編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述了Android編程設置TextView顏色setTextColor用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
android中設置TextView的顏色有方法setTextColor,這個方法被重載了,可以傳入兩種參數。
public void setTextColor(int color) {
mTextColor = ColorStateList.valueOf(color);
updateTextColors();
}
public void setTextColor(ColorStateList colors) {
if (colors == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
mTextColor = colors;
updateTextColors();
}
下邊就分別寫出怎麼使用這兩個方法設置TextView的顏色:
TextView tv = new TextView(this);
tv.setText("Test set TextView's color.");
//方案一:代碼中通過argb值的方式
tv.setTextColor(Color.rgb(255, 255, 255));
這種方法也就是傳入int color值,這個int不是R文件中自動分配的int值,所以要注意。這是Color類中的靜態方法構造出來的顏色int值。
Resources resource = (Resources) getBaseContext().getResources();
ColorStateList csl = (ColorStateList) resource.getColorStateList(R.color.my_color);
if (csl != null) {
tv.setTextColor(csl);
}
這種方法是通過ColorStateList得到xml中的配置的顏色的。好多需要xml中配置的都要類似這樣的映射xml文件。
還有種方法:
XmlResourceParser xrp = getResources().getXml(R.color.my_color);
try {
ColorStateList csl = ColorStateList.createFromXml(getResources(), xrp);
tv.setTextColor(csl);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
全部代碼:
package com.txlong;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ListViewDemoActivity extends Activity {
// private ListView listView;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView tv = new TextView(this);
tv.setText("Test set TextView's color.");
//方案一:通過ARGB值的方式
/**
* set the TextView color as the 0~255's ARGB,These component values
* should be [0..255], but there is no range check performed, so if they
* are out of range, the returned color is undefined
*/
// tv.setTextColor(Color.rgb(255, 255, 255));
/**
* set the TextView color as the #RRGGBB #AARRGGBB 'red', 'blue',
* 'green', 'black', 'white', 'gray', 'cyan', 'magenta', 'yellow',
* 'lightgray', 'darkgray'
*/
tv.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FFFFFF"));
/** 原來不知道有上邊的方法,就用這個笨笨方法了 */
// String StrColor = null;
// StrColor = "FFFFFFFF";
// int length = StrColor.length();
// if (length == 6) {
// tv.setTextColor(Color.rgb(
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(0, 2), 16),
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(2, 4), 16),
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(4, 6), 16)));
// } else if (length == 8) {
// tv.setTextColor(Color.argb(
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(0, 2), 16),
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(2, 4), 16),
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(4, 6), 16),
// Integer.valueOf(StrColor.substring(6, 8), 16)));
// }
//方案二:通過資源引用
// tv.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.my_color));
//方案三:通過資源文件寫在String.xml中
// Resources resource = (Resources) getBaseContext().getResources();
// ColorStateList csl = (ColorStateList) resource.getColorStateList(R.color.my_color);
// if (csl != null) {
// tv.setTextColor(csl);
// }
//方案四:通過xml文件,如/res/text_color.xml
// XmlPullParser xrp = getResources().getXml(R.color.text_color);
// try {
// ColorStateList csl = ColorStateList.createFromXml(getResources(), xrp);
// tv.setTextColor(csl);
// } catch (Exception e) {
// }
// listView = new ListView(this);
//
// Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(
// Uri.parse("content://contacts/people"), null, null, null, null);
//
// startManagingCursor(cursor);
//
// ListAdapter listAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
// android.R.layout.simple_expandable_list_item_2, cursor,
// new String[] { "name", "name" }, new int[] {
// android.R.id.text1, android.R.id.text2 });
//
// listView.setAdapter(listAdapter);
// setContentView(listView);
setContentView(tv);
}
}
String.xml文件為:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, ListViewDemoActivity!</string> <string name="app_name">ListViewDemo</string> <color name="my_color">#FFFFFF</color> </resources>
/res/color/text_color.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:state_pressed="true" android:color="#FF111111"/> <!-- pressed --> <item android:state_focused="true" android:color="#FF222222"/> <!-- focused --> <item android:state_selected="true" android:color="#FF333333"/> <!-- selected --> <item android:state_active="true" android:color="#FF444444"/> <!-- active --> <item android:state_checkable="true" android:color="#FF555555"/> <!-- checkable --> <item android:state_checked="true" android:color="#FF666666"/> <!-- checked --> <item android:state_enabled="true" android:color="#FF777777"/> <!-- enabled --> <item android:state_window_focused="true" android:color="#FF888888"/> <!-- window_focused --> </selector>
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
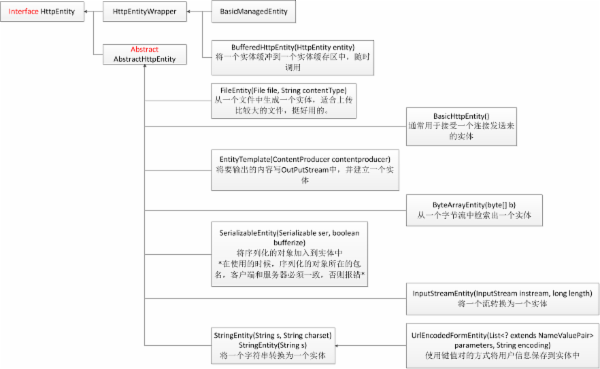 AndroidHttpClient詳解及調用示例
AndroidHttpClient詳解及調用示例
下面給大家展示了AndroidHttpClient結構:public final classAndroidHttpClientextends Objectimplemen
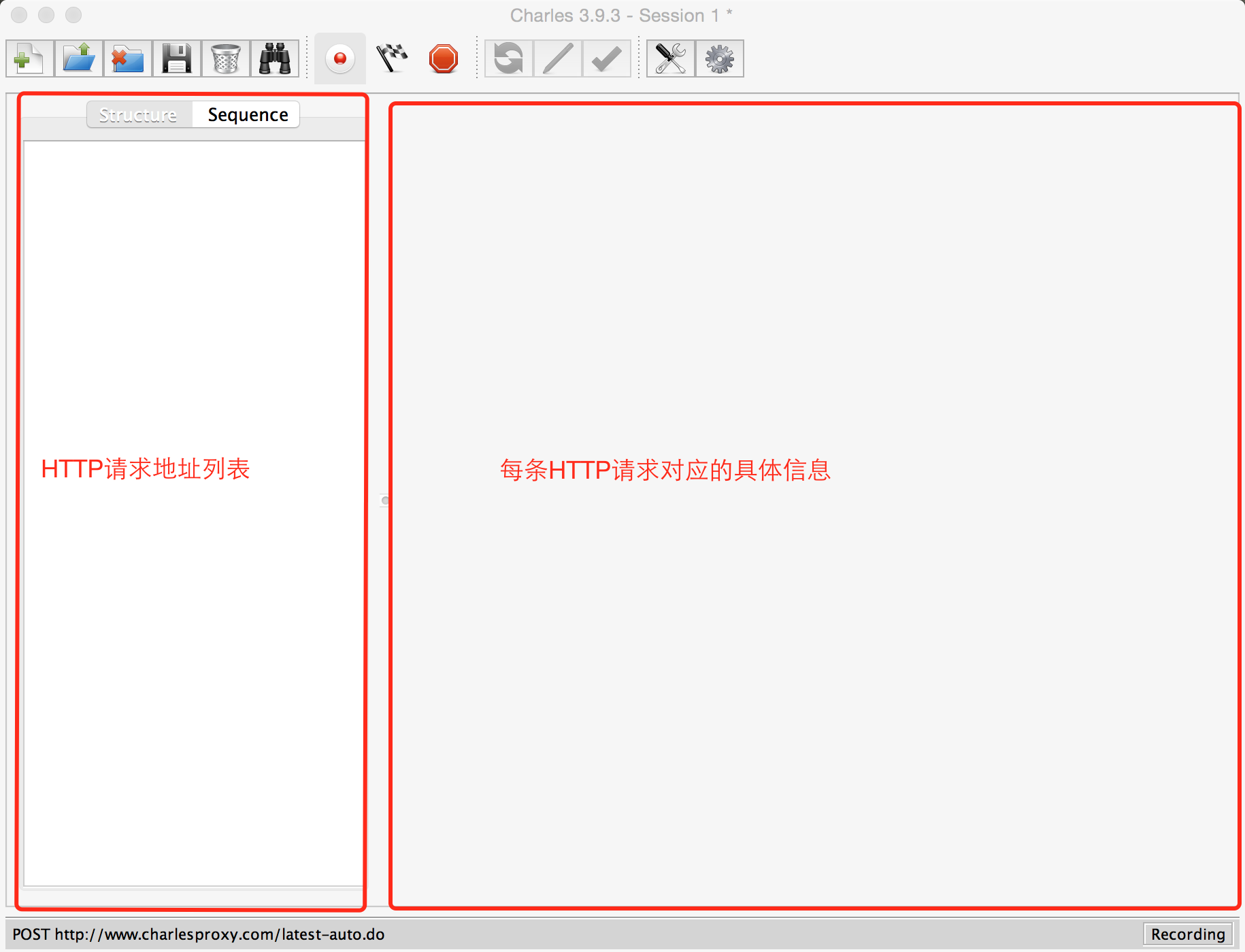 詳解Android/IOS平台下抓包工具使用以及如何模仿一個app
詳解Android/IOS平台下抓包工具使用以及如何模仿一個app
抓包(Packet Capture),實際上就是對網絡請求(包括發送與接收)的數據包進行截獲、重發、編輯、轉存等操作,在Android下,也經常被用來進行數據截取等。學會
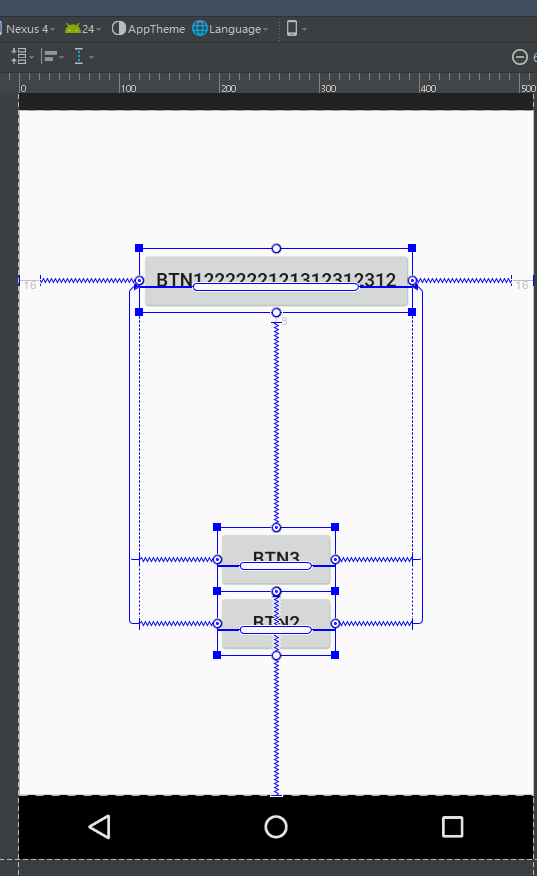 ConstraintLayout
ConstraintLayout
android studio升級到stable 2.2之後,發現還有了個ConstraintLayout。看名字就是約束布局,用各種約束來確定widget的展示。該Con
 Android啟動屏實現左右滑動切換查看功能
Android啟動屏實現左右滑動切換查看功能
本文介紹一個app最常見的特性,就是新功能屬性介紹和啟動屏,一般會怎麼實現呢,這不就打算告訴大家了麼。先說邏輯 先判斷是否第一次啟動app,如果是,則進入功能使用導航(