編輯:關於Android編程
本文主要介紹了隱式Intent匹配目標組件的規則,若有敘述不清晰或是不准確的地方希望大家指出,謝謝大家: )
1. Intent簡介
Intent用於在一個組件(Component,如Activity、Service、Broadcast Receiver)中打開另一個組件。
Intent可分為隱式(implicitly)和顯式(explicitly)兩種:
Explicitly Intent:在知道要打開哪個具體的Component時使用,通過指定調用者和被調用者即可打開目標Component;
Implicitly Intent:在不確切的知道要打開哪個Component的情況下,通過指出action、data、category,系統會尋找到匹配的Component。
(1)Explicitly Intent
當明確知道你想打開哪個Component時,它就是你的菜。通常這樣使用:
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("key", "value");
startActivity(intent);
執行以上代碼會導致目標Component(這裡是MainActivity)被創建(onCreate等一系列生命周期方法被調用)。在MainAcitivity中的相應生命周期方法中通過getIntent.getXxxExtra(“key”)即可得到隨Intent一起傳過來的數據。
(2)Implicitly Intent
Implicitly Intent很好的實現了調用者和被調用者之間的解耦:
調用者通過action、data、category這三個方面描述他的Intent,被調用者通過在manifest文件中聲明的一系列Intent Filter來描述自己能夠響應哪些意圖。如此一來,調用者和被調用者無需互相了解,通過Implicitly Intent這個聯系他們的紐帶就能很好的協同工作。
關於Intent更加詳細的介紹,大家可以參考官方文檔,這裡主要介紹下Implicitly Intent的匹配規則。
2.Intent Filter匹配規則
只有action、data、category三方都匹配,Intent才算是匹配成功,進而才能打開相應的Component。一個Component若聲明了多個Intent Filter,只需要匹配任意一個即可啟動該組件。
(1)action的匹配規則
一個Intent Filter中可聲明多個action,Intent中的action與其中的任一個action在字符串形式上完全相同(注意,區分大小寫),action方面就匹配成功。可通過setAction方法為Intent設置action,也可在構造Intent時傳入action。需要注意的是,隱式Intent必須指定action。比如我們在Manifest文件中為MyActivity定義了如下Intent Filter:
<intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND"/> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND_TO"/> </intent-filter>
那麼只要Intent的action為“SEND”或“SEND_TO”,那麼這個Intent在action方面就能和上面那個Activity匹配成功。比如我們的Intent定義如下:
Intent intent = new Intent("android.intent.action.SEND")
...
那麼我們的Intent在action方面就與MyActivity匹配了。
Android系統預定義了許多action,這些action代表了一些常見的操作。常見action如下(Intent類中的常量):
Intent.ACTION_VIEW
Intent.ACTION_DIAL
Intent.ACTION_SENDTO
Intent.ACTION_SEND
Intent.ACTION_WEB_SEARCH
(2)data的匹配規則
data可進一步分為uri(由scheme、host、port、path | pathPattern | pathPrefix這4部分組成)和mimetype。Intent的uri可通過setData方法設置,mimetype可通過setType方法設置。隱式Intent也必須指定data。同action類似,只要Intent的data只要與Intent Filter中的任一個data聲明完全相同,data方面就匹配成功。需要注意的是:若Intent Filter的data聲明部分未指定uri,則缺省uri為content或file,Intent中的uri的scheme部分需為content或file才能匹配;若要為Intent指定完整的data,必須用setDataAndType方法,原因請看setData和setType方法的源碼:
public Intent setData(Uri data) {
mData = data;
mType = null;
return this;
}
public Intent setType(String type) {
mData = null;
mType = type;
return this;
}
從以上代碼可以看到,setData會把mimeType置為null,setType會把uri置為null。下面我們來舉例說明一下data的匹配。首先我們先來看一下Intent Filter中指定data的語法:
<data android:scheme="...“
android:host="..."
android:port="..."
android:path="..."
android:pathPattern="..."
android:pathPrefix="..."
android:mimeType="..." />
其中scheme、host等各個部分無需全部指定。假如我們為MyActivity的Intent Filter指定了如下data:
<intent-filter> <data android:mimeType="vidoe/mpeg" android:scheme="http" android:host="www.xxx.com" /> <data android:mimeType="text/plain" android:scheme="http" /> </intent-filter>
那麼我們的Intent想要匹配,mimeType可以為”text/plain”或“video/mpeg”,scheme必須為”http“,host則沒有限制,因為第二個data沒有指定host。
(3)category的匹配規則
與action和data不同,Intent中的category必須都在Intent Filter中出現才算匹配成功。Intent可以不指定category,若Intent中未指定category,系統會自動為它帶上“android.intent.category.DEFAULT”。所以,想要接收Implicitly Intent的Component都必須在manifest文件中的Intent Filter聲明中帶上“android.intent.category.DEFAULT”。我們可以通過addCategory方法為Intent添加category。
(4)查詢是否有可接收指定Intent的Component
采用PackageManager的resolveActivity或者Intent的resolveActivity方法會獲得最適合Intent的一個Activity;調用PackageManager的queryIntentActivities會返回所有成功匹配Intent的Activity。關於這幾個方法的詳細定義大家可以參考官方文檔,這裡不再贅述。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助。
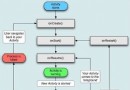 Activity
Activity
生命周期一.正常情況下生命周期如圖正常生命周期 開起activity調用onCreate() onStart() onResume(),按下返回鍵 onPause() o
 安卓動態調試七種武器之離別鉤 – Hooking(下)
安卓動態調試七種武器之離別鉤 – Hooking(下)
0x00 序隨著移動安全越來越火,各種調試工具也都層出不窮,但因為環境和需求的不同,並沒有工具是萬能的。另外工具是死的,人是活的,如果能搞懂工具的原理再結合上自身的經驗,
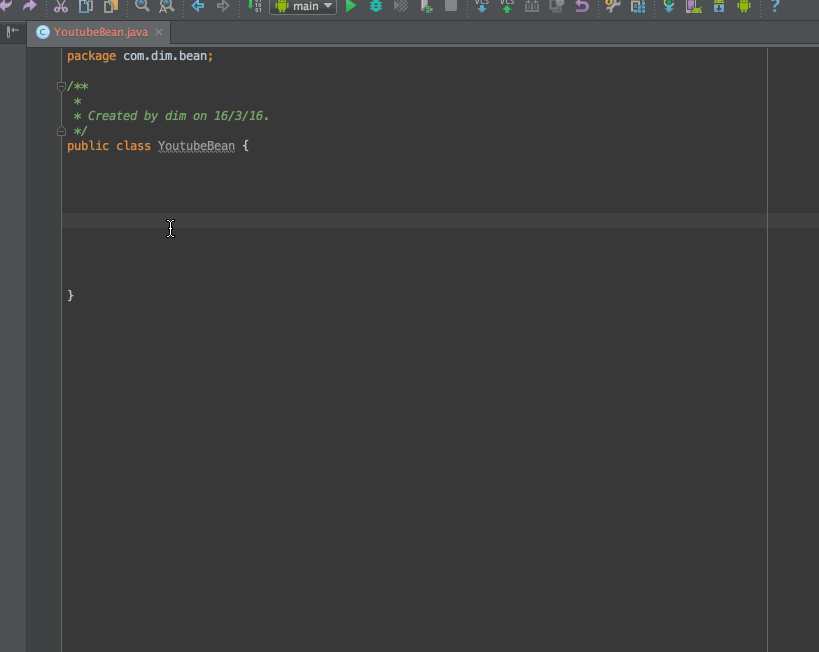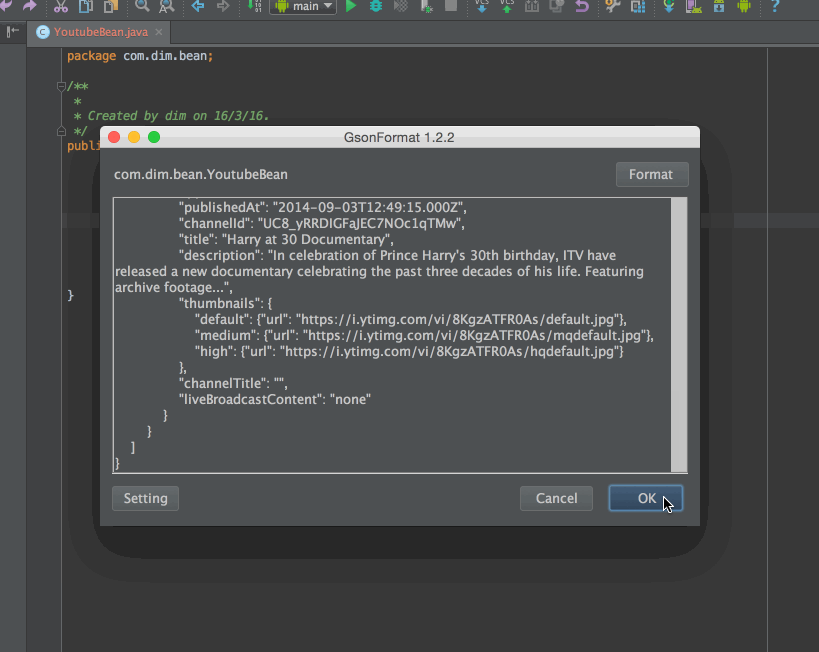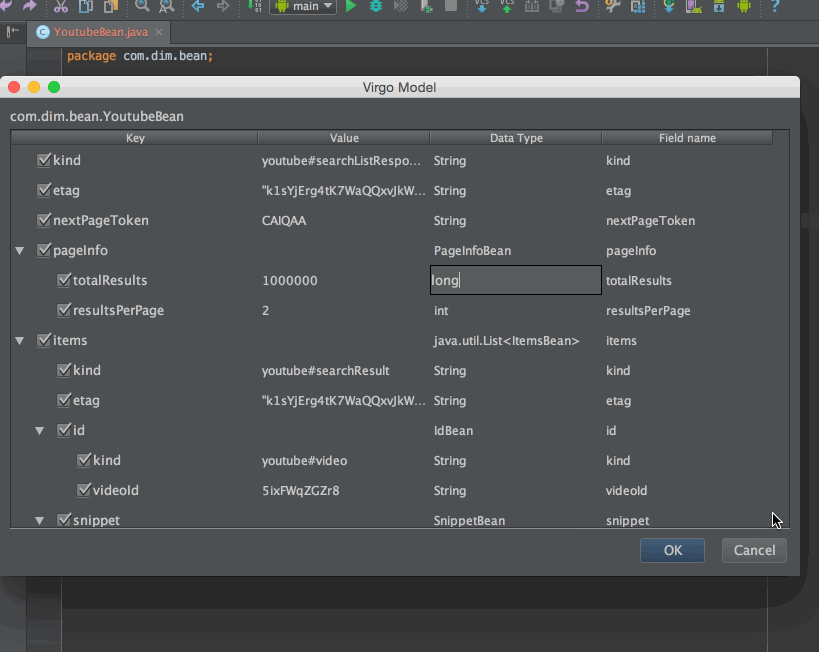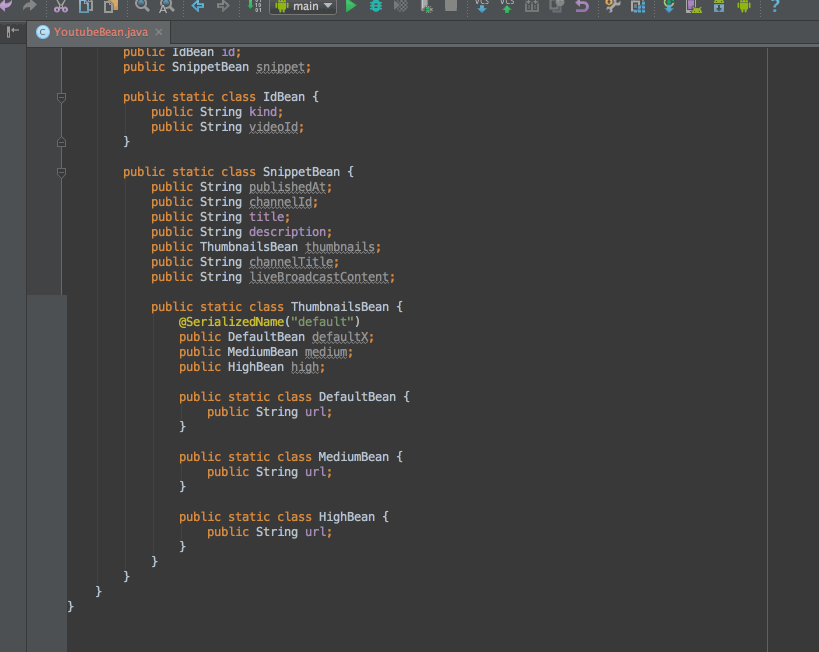 Android-androidstudio懶惰開發
Android-androidstudio懶惰開發
現在Android的開發者基本上都使用Android Studio進行開發(如果你還在使用eclipse那也行,畢竟你樂意怎麼樣都行)。使用好Android Studio
 android調試工具DDMS的使用詳解
android調試工具DDMS的使用詳解
具體可見http://developer.android.com/tools/debugging/ddms.html。 DDMS為IDE和emultor、真正的andro