲得存放Tab標簽頁內容的FrameLayout //是否將inflate 拴系到根布局元素上 myTabhost.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb(150, 22, 70, 150)); //設置一下TabHost的顏色
接著,在TabHost創建一個標簽,然後設置一下標題/圖標/標簽頁布局
myTabhost.addTab(myTabhost.newTabSpec("TT")// 制造一個新的標簽TT
.setIndicator("KK",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ajjc))
// 設置一下顯示的標題為KK,設置一下標簽圖標為ajjc
.setContent(R.id.widget_layout_red));
//設置一下該標簽頁的布局內容為R.id.widget_layout_red,這是FrameLayout中的一個子Layout
標簽切換事件處理,setOnTabChangedListener
myTabhost.setOnTabChangedListener(new OnTabChangeListener(){
@Override
public void onTabChanged(String tabId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
各個標簽頁的動態MENU
先把在XML中設計好的MENU放到一個int數組裡
private static final int myMenuResources[] = { R.menu.phonebook_menu,
R.menu.addphone_menu, R.menu.chatting_menu, R.menu.userapp_menu };
在setOnTabChangedListener()方法中根據標簽的切換情況來設置myMenuSettingTag
Override
public void onTabChanged(String tagString) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (tagString.equals("One")) {
myMenuSettingTag = 1;
}
if (tagString.equals("Two")) {
myMenuSettingTag = 2;
}
if (tagString.equals("Three")) {
myMenuSettingTag = 3;
}
if (tagString.equals("Four")) {
myMenuSettingTag = 4;
}
if (myMenu != null) {
onCreateOptionsMenu(myMenu);
}
}
然後onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) 方法中通過MenuInflater過濾器動態加入MENU
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// Hold on to this
myMenu = menu;
myMenu.clear();//清空MENU菜單
// Inflate the currently selected menu XML resource.
MenuInflater inflater = getMenuInflater();
//從TabActivity這裡獲取一個MENU過濾器
switch (myMenuSettingTag) {
case 1:
inflater.inflate(myMenuResources[0], menu);
//動態加入數組中對應的XML MENU菜單
break;
case 2:
inflater.inflate(myMenuResources[1], menu);
break;
case 3:
inflater.inflate(myMenuResources[2], menu);
break;
case 4:
inflater.inflate(myMenuResources[3], menu);
break;
default:
break;
}
return super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu);
}
menu 布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <group android:id="@+id/group_a"><item android:id="@+id/item_a" android:icon="@drawable/gimp" android:title="Gimp"></item> </group> </menu>
運行效果
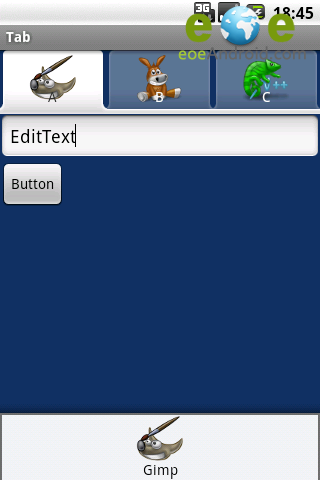
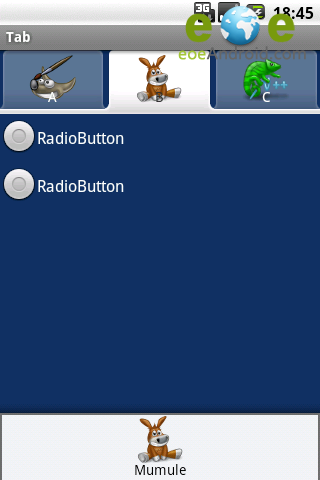
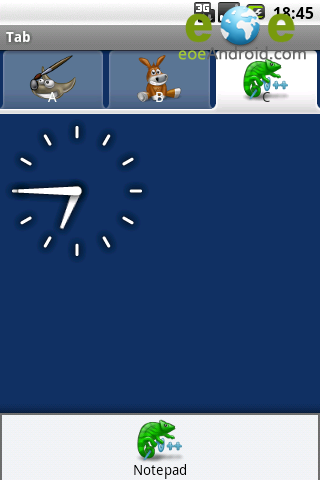
模仿微信導航實例:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0.0dip"
android:layout_weight="1.0" >
</FrameLayout>
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="gone" >
</TabWidget>
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/talk"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/take_bottom"
android:text="@string/talk" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/address"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/adrress_bottom"
android:text="@string/address" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/find"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/find_bottom"
android:text="@string/find" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/me"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/me_bottom"
android:text="@string/me" />
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/n_address_l" android:state_checked="true" android:state_enabled="true"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/n_address_h"/> </selector>
package com.android.xiong.bkclient;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener;
import android.widget.RadioButton;
import android.widget.TabHost;
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class MainActivity extends TabActivity implements
OnCheckedChangeListener {
private TabHost tabHost;
private Intent addressIntent;
private Intent meIntent;
private Intent takeIntent;
private Intent findIntent;
private RadioButton findBt;
private RadioButton addressBt;
private RadioButton meBt;
private RadioButton takeBt;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.tabhostmain);
addressIntent = new Intent(this, AddressActivity.class);
meIntent = new Intent(this, MeActivity.class);
takeIntent = new Intent(this, TakeActivity.class);
findIntent = new Intent(this, FindActivity.class);
findBt = (RadioButton) findViewById(R.id.find);
addressBt = (RadioButton) findViewById(R.id.address);
meBt = (RadioButton) findViewById(R.id.me);
takeBt = (RadioButton) findViewById(R.id.talk);
tabHost =getTabHost();
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("take").setIndicator("take")
.setContent(takeIntent));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("address").setIndicator("address")
.setContent(addressIntent));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("find").setIndicator("find")
.setContent(findIntent));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("me").setIndicator("me")
.setContent(meIntent));
findBt.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
meBt.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
takeBt.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
addressBt.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton view, boolean ischeak) {
if (ischeak) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.talk:
tabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("take");
break;
case R.id.find:
tabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("find");
break;
case R.id.me:
tabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("me");
break;
case R.id.address:
tabHost.setCurrentTabByTag("address");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.android.xiong.bkclient"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="19" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity android:name="com.android.xiong.bkclient.MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name="com.android.xiong.bkclient.AddressActivity"></activity>
<activity android:name="com.android.xiong.bkclient.FindActivity"></activity>
<activity android:name="com.android.xiong.bkclient.MeActivity"></activity>
<activity android:name="com.android.xiong.bkclient.TakeActivity"></activity>
</application>
</manifest>
 android blur 詳解 ---- 配效果圖
android blur 詳解 ---- 配效果圖
在android 中,邊緣模糊的效果是通過BlurMaskFilter實現的 , 它定義了一個邊緣模糊半徑和模糊效果 (Blur)。Blur 有四種模糊效果, inner
 Android 屏幕旋轉 處理 AsyncTask 和 ProgressDialog 的最佳方案
Android 屏幕旋轉 處理 AsyncTask 和 ProgressDialog 的最佳方案
1、概述 眾所周知,Activity在不明確指定屏幕方向和configChanges時,當用戶旋轉屏幕會重新啟動。當然了,應對這種情況,Android給
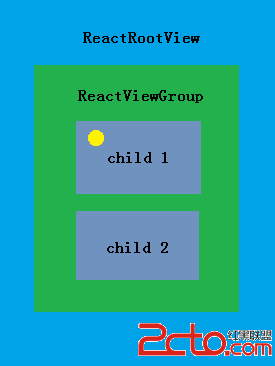 React-Native系列Android——Touch事件原理及狀態效果
React-Native系列Android——Touch事件原理及狀態效果
Native原生相比於Hybrid或H5最大優點是具有流暢和復雜的交互效果,觸摸事件便是其中重要一項,包括點擊(Click)、長按(LongClick)、手勢(gestu
 仿制慕課網app實現斗魚,全民k歌視頻引導頁(ViewVideoViewPaper)炫酷效果
仿制慕課網app實現斗魚,全民k歌視頻引導頁(ViewVideoViewPaper)炫酷效果
在幾個月前,我第一次玩全民k歌,下載完app,它彈出來的引導頁吸引了我,不像以前的引導頁一樣千篇一律,而是用了視頻的方式,用一種動態的方式來實現。在今天,我突然又想起了這