編輯:關於Android編程
一、WIndow和windowManager
Window是一個抽象類,它的具體實現是PhoneWindow,創建一個window很簡單,只需要創建一個windowManager即可,window具體實現在windowManagerService中,windowManager和windowManagerService的交互是一個IPC的過程。
下面是用windowManager的例子:
mFloatingButton = new Button(this);
mFloatingButton.setText( "window");
mLayoutParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams. WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 0, 0,
PixelFormat. TRANSPARENT);
mLayoutParams. flags = LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| LayoutParams. FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
| LayoutParams. FLAG_SHOW_WHEN_LOCKED;
mLayoutParams. type = LayoutParams. TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR;
mLayoutParams. gravity = Gravity. LEFT | Gravity. TOP;
mLayoutParams. x = 100;
mLayoutParams. y = 300;
mFloatingButton.setOnTouchListener( this);
mWindowManager.addView( mFloatingButton, mLayoutParams);
flags和type兩個屬性很重要,下面對一些屬性進行介紹,首先是flags:
FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL表示不需要獲取焦點,也不需要接收各種輸入,最終事件直接傳遞給下層具有焦點的window。
FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE:在此window外的區域單擊事件傳遞到底層window中。當前的區域則自己處理,這個一般都要設置,很重要。
FLAG_SHOW_WHEN_LOCKED :開啟可以讓window顯示在鎖屏界面上。
再來看下type這個參數:
window有三種類型:應用window,子window,系統window。應用類對應一個Activity,子Window不能單獨存在,需要附屬在父Window上,比如常用的Dialog。系統Window是需要聲明權限再創建的window,如toast等。
window有z-ordered屬性,層級越大,越在頂層。應用window層級1-99,子window1000-1999,系統2000-2999。這此層級對應著windowManager的type參數。系統層級常用的有兩個TYPE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY或者TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR。比如想用TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR,只需
mLayoutParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR。還要添加權限<uses-permission andorid:name="android.permission.SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW"/>。
有了對window的基本認識之後,我們來看下它底層如何實現加載View的。
二、window的創建
其實Window的創建跟之前我寫的一篇博客LayoutInflater源碼分析有點相似。Window的創建是在Activity創建的attach方法中,通過PolicyManager的makeNewWindow方法。Activity中實現了Window的Callback接口,因此當window狀態改變時就會回調Activity方法。如onAttachedToWindow等。PolicyManager的真正實現類是Policy,看下它的代碼:
public Window makeNewWindow(Context context) {
return new PhoneWindow(context);
}
到此Window創建完成。
下面分析view是如何附屬到window上的。看Activity的setContentView方法。
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
兩部分,設置內容和設置ActionBar。window的具體實現是PhoneWindow,看它的setContent。
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}
看到了吧,又是分析它。
這裡分三步執行:
1.如果沒有DecorView,在installDecor中的generateDecor()創建DecorView。之前就分析過,這次就不再分析它了。
2.將View添加到decorview中的mContentParent中。
3.回調Activity的onContentChanged接口。
經過以上操作,DecorView創建了,但還沒有正式添加到Window中。在ActivityResumeActivity中首先會調用Activity的onResume,再調用Activity的makeVisible,makeVisible中真正添加view ,代碼如下:
void makeVisible() {
if (!mWindowAdded) {
ViewManager wm = getWindowManager();
wm.addView(mDecor, getWindow().getAttributes());
mWindowAdded = true;
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
通過上面的addView方法將View添加到Window。
三、Window操作View內部機制
1.window的添加
一個window對應一個view和一個viewRootImpl,window和view通過ViewRootImpl來建立聯系,它並不存在,實體是view。只能通過 windowManager來操作它。
windowManager的實現類是windowManagerImpl。它並沒有直接實現三大操作,而是委托給WindowManagerGlobal。addView的實現分為以下幾步:
1).檢查參數是否合法。
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (display == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);
} else {
// If there's no parent and we're running on L or above (or in the
// system context), assume we want hardware acceleration.
final Context context = view.getContext();
if (context != null
&& context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
}
2).創建ViewRootImpl並將View添加到列表中。
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
3).通過ViewRootImpl來更新界面並完成window的添加過程 。
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
上面的root就是ViewRootImpl,setView中通過requestLayout()來完成異步刷新,看下requestLayout:
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
接下來通過WindowSession來完成window添加過程,WindowSession是一個Binder對象,真正的實現類是 Session,window的添加是一次IPC調用。
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
}
在Session內部會通過WindowManagerService來實現Window的添加。
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
InputChannel outInputChannel) {
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outInputChannel);
}
在WindowManagerService內部會為每一個應用保留一個單獨的session。
2.window的刪除
看下WindowManagerGlobal的removeView:
public void removeView(View view, boolean immediate) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
View curView = mRoots.get(index).getView();
removeViewLocked(index, immediate);
if (curView == view) {
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Calling with view " + view
+ " but the ViewAncestor is attached to " + curView);
}
}
首先調用findViewLocked來查找刪除view的索引,這個過程就是建立數組遍歷。然後再調用removeViewLocked來做進一步的刪除。
private void removeViewLocked(int index, boolean immediate) {
ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
View view = root.getView();
if (view != null) {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
if (imm != null) {
imm.windowDismissed(mViews.get(index).getWindowToken());
}
}
boolean deferred = root.die(immediate);
if (view != null) {
view.assignParent(null);
if (deferred) {
mDyingViews.add(view);
}
}
}
真正刪除操作是viewRootImpl來完成的。windowManager提供了兩種刪除接口,removeViewImmediate,removeView。它們分別表示異步刪除和同步刪除。具體的刪除操作由ViewRootImpl的die來完成。
boolean die(boolean immediate) {
// Make sure we do execute immediately if we are in the middle of a traversal or the damage
// done by dispatchDetachedFromWindow will cause havoc on return.
if (immediate && !mIsInTraversal) {
doDie();
return false;
}
if (!mIsDrawing) {
destroyHardwareRenderer();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Attempting to destroy the window while drawing!\n" +
" window=" + this + ", title=" + mWindowAttributes.getTitle());
}
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_DIE);
return true;
}
由上可知如果是removeViewImmediate,立即調用doDie,如果是removeView,用handler發送消息,ViewRootImpl中的Handler會處理消息並調用doDie。重點看下doDie:
void doDie() {
checkThread();
if (LOCAL_LOGV) Log.v(TAG, "DIE in " + this + " of " + mSurface);
synchronized (this) {
if (mRemoved) {
return;
}
mRemoved = true;
if (mAdded) {
dispatchDetachedFromWindow();
}
if (mAdded && !mFirst) {
destroyHardwareRenderer();
if (mView != null) {
int viewVisibility = mView.getVisibility();
boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility;
if (mWindowAttributesChanged || viewVisibilityChanged) {
// If layout params have been changed, first give them
// to the window manager to make sure it has the correct
// animation info.
try {
if ((relayoutWindow(mWindowAttributes, viewVisibility, false)
& WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_FIRST_TIME) != 0) {
mWindowSession.finishDrawing(mWindow);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
mSurface.release();
}
}
mAdded = false;
}
WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().doRemoveView(this);
}
主要做四件事:
1.垃圾回收相關工作,比如清數據,回調等。
2.通過Session的remove方法刪除Window,最終調用WindowManagerService的removeWindow
3.調用dispathDetachedFromWindow,在內部會調用onDetachedFromWindow()和onDetachedFromWindowInternal()。當view移除時會調用onDetachedFromWindow,它用於作一些資源回收。
4.通過doRemoveView刷新數據,刪除相關數據,如在mRoot,mDyingViews中刪除對象等。
void doRemoveView(ViewRootImpl root) {
synchronized (mLock) {
final int index = mRoots.indexOf(root);
if (index >= 0) {
mRoots.remove(index);
mParams.remove(index);
final View view = mViews.remove(index);
mDyingViews.remove(view);
}
}
if (HardwareRenderer.sTrimForeground && HardwareRenderer.isAvailable()) {
doTrimForeground();
}
}
3.更新window
看下WindowManagerGlobal中的updateViewLayout。
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params;
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
mParams.remove(index);
mParams.add(index, wparams);
root.setLayoutParams(wparams, false);
}
}
通過viewRootImpl的setLayoutParams更新viewRootImpl的layoutParams,接著scheduleTraversals對view重新布局,包括測量,布局,重繪,此外它還會通過WindowSession來更新window。這個過程由WindowManagerService實現。這跟上面類似,就不再重復,到此Window底層源碼就分析完啦。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助。
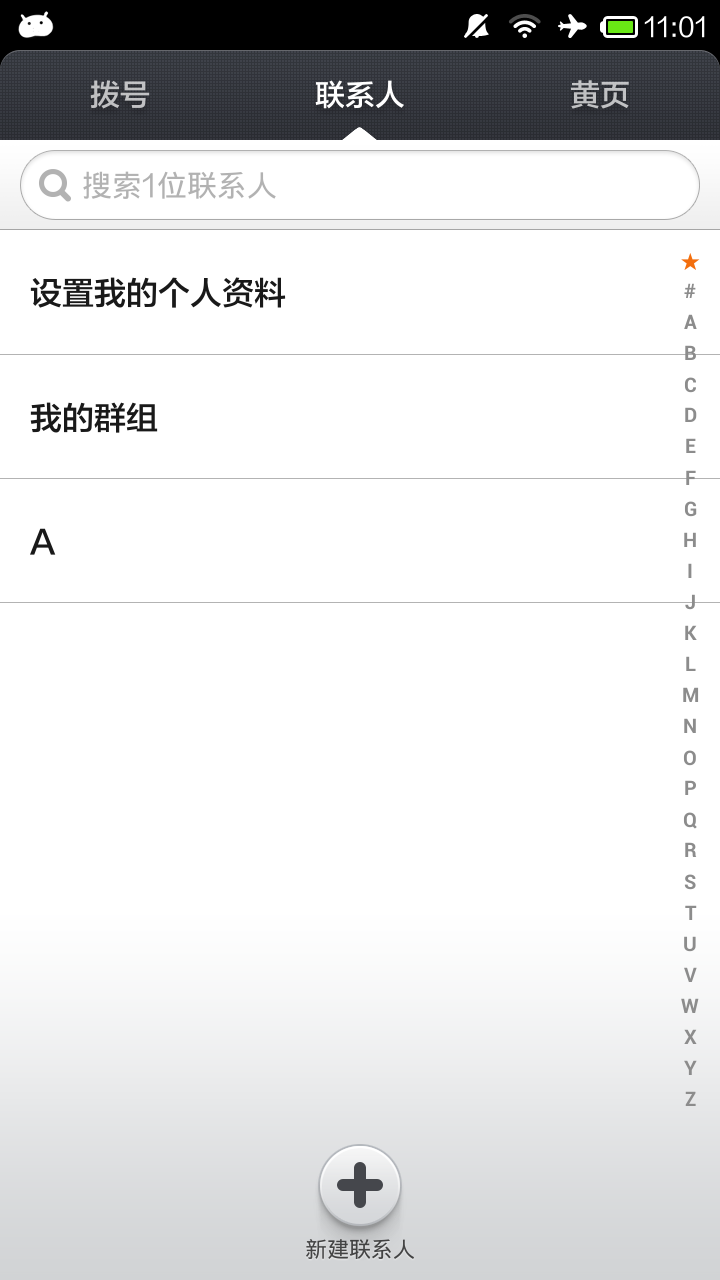 自定義字母索引View
自定義字母索引View
在聯系人,好友等列表中,為了能夠快速的根據名稱查找到相應的聯系人或者好友,通常會建立一個可以根據字母快速定位名稱的View。如下圖中右邊字母表所示:1.自定義View關於
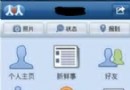 Android布局案例之人人android九宮格
Android布局案例之人人android九宮格
人人android是人人網推出的一款優秀的手機應用軟件,我們在使用的時候發現他的首頁布局是九宮格模式的,讓人覺得很別致,因為現在很多的 android軟件很少使用這種布局
 Android帶圓形數字進度的自定義進度條示例
Android帶圓形數字進度的自定義進度條示例
開發設計搞了一個帶圓形進度的進度條,在GitHub上逛了一圈,發現沒有,自己撸吧。先看界面效果:主要思路是寫一個繼承ProgressBar的自定義View,不廢話,直接上
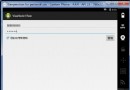 Android數據存儲之IO
Android數據存儲之IO
Android開發中免不了數據本地的存儲,今天我們來說一說如何利用IO流來進行數據存儲。這裡我們通過模擬一個QQ登陸界面的小demo來實際操作IO流。功能描述:點擊按鈕能