編輯:關於Android編程
android動態布局相比靜態布局,動態布局不用再將xml轉變了布局代碼,提高了一定的效率,當然可以忽略不記。動態布局主要是比較靈活,可以很快的在代碼中直接修改布局,並直接使用控件進行業務邏輯開發。但代碼量通常比較大,維護沒有靜態布局方便。不過,作為一個android開發人員,掌握一定的動態布局技巧,有時在工作中也是可以提高一定的代碼開發效率。
在動態布局中,要想實現一個布局,一般是先創建五大布局的對象。然後對這些對象進行屬性設置,之後再向裡面添加子布局或控件。
以RelativeLayout為例。
RelativeLayout mLayout = new RelativeLayout(); //設置RelativeLayout的子控件屬性對象,並設置其尺寸樣式。每個GroupView中都有一個LayoutPrams,都是用來給子控件設置發生的。 RelativeLayout.LayoutPrams params = new RelativeLayout.LayoutPrams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); //增加 子控件 ImageView iv = new ImageView(getActivity()); iv.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_icon_conversation_normal); //設置子控件在RealtiveLayout中的位置屬性。 params.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT, RelativeLayout.TRUE); //給iv 增加屬性 //將iv,增加到mLayout中 mLayout .addView(iv, params);
從最後一句,可以看出來,params對象引用設置的屬性都是作用有ImageView這個子控件上的,然後把iv與params一塊加入到RealtiveLayout中去。
整理android動態布局方法總結
//絕對布局
AbsoluteLayout abslayout=new AbsoluteLayout (this); setContentView(abslayout); Button btn1 = new Button(this); btn1.setText(”this is a button”); btn1.setId(1); AbsoluteLayout.LayoutParams lp1 = new AbsoluteLayout.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 0,100); abslayout.addView(btn1, lp1);
//相對布局
RelativeLayout relativeLayout = new RelativeLayout(this); setContentView(relativeLayout); AbsoluteLayout abslayout=new AbsoluteLayout (this); RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp1 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); lp1.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_TOP); lp1.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_HORIZONTAL, RelativeLayout.TRUE); relativeLayout.addView(abslayout ,lp1);
//線性布局
LinearLayout ll = new LinearLayout(this); EditText et = new EditText(); ll.addView(et); //動態添加布局的方法1. LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout)this.getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.main1,null); setContentView(ll); LinearLayout ll2 = (LinearLayout)this.getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.main2,ll); //這樣 main2 作為 main1的子布局 加到了 main1的 根節點下 //動態添加布局的方法2 addView. LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout)this.getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.main1,null); setContentView(ll); LinearLayout ll2 = (LinearLayout)this.getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.main2,null); ll.addView(ll2);
 Android App中使用Gallery制作幻燈片播放效果
Android App中使用Gallery制作幻燈片播放效果
零、Gallery的使用回顧我們有時候在iPhone手機上或者Windows上面看到動態的圖片,可以通過鼠標或者手指觸摸來移動它,產生動態的圖片滾動效果,還可以根據你的點
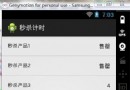 Android ListView顯示倒計時的流暢實現
Android ListView顯示倒計時的流暢實現
有人在群裡問他實現的倒計時在ListView中很卡,有沒有好的方案,我就閒來沒事,實現了一下,供參考 package com.microchange;impor
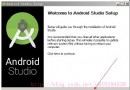 Android Studio安裝配置詳細步驟(圖文)
Android Studio安裝配置詳細步驟(圖文)
為什麼要使用Android StudioAndroid Studio是谷歌推出了新的Android開發環境,其重要性可想而知!1. 集成了Gradle 打包工具2. 所見
 Android自定義View實現驗證碼
Android自定義View實現驗證碼
本文章是基於鴻洋的Android 自定義View (一) 的一些擴展,以及對Android自定義View構造函數詳解裡面內容的一些轉載。首先我們定義一個declare-s