編輯:關於Android編程
廢話不多說,咱們第一篇文章就是模仿“知乎”的回答詳情頁的動畫效果,先上個原版的效果圖,咱們就是要做出這個效果
在實現之前,我們先根據上面的動畫效果,研究下需求,因為gif幀數有限,所以不是很連貫,推薦你直接下載一個知乎,找到這個界面自己玩玩
☞當文章往上移動到一定位置之後,最上面的標題欄Bar和問題布局Title是會隱藏的,回答者Author布局不會隱藏
☞當文章往下移動移動到一定位置之後,原先隱藏的標題欄Bar和問題布局Title會下降顯示
☞當文章往上移動的時候,下部隱藏的Tools布局會上升顯示
☞當文章往下移動的時候,如果Tools布局是顯示的,則隱藏
☞當標題欄Bar和問題布局Title下降顯示的時候,Title是從Bar的下面出來的,有個遮擋的效果
☞當快速滑動內容到達底部的時候,隱藏的Tools會顯示出來
☞當快速滑動內容到頂部的時候,隱藏的Bar和Title也會顯示出來
不分析不知道,這樣一個簡單地效果,經過分析需要完成不少東西呢,那麼下面根據要實現的需求,咱們分析一下解決方案。
在做這種仿界面之前,我們可以使用ADT帶的View Hierarchy工具看一下“知乎”原生是怎麼實現的
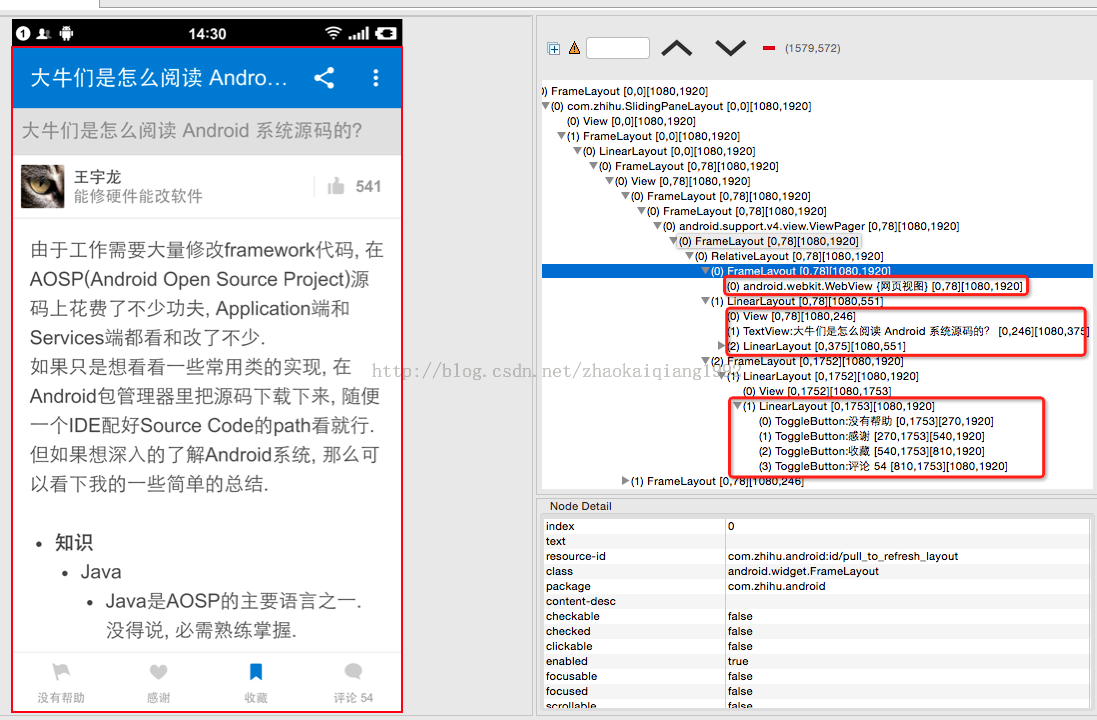
從右邊的分析圖可以看出,知乎的這個界面,內容用的WebView,這很正常,因為用戶的回答裡面格式比較復雜,用WebView是最好的解決方案,而標題欄是一個VIew,是ActionBar還是自定義View呢,不得而知,下面是就是一個LinearLayout包了4個ToggleButton,布局很簡單,我們沒有WebView,所以使用ScrollView代替,上面的布局直接ImageView了,設置個src,模擬一個布局。
其實布局很簡單,咱們一個效果一個效果的來實現。
首先是下面的Tools如何顯示和隱藏呢?當然是用動畫了!什麼動畫呢?能實現的有屬性動畫和幀動畫,屬性動畫能夠真實的改變View的屬性,幀動畫只是視覺上移動了,View的實際屬性並不改變,這兩種都可以,我們這裡使用屬性動畫
/**
* 顯示工具欄
*/
private void showTools() {
ObjectAnimator anim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(img_tools, "y", img_tools.getY(),
img_tools.getY() - img_tools.getHeight());
anim.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim.start();
isToolsHide = false;
}
/**
* 隱藏工具欄
*/
private void hideTools() {
ObjectAnimator anim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(img_tools, "y", img_tools.getY(),
img_tools.getY() + img_tools.getHeight());
anim.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim.start();
isToolsHide = true;
}
那麼什麼時候調用呢?從上面的需求分析中,我們知道,用戶手指下拉的時候,Tools顯示,反之隱藏,那麼我們就可以監聽ScrollView的onTouch,判斷手指方向,實現動畫效果的調用
mScroller.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastY = event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
float disY = event.getY() - lastY;
//垂直方向滑動
if (Math.abs(disY) > viewSlop) {
//是否向上滑動
isUpSlide = disY < 0;
//實現底部tools的顯示與隱藏
if (isUpSlide) {
if (!isToolsHide)
hideTools();
} else {
if (isToolsHide)
showTools();
}
}
break;
}
return false;
}
});
用變量isToolsHide放置代碼重復調用。
下面的Tools的問題解決了,我們再看一下上面的布局動畫如何來實現。上面的思路和下面一樣,也是通過屬性動畫,完成位置的移動,移動的布局有Bar、Title和根布局。為什麼答題人布局Author不移動呢?因為根布局必須移動,否則就會擋住下面的文字內容,根布局的移動會讓子布局都跟著移動,所以只移動根布局即可。
對了,為了更大范圍的現實文本,“知乎”的WebView是占據整個布局的,其他布局都是在根布局FrameLayout裡面,所以,在首次加載的時候,下面的文本在開頭需要留出一定的間隔,防止被遮擋,當上面的布局隱藏之後,就沒有問題了。
在簡單分析之後,我再給出實現的布局的代碼
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@android:color/white"
>
<com.socks.zhihudetail.MyScrollView
android:id="@+id/scroller"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:text="@string/hello_world"/>
</com.socks.zhihudetail.MyScrollView>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/ll_top"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_gravity="top">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img_author"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/bg_author"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="55dp"
android:text="為什麼美國有那麼多肌肉極其強大的肌肉男?"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:background="#DBDBDB"
android:gravity="center|left"
android:paddingLeft="15dp"
android:paddingRight="15dp"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:textColor="@android:color/darker_gray"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="55dp"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/bg_actionbar"/>
</FrameLayout>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img_tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:src="@drawable/bg_bottom"/>
</FrameLayout>
效果圖如下,文本留了一些空行,保證不被遮擋。
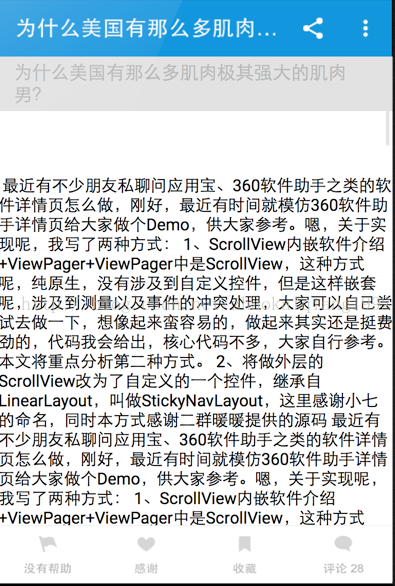
有的同學看了上面的效果圖可能會疑惑,這裡為什麼沒有答題人的布局呢?
其實是這樣的,為了模擬上部的布局顯示時,Title從Bar下面出現的效果,所以特意這樣設計的。我試過用linearLayout實現,效果也是可以實現的,但是當Title往下移動顯示的時候,會覆蓋在Bar上面,這也很好理解,LinearLayout沒有層次順序,所以會遮擋。我試過View.bringToFront(),試圖把Bar的布局提高層次,但是這樣會導致布局的紊亂,在首次加載的時候,Bar會顯示在最下面,是因為提高層次之後,Bar的布局重新計算,所以不按照LinearLayout的布局規則來了。無奈之下,換成了Framelayout,但是又出現了問題,Bar的高度可以設置,但是Title的高度會隨著文本的增加而改變,這樣一來,最下面Author的布局的位置就不能設置了,因為不知道距離上面多遠,所以我們只能在代碼裡面動態的計算Bar和Title的高度,然後在界面加載的時候,動態的給Author的布局設置MargenTop,保證位置的正確。
因為在onCreate裡面,還沒有開始View的繪制,所以得不到控件的真實高度,我們可以用下面的方法,獲取這個時期的高度
//獲取Bar和Title的高度,完成auther布局的margenTop設置
ViewTreeObserver viewTreeObserver = fl_top.getViewTreeObserver();
viewTreeObserver.addOnPreDrawListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener() {
@Override
public boolean onPreDraw() {
if (!hasMeasured) {
FrameLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(FrameLayout
.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, FrameLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
layoutParams.setMargins(0, img_bar.getHeight() + tv_title.getHeight(), 0, 0);
img_author.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
hasMeasured = true;
}
return true;
}
});
獲取了高度之後,我們就可以正確地設置位置了。但是,如果保證上面的布局隨著我們的內容的移動,而改變現實狀態呢?
經過我手動直觀測試,知乎的這個界面是根據一個固定的值,來改變顯示狀態的,因此,我們可以監聽ScrollView的滑動距離,來判斷。但是ScrollView並沒有給我們這樣一個監聽器,咋辦?重寫!
/**
* Created by zhaokaiqiang on 15/2/26.
*/
public class MyScrollView extends ScrollView {
private BottomListener bottomListener;
private onScrollListener scrollListener;
public MyScrollView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
protected void onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt) {
super.onScrollChanged(l, t, oldl, oldt);
if (getScrollY() + getHeight() >= computeVerticalScrollRange()) {
if (null != bottomListener) {
bottomListener.onBottom();
}
}
if (null != scrollListener) {
scrollListener.onScrollChanged(l, t, oldl, oldt);
}
}
public void setBottomListener(BottomListener bottomListener) {
this.bottomListener = bottomListener;
}
public void setScrollListener(onScrollListener scrollListener) {
this.scrollListener = scrollListener;
}
public interface onScrollListener {
public void onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt);
}
public interface BottomListener {
public void onBottom();
}
}
我們只需要重寫onScrollChange()方法即可,在裡面不光可以時時的得到位置的變化,還添加了一個BottomListener接口來監聽滑動到底部的事件,寫好之後就很簡單了
mScroller.setBottomListener(this); mScroller.setScrollListener(this);
/**
* 顯示上部的布局
*/
private void showTop() {
ObjectAnimator anim1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(img_bar, "y", img_bar.getY(),
0);
anim1.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim1.start();
ObjectAnimator anim2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_title, "y", tv_title.getY(),
img_bar.getHeight());
anim2.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
anim2.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION + 200);
anim2.start();
ObjectAnimator anim4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(fl_top, "y", fl_top.getY(),
0);
anim4.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim4.start();
isTopHide = false;
}
/**
* 隱藏上部的布局
*/
private void hideTop() {
ObjectAnimator anim1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(img_bar, "y", 0,
-img_bar.getHeight());
anim1.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim1.start();
ObjectAnimator anim2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_title, "y", tv_title.getY(),
-tv_title.getHeight());
anim2.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim2.start();
ObjectAnimator anim4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(fl_top, "y", 0,
-(img_bar.getHeight() + tv_title.getHeight()));
anim4.setDuration(TIME_ANIMATION);
anim4.start();
isTopHide = true;
}
@Override
public void onBottom() {
if (isToolsHide) {
showTools();
}
}
@Override
public void onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt) {
if (t <= dp2px(TOP_DISTANCE_Y) && isTopHide && isAnimationFinish) {
showTop();
Log.d(TAG, "顯示");
} else if (t > dp2px(TOP_DISTANCE_Y) && !isTopHide && isAnimationFinish) {
hideTop();
Log.d(TAG, "隱藏");
}
}
我們只需要根據當前的位置,來實現布局的顯示和隱藏就可以啦!
OK,這篇文章就到這裡,希望對大家的學習有所幫助。
 android Watchdog 實現剖析
android Watchdog 實現剖析
系統啟動過程圖: Framework層所有的Service都是運行在SystemServer進程中;SystemServer進程是由Zygote進程創建。 S
 Android Fragment概述及用法
Android Fragment概述及用法
Fragment一般是宿主Activity UI的一部分或一種行為,作為Activity的整個V
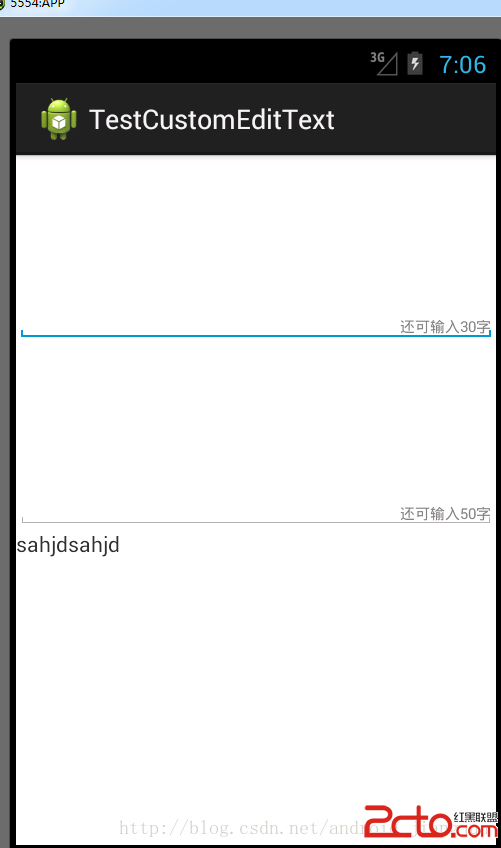 Android 中自定義控件之判斷還剩多少可輸入字符的EditText
Android 中自定義控件之判斷還剩多少可輸入字符的EditText
最近做的項目有個需求就是判斷一下還 剩多少字符可輸入,也就是對EditText 的文本變化做監聽 ,功能實現了,但是感覺使用組合方式,每次都要編寫,還不如寫
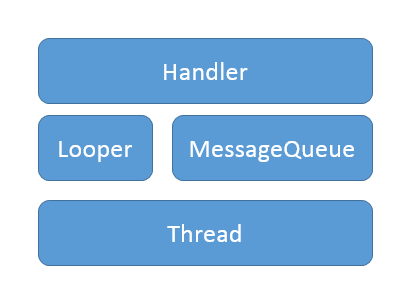 詳解Android中Handler的內部實現原理
詳解Android中Handler的內部實現原理
本文主要是對Handler和消息循環的實現原理進行源碼分析,如果不熟悉Handler可以參見博文《詳解Android中Handler的使用方法》,裡面對Android為何