編輯:關於Android編程
推薦閱讀:
先給大家分享一下,側滑刪除,布局也就是前面一個item,然後有兩個隱藏的按鈕(TextView也可以),然後我們可以向左側滑動,然後顯示出來,然後對delete(刪除鍵)實現監聽,就可以了哈。好了那就來看看代碼怎麼實現的吧。
首先和之前一樣
自定義View,初始化ViewDragHelper:
package com.example.removesidepull;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.v4.widget.ViewDragHelper;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
/**
* Created by 若蘭 on 2016/2/2.
* 一個懂得了編程樂趣的小白,希望自己
* 能夠在這個道路上走的很遠,也希望自己學習到的
* 知識可以幫助更多的人,分享就是學習的一種樂趣
* QQ:1069584784
* csdn:http://blog.csdn.net/wuyinlei
*/
public class SwipeLayout extends FrameLayout {
private ViewDragHelper mDragHelper;
public SwipeLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public SwipeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public SwipeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//第一步 初始化ViewDragHelper
mDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, mCallback);
}
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
//返回true
return true;
}
};
}
然後我們就要去處理攔截事件也就是重寫一些onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent方法,默認是不攔截的:
/**
* 傳遞觸摸事件
*
* @param ev
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//交給ViewDragHelper判斷是否去攔截事件
return mDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
try {
mDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回true,這裡表示去攔截事件
return true;
}
然後我們去重寫一下ViewDragHelper裡面的clampViewPositionHorizontal方法:
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
return left;
}
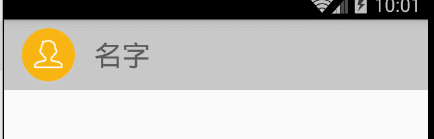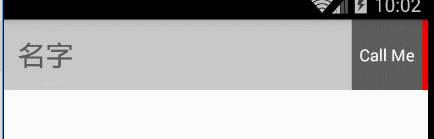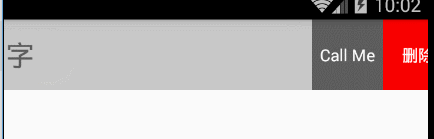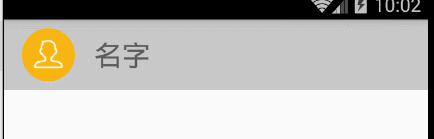
好了這個時候,就已經可以實現滑動了,我們先來看下結果:

這裡我們可以看到,已經可以滑動了,好了接下來的就是要處理滑動事件,去放置到正確的地方(call me 和刪除剛開始不能見,還有只能左滑顯示,右滑隱藏)。
好了,我們先獲取兩個View吧:
/**
* 當xml填充完畢的時候
*/
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
/**
* 後view
*/
mBackView = getChildAt(0);
/**
* 前view
*/
mFrontView = getChildAt(1);
}
獲取想要的寬和高:
/**
* 在這裡獲取寬和高
*
* @param w
* @param h
* @param oldw
* @param oldh
*/
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
/**
* 高度
*/
mHeight = mFrontView.getMeasuredHeight();
/**
* 寬度
*/
mWidth = mFrontView.getMeasuredWidth();
/**
* 移動距離
*/
mRange = mBackView.getMeasuredWidth();
}
擺放這兩個view的位置:
/**
* 擺放位置
* @param changed
* @param left
* @param top
* @param right
* @param bottom
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
layoutContent(false);
}
private void layoutContent(boolean isOpen) {
//擺放前view
Rect frontRect = computeFrontViewRect(isOpen);
mFrontView.layout(frontRect.left, frontRect.top, frontRect.right, frontRect.bottom);
//擺放後view
Rect backRect = computeBackViewRect(frontRect);
mBackView.layout(backRect.left,backRect.top,backRect.right,backRect.bottom);
//前置前view
bringChildToFront(mFrontView);
}
/**
* 我們可以把前view相當於一個矩形
*
* @param frontRect
* @return
*/
private Rect computeBackViewRect(Rect frontRect) {
int left = frontRect.right;
return new Rect(left, 0, left + mRange, 0 + mHeight);
}
private Rect computeFrontViewRect(boolean isOpen) {
int left = 0;
if (isOpen) {
left = -mRange;
}
return new Rect(left, 0, left + mWidth, 0 + mHeight);
}
當然這個實現,只是可以拖拽了前view,因為我們沒有把改變的dx傳遞下去,好了來實現拖拽前view的時候,後view也跟著出來(ViewDragHelper裡面的方法):
/**
* 當view位置改變的時候
* @param changedView 改變的view
* @param left
* @param top
* @param dx x軸偏移量
* @param dy
*/
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
//傳遞事件,如果是拖拽的前view,
if (changedView == mFrontView){
//Offset this view's horizontal location by the specified amount of pixels.
//也就是說我的我的前view左滑了dx,那麼我的後view也是左滑dx,右滑同理
mBackView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
} else if (changedView == mBackView){
//拖拽的是後view的話,前View的處理方式一樣
mFrontView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}
//兼容老版本
invalidate();
}
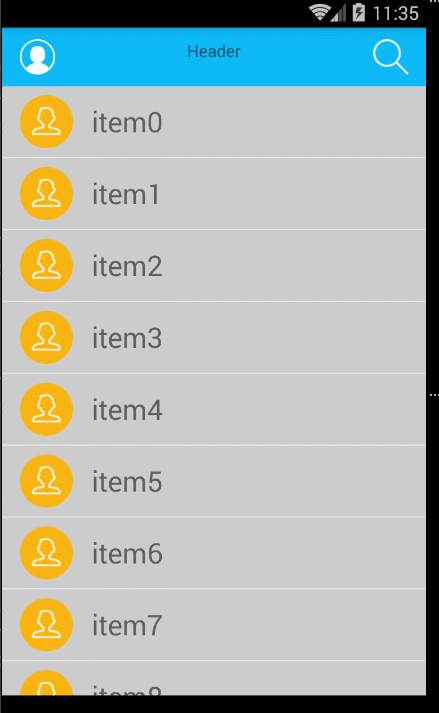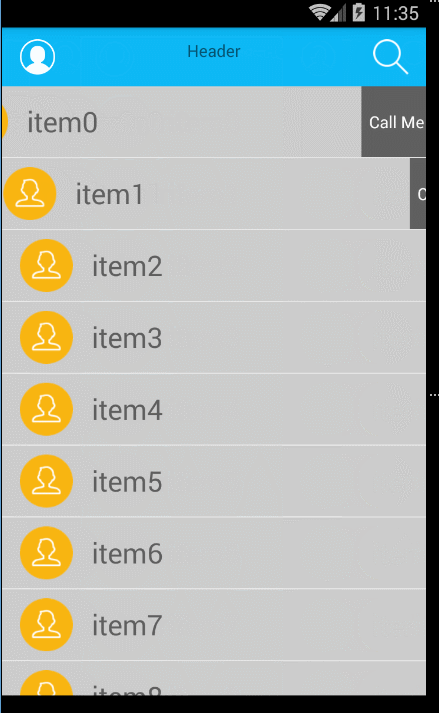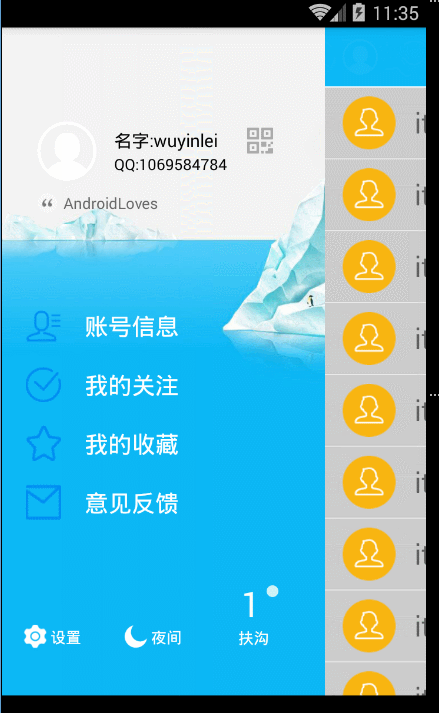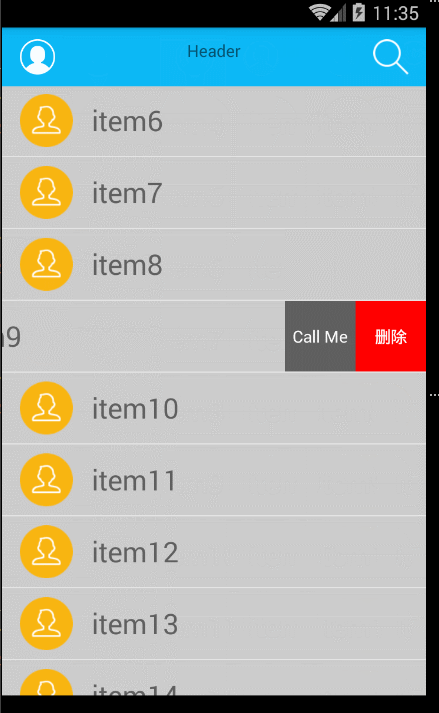
好了這個時候我們來看下效果:

是不是發現了問題,就是我的前view想要的結果是不能右滑的(只允許左滑和返回),那麼接下來就實現這個想要的結果吧。以下的代碼是在clampViewPositionHorizontal()方法裡面:
//在這裡處理放置的邏輯拖拽的前view
if (child == mFrontView) {
if (left > 0) {
return 0;
} else if (left < -mRange) {
return -mRange;
}
}//拖拽的後view
else if (child == mBackView) {
if (left > mWidth) {
return mWidth;
} else if (left < mWidth - mRange) {
return mWidth - mRange;
}
}
看下效果圖:

好了,這個時候已經基本實現了,接下來實現以下滑動的距離和速度【判斷是否打開和關閉:
/**
* 拖拽的view釋放的時候
*
* @param releasedChild
* @param xvel
* @param yvel
*/
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
if (xvel == 0 && mFrontView.getLeft() < -mRange / 2.0f) {
open();
} else if (xvel < 0) {
open();
} else {
close();
}
}
/**
* 關閉
*/
public void close() {
Utils.showToast(getContext(), "close");
layoutContent(false);
}
//打開
public void open() {
//Utils.showToast(getContext(), "open");
layoutContent(true);
}
好了,接下來實現以下平滑的關閉和打開:
public void close() {
close(true);
}
/**
* 關閉
*
* @param isSmooth
*/
public void close(boolean isSmooth) {
int finalLeft = 0;
if (isSmooth) {
//開始動畫 如果返回true表示沒有完成動畫
if (mDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mFrontView, finalLeft, 0)) {
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
} else {
layoutContent(false);
}
}
public void open() {
open(true);
}
/**
* 打開
*
* @param isSmooth
*/
public void open(boolean isSmooth) {
int finalLeft = -mRange;
if (isSmooth) {
//開始動畫
if (mDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mFrontView, finalLeft, 0)) {
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
} else {
layoutContent(true);
}
}
/**
* 持續動畫
*/
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
//這個是固定的
if (mDragHelper.continueSettling(true)) {
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
我們看下最終的效果吧:
好了,在這裡我們加上一些回調,以方便外部使用的時候可以回調:
/**
* 默認狀態是關閉
*/
private Status status = Status.Close;
private OnSwipeLayoutListener swipeLayoutListener;
public Status getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Status status) {
this.status = status;
}
public OnSwipeLayoutListener getSwipeLayoutListener() {
return swipeLayoutListener;
}
public void setSwipeLayoutListener(OnSwipeLayoutListener swipeLayoutListener) {
this.swipeLayoutListener = swipeLayoutListener;
}
/**
* 定義三種狀態
*/
public enum Status {
Close, Open, Draging
}
/**
* 定義回調接口 這個在我們
*/
public interface OnSwipeLayoutListener {
/**
* 關閉
*
* @param mSwipeLayout
*/
void onClose(SwipeLayout mSwipeLayout);
/**
* 打開
*
* @param mSwipeLayout
*/
void onOpen(SwipeLayout mSwipeLayout);
/**
* 繪制
*
* @param mSwipeLayout
*/
void onDraging(SwipeLayout mSwipeLayout);
/**
* 要去關閉
*/
void onStartClose(SwipeLayout mSwipeLayout);
/**
* 要去開啟
*/
void onStartOpen(SwipeLayout mSwipeLayout);
}
dispatchSwipeEvent()方法(在onViewPositionChanged()方法中調用)
protected void dispatchSwipeEvent() {
//判斷是否為空
if (swipeLayoutListener != null) {
swipeLayoutListener.onDraging(this);
}
// 記錄上一次的狀態
Status preStatus = status;
// 更新當前狀態
status = updateStatus();
if (preStatus != status && swipeLayoutListener != null) {
if (status == Status.Close) {
swipeLayoutListener.onClose(this);
} else if (status == Status.Open) {
swipeLayoutListener.onOpen(this);
} else if (status == Status.Draging) {
if (preStatus == Status.Close) {
swipeLayoutListener.onStartOpen(this);
} else if (preStatus == Status.Open) {
swipeLayoutListener.onStartClose(this);
}
}
}
}
updateStatus()方法:
/**
* 更新狀態
*
* @return
*/
private Status updateStatus() {
//得到前view的左邊位置
int left = mFrontView.getLeft();
if (left == 0) {
//如果位置是0,就是關閉狀態
return Status.Close;
} else if (left == -mRange) {
//如果左側邊距是後view的寬度的負值,狀態為開
return Status.Open;
}
//其他狀態就是拖拽
return Status.Draging;
}
好了,事件基本上已經實現完畢了,這個側拉刪除的我會更新至我的項目中,同時希望Android高仿QQ6.0側滑刪除實例代碼對大家有所幫助。
 android知識回顧--view的事件體系
android知識回顧--view的事件體系
1.view的滑動,六種滑動方式:一:通過layout來實現滑動效果package com.example.testdragview;import android.con
 Android事件分發機制-------View
Android事件分發機制-------View
當觸摸一個View時,首先會調用View的dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)方法,關乎著事件的分發,所以首先看看這個方法publi
 Android多點觸控實現對圖片放大縮小平移,慣性滑動等功能
Android多點觸控實現對圖片放大縮小平移,慣性滑動等功能
文章將在原有基礎之上做了一些擴展功能: 1.圖片的慣性滑動 2.圖片縮放小於正常比例時,松手會自動回彈成正常比例 3.圖片縮放大於最大比例時,松手會自動回彈成最大比例實現
 一、初識GVR ---- Android VR視頻/Google VR for Android /VR Pano/VR Video
一、初識GVR ---- Android VR視頻/Google VR for Android /VR Pano/VR Video
業余時間充足,於是想弄點自己的東西,找來找去還是回到當初感興趣的VR。目前好像沒有太多關於VR方面的教程,於是有了寫‘學習筆記’的想法。說干就干~