編輯:關於Android編程
我們從Activity的setContentView()入手,開始源碼解析,
//Activity.setContentView
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initActionBar();
}
//PhoneWindow.setContentView
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}
發現是使用mLayoutInflater創建View的,所以我們去LayoutInflater.inflate()裡面看下,
public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
if (DEBUG) System.out.println("INFLATING from resource: " + resource);
XmlResourceParser parser = getContext().getResources().getLayout(resource);
try {
return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
} finally {
parser.close();
}
}
先根據resource id 獲取到XmlResourceParseer,意如其名,就是xml的解析器,繼續往下,進入到inflate的核心方法,有些長,我們只分析關鍵部分:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
......
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
rInflate(parser, root, attrs, false);
} else {
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
View temp;
if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
temp = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
} else {
temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, attrs);
}
......
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} catch (IOException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(
parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": " + e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} finally {
// Don't retain static reference on context.
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
mConstructorArgs[1] = null;
}
return result;
}
}
如果tag的名字不是TAG_1995(名字是個梗),就調用函數createViewFromTag()創建View,進去看看,
View createViewFromTag(View parent, String name, AttributeSet attrs) {
if (name.equals("view")) {
name = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "class");
}
......
View view;
if (mFactory2 != null) view = mFactory2.onCreateView(parent, name, mContext, attrs);
else if (mFactory != null) view = mFactory.onCreateView(name, mContext, attrs);
else view = null;
if (view == null && mPrivateFactory != null) {
view = mPrivateFactory.onCreateView(parent, name, mContext, attrs);
}
if (view == null) {
if (-1 == name.indexOf('.')) {
view = onCreateView(parent, name, attrs);
} else {
view = createView(name, null, attrs);
}
}
if (DEBUG) System.out.println("Created view is: " + view);
return view;
......
}
首先嘗試用3個Fractory創建View,如果成功就直接返回了。注意,我們可以利用這個機制,創建自己的Factory來控制View的創建過程。
如果沒有Factory或創建失敗,那麼走默認邏輯。
先判斷name中是否有'.'字符,如果沒有,則認為使用android自己的View,此時會在name的前面加上包名"android.view.";如果有這個'.',則認為使用的自定義View,這時無需添加任何前綴,認為name已經包含全包名了。
最終,使用這個全包名的name來創建實例,
private static final HashMap<String, Constructor<? extends View>> sConstructorMap =
new HashMap<String, Constructor<? extends View>>();
protected View onCreateView(String name, AttributeSet attrs)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return createView(name, "android.view.", attrs);
}
public final View createView(String name, String prefix, AttributeSet attrs)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InflateException {
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = sConstructorMap.get(name);
Class<? extends View> clazz = null;
......
if (constructor == null) {
// Class not found in the cache, see if it's real, and try to add it
clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(
prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name).asSubclass(View.class);
if (mFilter != null && clazz != null) {
boolean allowed = mFilter.onLoadClass(clazz);
if (!allowed) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
}
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
sConstructorMap.put(name, constructor);
} else {
// If we have a filter, apply it to cached constructor
if (mFilter != null) {
// Have we seen this name before?
Boolean allowedState = mFilterMap.get(name);
if (allowedState == null) {
// New class -- remember whether it is allowed
clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(
prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name).asSubclass(View.class);
boolean allowed = clazz != null && mFilter.onLoadClass(clazz);
mFilterMap.put(name, allowed);
if (!allowed) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
} else if (allowedState.equals(Boolean.FALSE)) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
}
}
Object[] args = mConstructorArgs;
args[1] = attrs;
return constructor.newInstance(args);
......
}
從源碼中看到,在創建實例前,會先從一個靜態Map中獲取緩存,
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = sConstructorMap.get(name);
緩存的是Constructor對象,目的是用於創建實例,這裡要注意sConstructorMap是靜態的,並且通過Constructor創建的實例,是使用和Constructor對象同一個ClassLoader來創建的,換句話說,在同一個進程中,同一個自定義View對象,是無法用不同ClassLoader加載的,如果想解決這個問題,就不要讓系統使用createView()接口創建View,做法就是自定義Factory或Factory2來自行創建View。
繼續往下看,如果緩存裡沒有,則創建View的Class對象clazz,並緩存到sConstructorMap中,
if (constructor == null) {
// Class not found in the cache, see if it's real, and try to add it
clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(
prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name).asSubclass(View.class);
if (mFilter != null && clazz != null) {
boolean allowed = mFilter.onLoadClass(clazz);
if (!allowed) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
}
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
sConstructorMap.put(name, constructor);
}
然後就是newInstance了,至此這個View便從xml中變成了java對象,我們繼續返回到inflate函數中,看看這個View返回之後做了什麼,
......
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
View temp;
if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
temp = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
} else {
temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, attrs);
}
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
// Create layout params that match root, if supplied
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
// Set the layout params for temp if we are not
// attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
// Inflate all children under temp
rInflate(parser, temp, attrs, true);
// We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp)
// to root. Do that now.
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
// Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
// top view found in xml.
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp;
}
......
return result;
從createViewFromTag返回後,會調用個rInflate(),其中parent參數就是剛才創建出的View,應該能猜到裡面做了什麼,
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs,
boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
}
parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
} else if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
final View view = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
} else {
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
}
}
if (finishInflate) parent.onFinishInflate();
}
沒錯,就是遞歸的使用createViewFromTag()創建子View,並通過ViewGroup.addView添加到parent view中。
之後,這個View樹上的所有View都創建完畢。然後會根據inflate()的參數(root和attachToRoot)判斷是否將新創建的View添加到root view中,
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
然後,inflate()就將View返回了。
以上內容是小編給大家介紹的android從xml加載到view對象過程解析,希望對大家有所幫助!
 Android Xutils框架使用問題及解決辦法
Android Xutils框架使用問題及解決辦法
剛剛寫了篇博客,提了下在使用XUtils時遇到的一個問題Android Xutils框架HttpUtil Get請求緩存問題 ,既然已經提起來這個問題,那我想了下,就把之
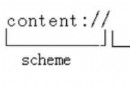 Android中ContentProvider組件詳解
Android中ContentProvider組件詳解
一.Android四大組件Android四大組件是Activity, Service, Content Provider,Broadcast Receiver。Activ
 Launcher3--抽屜
Launcher3--抽屜
抽屜是用來放置安卓手機中所有需要顯示到Launcher上的(當然也可以進行過濾,將不想顯示的隱藏起來)應用和小部件,啟動應用、添加快捷方式到桌面、卸載等。之前也提到過,有
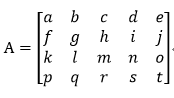 Android色彩矩陣——ColorMatrix
Android色彩矩陣——ColorMatrix
在Android的開發中,我們少不了對圖片進行處理,其中最常使用的數據結構就是位圖Bitmap,它包含了一張圖片的所有數據。既然是位圖那它就是由一個個像素點組成的。每一個