編輯:關於Android編程
Fragment 的出現一方面是為了緩解 Activity 任務過重的問題,另一方面是為了處理在不同屏幕上 UI 組件的布局問題,而且它還提供了一些新的特性(例如 Retainable)來處理一些在 Activity 中比較棘手的問題。Fragment 擁有和 Activity 一致的生命周期,它和 Activity 一樣被定義為 Controller 層的類。有過中大型項目開發經驗的開發者,應該都會遇到過 Activity 過於臃腫的情況,而 Fragment 的出現就是為了緩解這一狀況,可以說 它將屏幕分解為多個「Fragment(碎片)」(這句話很重要),但它又不同於 View,它干的實質上就是 Activity 的事情,負責控制 View 以及它們之間的邏輯。將屏幕碎片化為多個 Fragment 後,其實 Activity 只需要花精力去管理當前屏幕內應該顯示哪些 Fragments,以及應該對它們進行如何布局就行了。這是一種組件化的思維,用 Fragment 去組合了一系列有關聯的 UI 組件,並管理它們之間的邏輯,而 Activity 負責在不同屏幕下(例如橫豎屏)布局不同的 Fragments 組合。這種碎片不單單能管理可視的 Views,它也能執行不可視的 Tasks,它提供了 retainInstance 屬性,能夠在 Activity 因為屏幕狀態發生改變(例如切換橫豎屏時)而銷毀重建時,依然保留實例。這示意著我們能在 RetainedFragment 裡面執行一些在屏幕狀態發生改變時不被中斷的操作。
下面我們就來具體看一個Android Fragment功能的例子。
實現的功能很簡單,也是最基本的,上下分別是兩個Fragment,上面的Fragment中是一個listview,當點擊item時,下面的Fragment顯示對應的文字詳細信息:


具體的實現步驟如下:
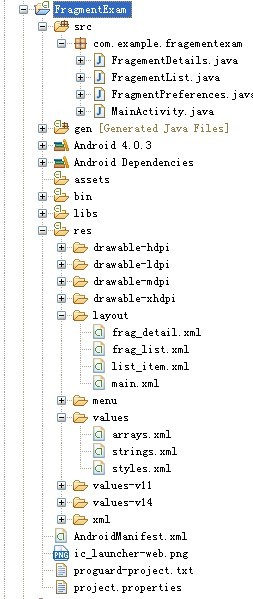
①創建工程FragmentExam,目錄視圖如下(把之前的FragmentPreference的demo也加到了一起):
②main.xml文件布局,垂直方向上兩個Fragment,用<Fragment>標簽聲明
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#7ecef4">
<fragment
android:name="com.example.fragementexam.FragementList"
android:id="@+id/frag_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="2"/>
<fragment
android:name="com.example.fragementexam.FragementDetails"
android:id="@+id/frag_detail"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
③FragmentList.java的代碼,它繼承了ListFragment,注意在onCreateView方法中使用inflater的inflate方法將布局頁面引進:
package com.example.fragementexam;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.ListFragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class FragementList extends ListFragment {
private String[] values = new String[] { "侏儒", "人類", "暗夜精靈", "矮人", "德萊尼",
"狼人" };
private int[] images = new int[] { R.drawable.gnome,
R.drawable.human, R.drawable.nightelf,
R.drawable.dwarf, R.drawable.draenei,
R.drawable.werewolf };
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_list, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
List<Map<String, Object>> listItems = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
Map<String, Object> listItem = new HashMap<String, Object>();
listItem.put("values", values[i]);
listItem.put("images", images[i]);
listItems.add(listItem);
}
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(getActivity(), listItems,
R.layout.list_item, new String[] { "values", "images" },
new int[] { R.id.txt_title, R.id.img });
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
// String item = (String) getListAdapter().getItem(position);
FragementDetails frag = (FragementDetails) getFragmentManager()
.findFragmentById(R.id.frag_detail);
if (frag != null && frag.isInLayout()) {
switch (position) {
case 0:
frag.setText(getString(R.string.Gnome));
break;
case 1:
frag.setText(getString(R.string.Human));
break;
case 2:
frag.setText(getString(R.string.NightElf));
break;
case 3:
frag.setText(getString(R.string.Dwarf));
break;
case 4:
frag.setText(getString(R.string.Draenei));
break;
case 5:
frag.setText(getString(R.string.Werewolf));
break;
}
}
Log.i("PDA", "position = " + position);
}
}
④FragementDetails.java的代碼,這個比較簡單,裡面有一個設置TextView內容的方法,其布局頁面也僅僅是一個TextView
package com.example.fragementexam;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class FragementDetails extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.frag_detail, container,false);
}
public void setText(String item){
TextView txt = (TextView) getView().findViewById(R.id.txt_detail);
txt.setText(item);
}
}
其他的部分就是一些數組,String的定義了,這個demo雖然簡單,卻將Android Fragment方面常用到的做了一個綜述,如果自己寫明白了這個的話,今後遇到類似的項目應該要好應付的多,好了,收工!
 Android項目之_硅谷商城項目全套源碼解析(一、綜述)
Android項目之_硅谷商城項目全套源碼解析(一、綜述)
一、簡介硅谷商城是一款按照企業級標准研發的項目。本套代碼是目前國內市場第一套詳細講解商城類項目的免費代碼。該代碼中的內容包括但不僅限於,框架的搭建、主頁模塊、分類模塊、發
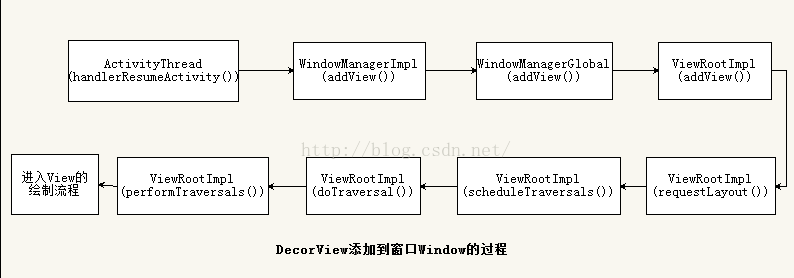 android6.0 Activity(五) Activity的測量(Measure)、布局(Layout)和繪制(Draw)
android6.0 Activity(五) Activity的測量(Measure)、布局(Layout)和繪制(Draw)
Android應用程序窗口的繪圖表面在創建完成之後,我們就可以從上到下地繪制它裡面的各個視圖了,即各個UI元素了。不過在繪制這些UI元素之前,我們還需要從上到下地測量它們
 android 音樂播放器總結
android 音樂播放器總結
學習從模仿開始一個星期完成的音樂播放器基本功能,具有下一首,上一首,暫停和隨機、順序和單曲等播放,以及保存上一次播放的狀態,缺少了歌詞顯示功能。使用了andbase框架的
 Android手機可以實現隨時隨地快遞查詢
Android手機可以實現隨時隨地快遞查詢
隨著網絡購物的流行,我們經常要和不同的快遞公司打交道,大多數人都知道通過快遞單號可以在快遞公司網站上查詢快遞的狀態。但是如果自己不在電腦旁邊,是不是就查詢不