編輯:關於Android編程
隨著移動互聯網的快速發展,它已經和我們的生活息息相關了,在公交地鐵裡面都能看到很多人的人低頭看著自己的手機屏幕,從此“低頭族”一詞就產生了,作為一名移動行業的開發人員,我自己也是一名“低頭族”,上下班時間在公交地鐵上看看新聞來打發下時間,有時候也會看看那些受歡迎的App的一些界面效果,為什麼人家的app那麼受歡迎?跟用戶體驗跟UI設計也有直接的關系,最近在美團和大眾點評的App看到如下效果,我感覺用戶好,很人性化,所以自己也嘗試著實現了下,接下來就講解下實現思路!

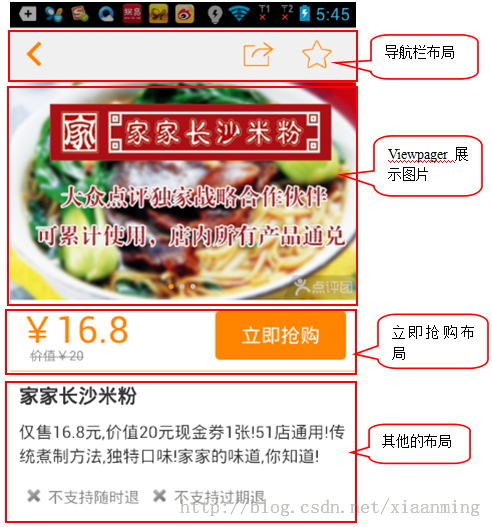
如上圖(2)我們看到了,當立即搶購布局向上滑動到導航欄布局的時候,立即搶購布局就貼在導航欄布局下面,下面的其他的布局還是可以滑動,當我們向下滑動的時候,立即搶購的布局又隨著往下滑動了,看似有點復雜,但是一說思路可能你就頓時恍然大悟了。
當我們向上滑動過程中,我們判斷立即搶購的布局是否滑到導航欄布局下面,如果立即搶購的上面頂到了導航欄,我們新建一個立即搶購的懸浮框來顯示在導航欄下面,這樣子就實現了立即搶購貼在導航欄下面的效果啦,而當我們向下滑動的時候,當立即搶購布局的下面剛好到了剛剛新建的立即搶購懸浮框的下面的時候,我們就移除立即搶購懸浮框,可能說的有點拗口,既然知道了思路,接下來我們就來實現效果。
新建一個Android項目,取名MeiTuanDemo,先看立即搶購(buy_layout.xml)的布局,這裡為了方便我直接從美團上面截去了圖片
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/buy_layout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/buy" />
</LinearLayout>
立即搶購的布局實現了,接下來實現主界面的布局,上面是導航欄布局,為了方便還是直接從美團截取的圖片,然後下面的ViewPager布局,立即搶購布局,其他布局 放在ScrollView裡面,界面還是很簡單的
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView1"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="45dip"
android:src="@drawable/navigation_bar" />
<com.example.meituandemo.MyScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iamge"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/pic"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
<include
android:id="@+id/buy"
layout="@layout/buy_layout" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/one"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/one"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/one"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
</LinearLayout>
</com.example.meituandemo.MyScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
你會發現上面的主界面布局中並不是ScrollView,而是自定義的一個MyScrollView,接下來就看看MyScrollView類中的代碼
package com.example.meituandemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
/**
* 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming
*
* @author xiaanming
*
*/
public class MyScrollView extends ScrollView {
private OnScrollListener onScrollListener;
/**
* 主要是用在用戶手指離開MyScrollView,MyScrollView還在繼續滑動,我們用來保存Y的距離,然後做比較
*/
private int lastScrollY;
public MyScrollView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
/**
* 設置滾動接口
* @param onScrollListener
*/
public void setOnScrollListener(OnScrollListener onScrollListener) {
this.onScrollListener = onScrollListener;
}
/**
* 用於用戶手指離開MyScrollView的時候獲取MyScrollView滾動的Y距離,然後回調給onScroll方法中
*/
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
int scrollY = MyScrollView.this.getScrollY();
//此時的距離和記錄下的距離不相等,在隔5毫秒給handler發送消息
if(lastScrollY != scrollY){
lastScrollY = scrollY;
handler.sendMessageDelayed(handler.obtainMessage(), 5);
}
if(onScrollListener != null){
onScrollListener.onScroll(scrollY);
}
};
};
/**
* 重寫onTouchEvent, 當用戶的手在MyScrollView上面的時候,
* 直接將MyScrollView滑動的Y方向距離回調給onScroll方法中,當用戶抬起手的時候,
* MyScrollView可能還在滑動,所以當用戶抬起手我們隔5毫秒給handler發送消息,在handler處理
* MyScrollView滑動的距離
*/
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if(onScrollListener != null){
onScrollListener.onScroll(lastScrollY = this.getScrollY());
}
switch(ev.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
handler.sendMessageDelayed(handler.obtainMessage(), 5);
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(ev);
}
/**
*
* 滾動的回調接口
*
* @author xiaanming
*
*/
public interface OnScrollListener{
/**
* 回調方法, 返回MyScrollView滑動的Y方向距離
* @param scrollY
* 、
*/
public void onScroll(int scrollY);
}
}
一看代碼你也許明白了,就是對ScrollView的滾動Y值進行監聽,我們知道ScrollView並沒有實現滾動監聽,所以我們必須自行實現對ScrollView的監聽,我們很自然的想到在onTouchEvent()方法中實現對滾動Y軸進行監聽,可是你會發現,我們在滑動ScrollView的時候,當我們手指離開ScrollView。它可能還會繼續滑動一段距離,所以我們選擇在用戶手指離開的時候每隔5毫秒來判斷ScrollView是否停止滑動,並將ScrollView的滾動Y值回調給OnScrollListener接口的onScroll(int scrollY)方法中,我們只需要對ScrollView調用我們只需要對ScrollView調用setOnScrollListener方法就能監聽到滾動的Y值。
實現了對ScrollView滾動的Y值進行監聽,接下來就簡單了,我們只需要顯示立即搶購懸浮框和移除懸浮框了,接下來看看主界面Activity的代碼編寫
package com.example.meituandemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import com.example.meituandemo.MyScrollView.OnScrollListener;
/**
* 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming
*
* @author xiaanming
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnScrollListener{
private MyScrollView myScrollView;
private LinearLayout mBuyLayout;
private WindowManager mWindowManager;
/**
* 手機屏幕寬度
*/
private int screenWidth;
/**
* 懸浮框View
*/
private static View suspendView;
/**
* 懸浮框的參數
*/
private static WindowManager.LayoutParams suspendLayoutParams;
/**
* 購買布局的高度
*/
private int buyLayoutHeight;
/**
* myScrollView與其父類布局的頂部距離
*/
private int myScrollViewTop;
/**
* 購買布局與其父類布局的頂部距離
*/
private int buyLayoutTop;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
myScrollView = (MyScrollView) findViewById(R.id.scrollView);
mBuyLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.buy);
myScrollView.setOnScrollListener(this);
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
screenWidth = mWindowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
}
/**
* 窗口有焦點的時候,即所有的布局繪制完畢的時候,我們來獲取購買布局的高度和myScrollView距離父類布局的頂部位置
*/
@Override
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
if(hasFocus){
buyLayoutHeight = mBuyLayout.getHeight();
buyLayoutTop = mBuyLayout.getTop();
myScrollViewTop = myScrollView.getTop();
}
}
/**
* 滾動的回調方法,當滾動的Y距離大於或者等於 購買布局距離父類布局頂部的位置,就顯示購買的懸浮框
* 當滾動的Y的距離小於 購買布局距離父類布局頂部的位置加上購買布局的高度就移除購買的懸浮框
*
*/
@Override
public void onScroll(int scrollY) {
if(scrollY >= buyLayoutTop){
if(suspendView == null){
showSuspend();
}
}else if(scrollY <= buyLayoutTop + buyLayoutHeight){
if(suspendView != null){
removeSuspend();
}
}
}
/**
* 顯示購買的懸浮框
*/
private void showSuspend(){
if(suspendView == null){
suspendView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.buy_layout, null);
if(suspendLayoutParams == null){
suspendLayoutParams = new LayoutParams();
suspendLayoutParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE; //懸浮窗的類型,一般設為2002,表示在所有應用程序之上,但在狀態欄之下
suspendLayoutParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
suspendLayoutParams.flags = LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE; //懸浮窗的行為,比如說不可聚焦,非模態對話框等等
suspendLayoutParams.gravity = Gravity.TOP; //懸浮窗的對齊方式
suspendLayoutParams.width = screenWidth;
suspendLayoutParams.height = buyLayoutHeight;
suspendLayoutParams.x = 0; //懸浮窗X的位置
suspendLayoutParams.y = myScrollViewTop; ////懸浮窗Y的位置
}
}
mWindowManager.addView(suspendView, suspendLayoutParams);
}
/**
* 移除購買的懸浮框
*/
private void removeSuspend(){
if(suspendView != null){
mWindowManager.removeView(suspendView);
suspendView = null;
}
}
}
上面的代碼比較簡單,根據ScrollView滑動的距離來判斷顯示和移除懸浮框,懸浮框的實現主要是通過WindowManager這個類來實現的,調用這個類的addView方法用於添加一個懸浮框,removeView用於移除懸浮框。
通過上述代碼就實現了美團,大眾點評的這種效果,在運行項目之前我們必須在AndroidManifest.xml中加入<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW" />
我們運行下項目看下效果吧
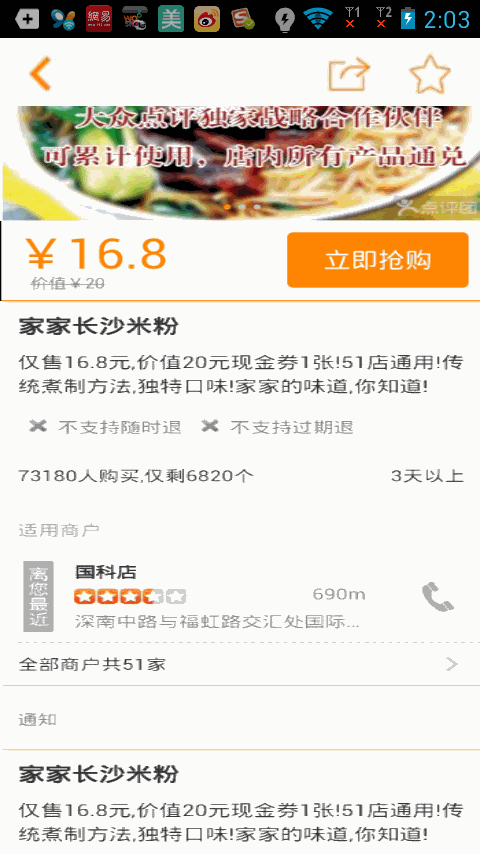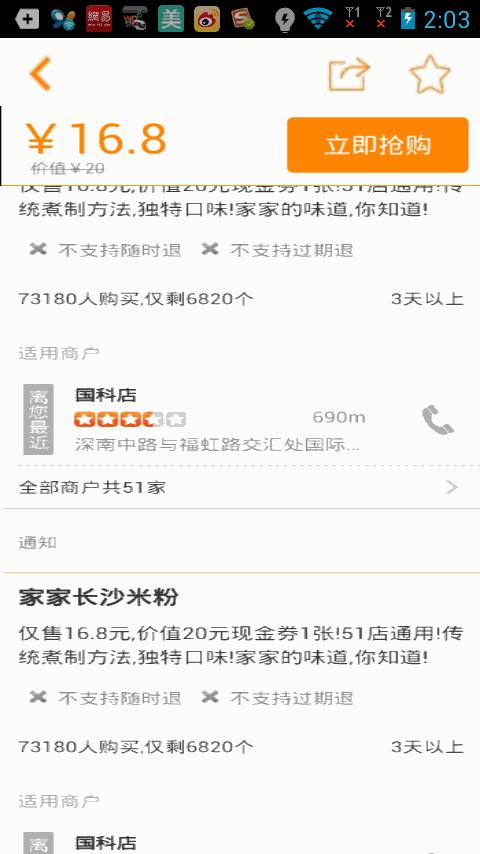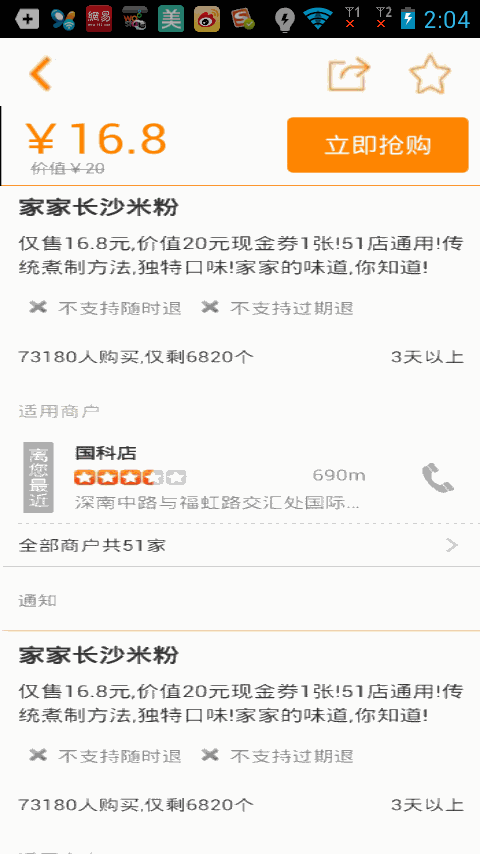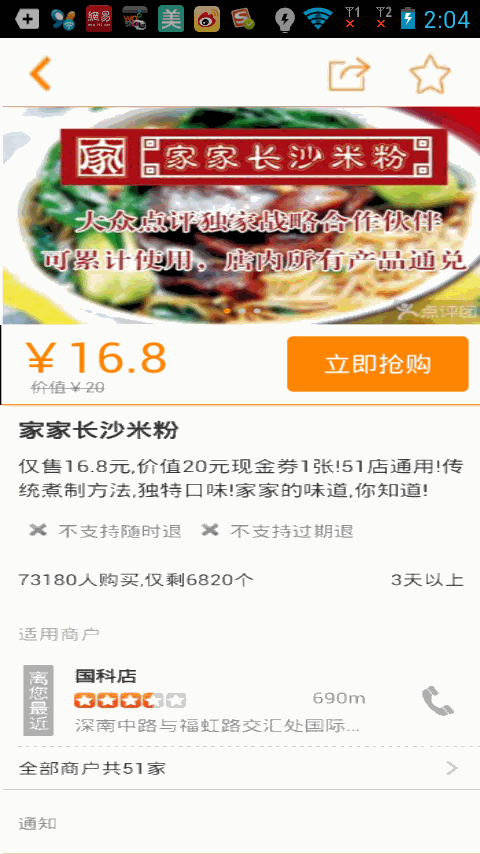
一個修改版
上面的代碼,其實我自己感覺效果並不是很好,如果快速滑動界面,顯示懸浮框的時候會出現一卡的現象,有些朋友說有時候會出現兩個布局的情況,特別是對ScrollView滾動的Y值得監聽,我還使用了Handler來獲取,還有朋友給我介紹了Scrolling Tricks這個東西,我下載試了下,確實美團網,大眾點評的購買框用的是這種效果,但是Scrolling Tricks只能在API11以上使用,這個有點小悲劇,然後我做了下修改,並將實現思路分享給大家,實現起來很簡單
首先還是要先對ScrollView進行滾動監聽,直接在onScrollChanged()方法中就能獲取滾動的Y值,之前那裡使用了Handler,走彎路了,直接看代碼吧
package com.example.meituandemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
public class MyScrollView extends ScrollView {
private OnScrollListener onScrollListener;
public MyScrollView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
/**
* 設置滾動接口
* @param onScrollListener
*/
public void setOnScrollListener(OnScrollListener onScrollListener) {
this.onScrollListener = onScrollListener;
}
@Override
public int computeVerticalScrollRange() {
return super.computeVerticalScrollRange();
}
@Override
protected void onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt) {
super.onScrollChanged(l, t, oldl, oldt);
if(onScrollListener != null){
onScrollListener.onScroll(t);
}
}
/**
*
* 滾動的回調接口
*/
public interface OnScrollListener{
/**
* 回調方法, 返回MyScrollView滑動的Y方向距離
* @param scrollY
* 、
*/
public void onScroll(int scrollY);
}
}
接下來看看主界面的布局文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/parent_layout"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="45dip"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:src="@drawable/navigation_bar" />
<com.example.meituandemo.MyScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iamge"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/pic"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
<include
android:id="@+id/buy"
layout="@layout/buy_layout" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/one"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/one"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/one"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />
</LinearLayout>
<include
android:id="@+id/top_buy_layout"
layout="@layout/buy_layout" />
</FrameLayout>
</com.example.meituandemo.MyScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
下面是布局的效果圖
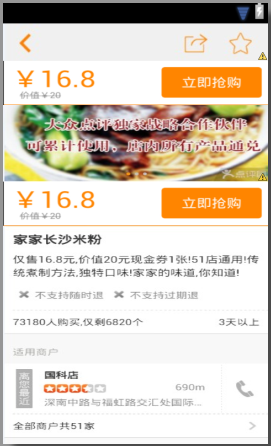
從主界面的布局你可以看出,我們在上面放置了一個購買的布局,可能你會想,先讓上面的布局隱藏起來,等下面的布局滑動上來就將其顯示出來,如果這樣子就跟我之前寫的那篇文章差不多,效果不是很棒,所以這篇修改版的肯定不是這樣子的,我們還是先看主界面的代碼吧
package com.example.meituandemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import com.example.meituandemo.MyScrollView.OnScrollListener;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnScrollListener{
/**
* 自定義的MyScrollView
*/
private MyScrollView myScrollView;
/**
* 在MyScrollView裡面的購買布局
*/
private LinearLayout mBuyLayout;
/**
* 位於頂部的購買布局
*/
private LinearLayout mTopBuyLayout;
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
myScrollView = (MyScrollView) findViewById(R.id.scrollView);
mBuyLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.buy);
mTopBuyLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.top_buy_layout);
myScrollView.setOnScrollListener(this);
//當布局的狀態或者控件的可見性發生改變回調的接口
findViewById(R.id.parent_layout).getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
//這一步很重要,使得上面的購買布局和下面的購買布局重合
onScroll(myScrollView.getScrollY());
}
});
}
@Override
public void onScroll(int scrollY) {
int mBuyLayout2ParentTop = Math.max(scrollY, mBuyLayout.getTop());
mTopBuyLayout.layout(0, mBuyLayout2ParentTop, mTopBuyLayout.getWidth(), mBuyLayout2ParentTop + mTopBuyLayout.getHeight());
}
}
主界面就短短的幾行代碼,可能看完這些代碼你還是沒有明白到底是怎麼做到的,沒關系,我給大家說說,其實我們是讓上面的購買布局和下面的購買布局重合起來了,layout()這個方法是確定View的大小和位置的,然後將其繪制出來,裡面的四個參數分別是View的四個點的坐標,他的坐標不是相對屏幕的原點,而且相對於他的父布局來說的,
我們在主頁面最外層的ViewGroup添加了布局狀態改變的監聽器,當繪制完了屏幕會回調到方法onGlobalLayout()中,我們在onGlobalLayout()方法中手動調用了下onScroll()方法,剛開始myScrollView.getScrollY()等於0,所以說當scrollY小於mBuyLayout.getTop()的時候,上面的購買布局的上邊緣到myScrollView的上邊緣的距離等於mBuyLayout.getTop()(即下面布局的上邊緣到myScrollView的上邊緣)所以剛開始上面的購買布局和下面的購買布局重合了。
當myScrollView向上滾動,而上面購買布局的上邊緣始終要和myScrollView的上邊緣保持mBuyLayout.getTop()這個距離,所以上面的購買布局也跟著向上滾動,當scrollY大於mBuyLayout.getTop()的時候,表示購買布局上邊緣滑動到了導航欄布局,所以此時購買布局的上邊緣與myScrollView的上邊緣始終要保持scrollY這個距離,所以購買布局才會一直在導航欄下面,就好像粘住了一樣,不知道你了解了沒有?好了,不過根據這種思路你也可以剛開始使用一個懸浮框來覆蓋在下面的購買布局上面,然後onScroll()方法中更新懸浮框的位置,不過懸浮框的x,y不是相對於父布局的,這點要注意下,這樣子也能實現效果,不過相對於此,要復雜的多,所以我們遇到類似的功能直接使用這種就行了,簡潔明了,好了,你是不迫不及待的想看下效果,那我們接下來就運行下程序吧
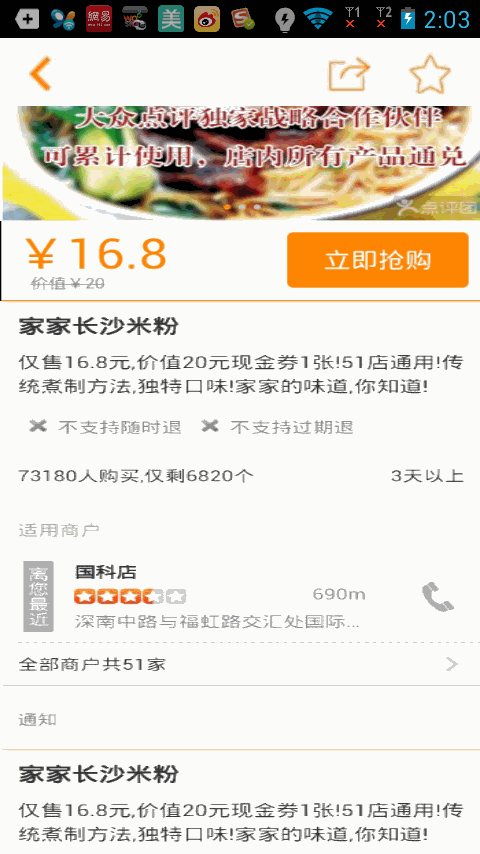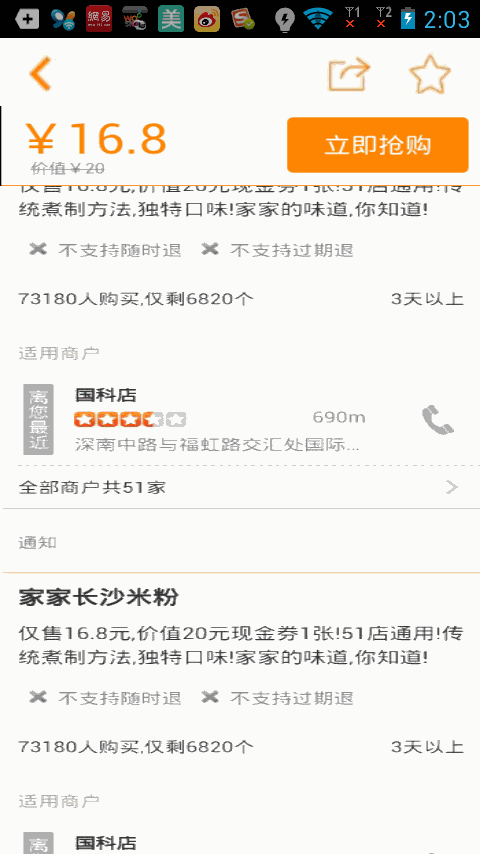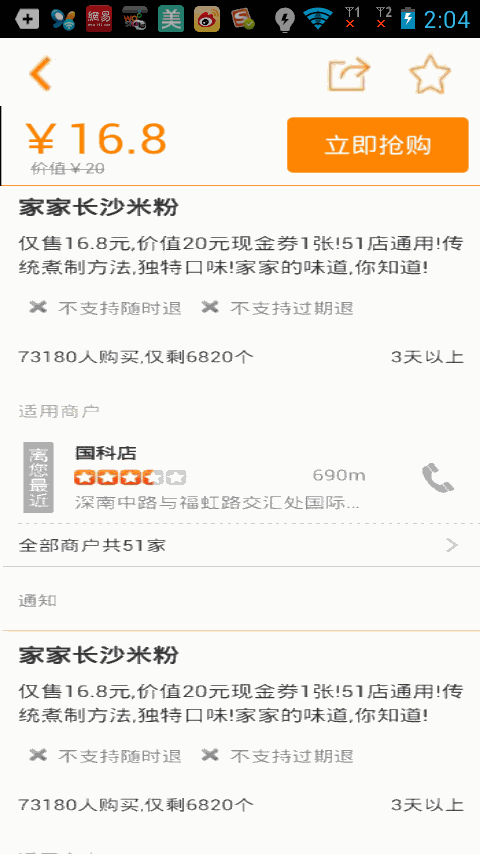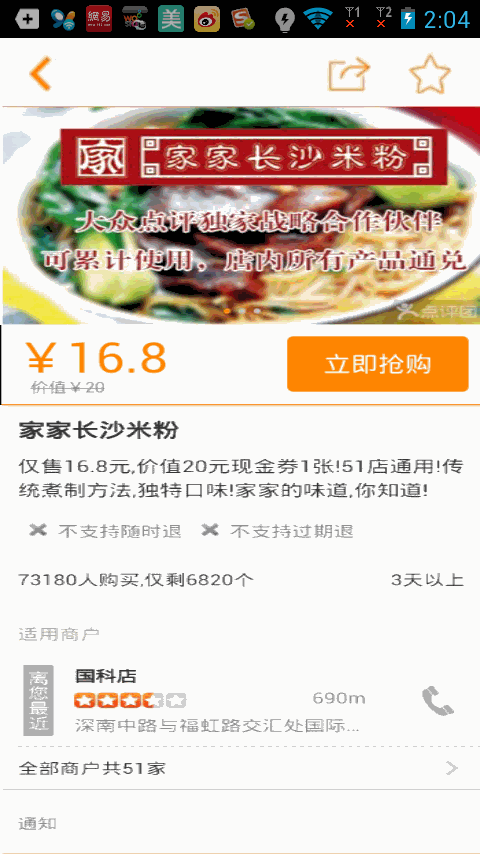
含有多個購買布局的效果,下一個購買布局會將上一個購買布局頂上去,使用方法也很簡單,只需要將你需要設置的布局設置Tag為sticky, 如
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="100dip"
android:background="#ff00ffff"
android:tag="sticky" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
</FrameLayout>
這樣子這個布局滾動到了頂部就會粘在頂部,大家可以試試!
 手把手教你解析Resources.arsc
手把手教你解析Resources.arsc
一、前言對於APK裡面的Resources.arsc文件大家應該都知道是干什麼的,它實際上就是App的資源索引表。下面我會結合實例對它的格式做一下剖析,讀完這篇文章應該能
 米SIM是什麼?米SIM怎麼開通?
米SIM是什麼?米SIM怎麼開通?
米SIM是小米推出的一款數據流量上網的服務,只要接通了米SIM,不需要用電話卡,就能夠實現數據流量的上網,能夠讓用戶體會到一個上網的樂趣,並且還不用花費其他
 Android自定義View—滑動開關
Android自定義View—滑動開關
MainActivity如下:+currentStatus, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } } Sw
 創建Material Design風格的Android應用--應用主題
創建Material Design風格的Android應用--應用主題
本人所有文章首先發布於個人博客,歡迎關注,地址:http://blog.isming.me 昨天正式發布了android 5,同時android developer