編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述了Android編程實現動態更新ListView的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
有時候我們需要修改已經生成的列表,添加或者修改數據,notifyDataSetChanged()可以在修改適配器綁定的數組後,不用重新刷新Activity,通知Activity更新ListView。今天的例子就是通過Handler AsyncTask兩種方式來動態更新ListView.從今天起,每次學習的源代碼都會打包上傳,方便各位同學學習,注冊帳號即可下載。
布局main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ListView android:id="@+id/lv" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" /> </LinearLayout>
ListView列表布局playlist.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="30px" android:textSize="18sp" > </TextView>
程序代碼:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
publicclass main extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
ListView lv;
ArrayAdapter<String> Adapter;
ArrayList<String> arr=new ArrayList<String>();
@Override
publicvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
lv=(ListView)findViewById(R.id.lv);
arr.add("123");
arr.add("234");
arr.add("345");
Adapter =new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,R.layout.playlist, arr);
lv.setAdapter(Adapter);
lv.setOnItemClickListener(lvLis);
editItem edit=new editItem();
edit.execute("0","第1項");//把第一項內容改為"第一項"
Handler handler=new Handler();
handler.postDelayed(add,3000);//延遲3秒執行
}
Runnable add=new Runnable(){
@Override
publicvoid run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
arr.add("增加一項");//增加一項
Adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
};
class editItem extends AsyncTask<String,Integer,String>{
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
arr.set(Integer.parseInt(params[0]),params[1]);
//params得到的是一個數組,params[0]在這裡是"0",params[1]是"第1項"
//Adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
//執行添加後不能調用 Adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()更新UI,因為與UI不是同線程
//下面的onPostExecute方法會在doBackground執行後由UI線程調用
returnnull;
}
@Override
protectedvoid onPostExecute(String result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPostExecute(result);
Adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
//執行完畢,更新UI
}
}
private OnItemClickListener lvLis=new OnItemClickListener(){
@Override
publicvoid onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2,
long arg3) {
//點擊條目時觸發
//arg2即為點中項的位置
setTitle(String.valueOf(arr.get(arg2)));
}
};
}
更多關於Android相關內容感興趣的讀者可查看本站專題:《Android開發入門與進階教程》、《Android數據庫操作技巧總結》及《Android控件用法總結》
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
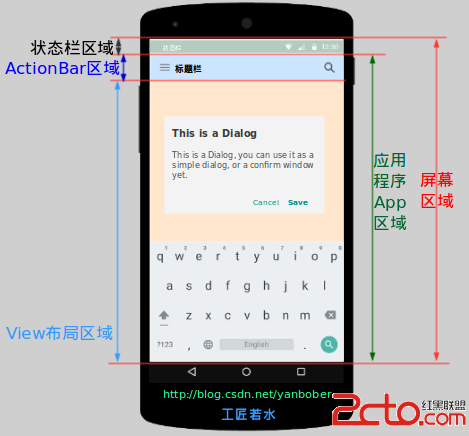 Android應用坐標系統全面詳解
Android應用坐標系統全面詳解
1 背景去年有很多人私信告訴我讓說說自定義控件,其實通觀網絡上的很多博客都在講各種自定義控件,但是大多數都是授之以魚,卻很少有較為系統性授之於漁的文章,同時由於自己也遲遲
 android 自定義組合控件
android 自定義組合控件
自定義控件是一些android程序員感覺很難攻破的難點,起碼對我來說是這樣的,但是我們可以在網上找一些好的博客關於自定義控件好好拿過來學習研究下,多練,多寫點也能找到感覺
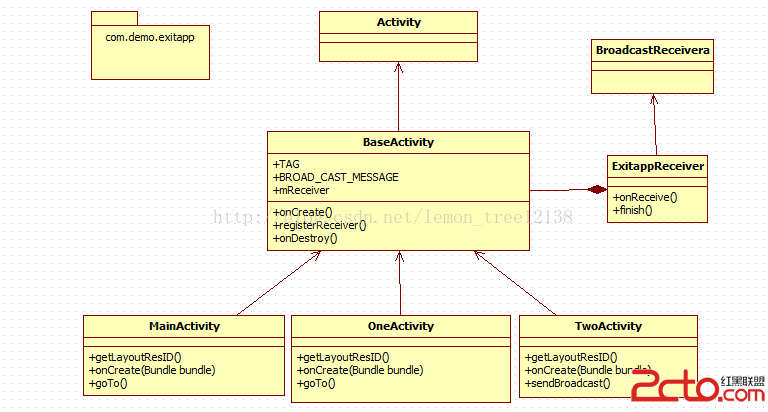 Android退出程序(下)——利用廣播機制
Android退出程序(下)——利用廣播機制
概述: 基於上一篇博客《Android退出程序(上)——單例模式》的學習,我們知道了如何利用單例和循環遍歷的方式來退出我們的應用程序。這篇博客則要從另一個角度來解決問題—
 Android Navigation TabBar控件實現多彩標簽欄
Android Navigation TabBar控件實現多彩標簽欄
先看看效果圖:源碼下載:Android Navigation TabBar控件實現多彩標簽欄代碼:MainActivity.javapackage com.bzu.gxs