編輯:關於Android編程
一、概述:
在日常的app使用中,我們會在android 的app中看見 熱門標簽等自動換行的流式布局,今天,我們就來看看如何
自定義一個類似熱門標簽那樣的流式布局吧(源碼下載在下面最後給出)
類似的自定義布局。下面我們就來詳細介紹流式布局的應用特點以及用的的技術點:
1.流式布局的特點以及應用場景
特點:當上面一行的空間不夠容納新的TextView時候,
才開辟下一行的空間
原理圖:
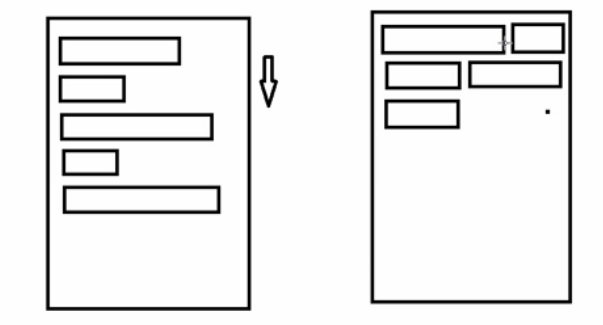
場景:主要用於關鍵詞搜索或者熱門標簽等場景
2.自定義ViewGroup,重點重寫下面兩個方法
1)、onMeasure:測量子view的寬高,設置自己的寬和高
2)、onLayout:設置子view的位置
onMeasure:根據子view的布局文件中屬性,來為子view設置測量模式和測量值
測量=測量模式+測量值;
測量模式有3種:
EXACTLY:表示設置了精確的值,一般當childView設置其寬、高為精確值、match_parent時,ViewGroup會將其設置為EXACTLY;
AT_MOST:表示子布局被限制在一個最大值內,一般當childView設置其寬、高為wrap_content時,ViewGroup會將其設置為AT_MOST;
UNSPECIFIED:表示子布局想要多大就多大,一般出現在AadapterView的item的heightMode中、ScrollView的childView的heightMode中;此種模式比較少見。
3.LayoutParams
ViewGroup LayoutParams :每個 ViewGroup 對應一個 LayoutParams; 即 ViewGroup -> LayoutParams
getLayoutParams 不知道轉為哪個對應的LayoutParams ,其實很簡單,就是如下:
子View.getLayoutParams 得到的LayoutParams對應的就是 子View所在的父控件的LayoutParams;
例如,LinearLayout 裡面的子view.getLayoutParams ->LinearLayout.LayoutParams
所以 咱們的FlowLayout 也需要一個LayoutParams,由於上面的效果圖是子View的 margin,
所以應該使用MarginLayoutParams。即FlowLayout->MarginLayoutParams
4.最後來看看實現的最終效果圖:
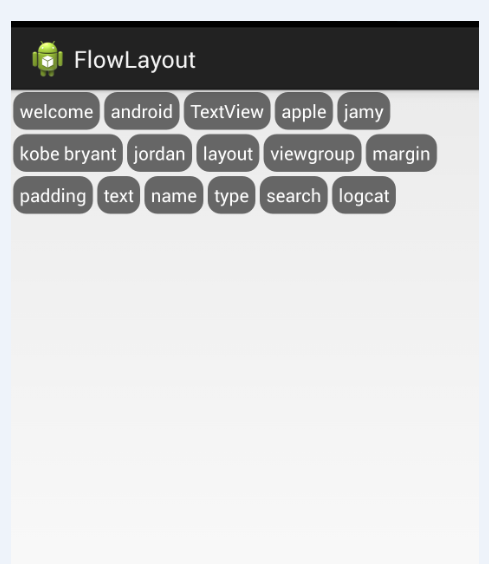
二、熱門標簽的流式布局的實現:
1. 自定義熱門標簽的ViewGroup實現
根據上面的技術分析,自定義類繼承於ViewGroup,並重寫 onMeasure和onLayout等方法。具體實現代碼如下:
<font color="#362e2b"><font ><font face="Arial"><font >package com.czm.flowlayout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
*
* @author caizhiming
* @created on 2015-4-13
*/
public class XCFlowLayout extends ViewGroup{
//存儲所有子View
private List<List<View>> mAllChildViews = new ArrayList<>();
//每一行的高度
private List<Integer> mLineHeight = new ArrayList<>();
public XCFlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public XCFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public XCFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//父控件傳進來的寬度和高度以及對應的測量模式
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//如果當前ViewGroup的寬高為wrap_content的情況
int width = 0;//自己測量的 寬度
int height = 0;//自己測量的高度
//記錄每一行的寬度和高度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
//獲取子view的個數
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0;i < childCount; i ++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
//測量子View的寬和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
//子View占據的寬度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
//子View占據的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//換行時候
if(lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth){
//對比得到最大的寬度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
//重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
//記錄行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
}else{//不換行情況
//疊加行寬
lineWidth += childWidth;
//得到最大行高
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
//處理最後一個子View的情況
if(i == childCount -1){
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
//wrap_content
setMeasuredDimension(modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width,
modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mAllChildViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
//獲取當前ViewGroup的寬度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
//記錄當前行的view
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0;i < childCount; i ++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
//如果需要換行
if(childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width){
//記錄LineHeight
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
//記錄當前行的Views
mAllChildViews.add(lineViews);
//重置行的寬高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//重置view的集合
lineViews = new ArrayList();
}
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}
//處理最後一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllChildViews.add(lineViews);
//設置子View的位置
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
//獲取行數
int lineCount = mAllChildViews.size();
for(int i = 0; i < lineCount; i ++){
//當前行的views和高度
lineViews = mAllChildViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
for(int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j ++){
View child = lineViews.get(j);
//判斷是否顯示
if(child.getVisibility() == View.GONE){
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int cLeft = left + lp.leftMargin;
int cTop = top + lp.topMargin;
int cRight = cLeft + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int cBottom = cTop + child.getMeasuredHeight();
//進行子View進行布局
child.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cBottom);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
}
/**
* 與當前ViewGroup對應的LayoutParams
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
}</font></font></font></font>
2.相關的布局文件:
引用自定義控件:
<font color="#362e2b"><font ><font face="Arial"><font ><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<com.czm.flowlayout.XCFlowLayout
android:id="@+id/flowlayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
</com.czm.flowlayout.XCFlowLayout>
</RelativeLayout></font></font></font></font>
TextView的樣式文件:
<font color="#362e2b"><font ><font face="Arial"><font ><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<solid android:color="#666666" />
<corners android:radius="10dp" />
<padding
android:left="5dp"
android:right="5dp"
android:top="5dp"
android:bottom="5dp"
/>
</shape></font></font></font></font>
三、使用該自定義布局控件類
最後,如何使用該自定義的熱門標簽控件類呢?很簡單,請看下面實例代碼:
<font color="#362e2b"><font ><font face="Arial"><font >package com.czm.flowlayout;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.view.ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
*
* @author caizhiming
* @created on 2015-4-13
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private String mNames[] = {
"welcome","android","TextView",
"apple","jamy","kobe bryant",
"jordan","layout","viewgroup",
"margin","padding","text",
"name","type","search","logcat"
};
private XCFlowLayout mFlowLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initChildViews();
}
private void initChildViews() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mFlowLayout = (XCFlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.flowlayout);
MarginLayoutParams lp = new MarginLayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp.leftMargin = 5;
lp.rightMargin = 5;
lp.topMargin = 5;
lp.bottomMargin = 5;
for(int i = 0; i < mNames.length; i ++){
TextView view = new TextView(this);
view.setText(mNames[i]);
view.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
view.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.textview_bg));
mFlowLayout.addView(view,lp);
}
}
}</font></font></font></font>
以上就是本文的全部內容,下面在給大家一個小福利:
// 流式布局 話不多說,比較簡單,注釋都寫的很清楚
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
*
* @author Mr.Himan
* @version 1.0<br>
* 2015年11月4日 11:12:06 <br>
* 流式布局 設置MarginTop 和MarginLeft有效 MarginRight 暫未實現
*/
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
/**
* 存儲所有的子View
*/
private List<List<View>> mAllChildViews = new ArrayList<List<View>>();
/**
* 存儲每一行的高度
*/
private List<Integer> mLineHeight = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
mAllChildViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
// 獲取當前ViewGroup的寬度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 記錄當前行的view
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 如果需要換行
if (childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width) {
// 記錄LineHeight
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 記錄當前行的Views
mAllChildViews.add(lineViews);
// 重置行的寬高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
// 重置view的集合
lineViews = new ArrayList();
}
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}
// 處理最後一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllChildViews.add(lineViews);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) this.getLayoutParams();
// 設置子View的位置
int left = 0;
// 添加marginTop
int top = 0 + params.topMargin;
// 獲取行數
int lineCount = mAllChildViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineCount; i++) {
// 當前行的views和高度
lineViews = mAllChildViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
// 為每一列設置marginLeft
if (j == 0) {
left = 0 + params.leftMargin;
}
View child = lineViews.get(j);
// 判斷是否顯示
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int cLeft = left + lp.leftMargin;
int cTop = top + lp.topMargin;
int cRight = cLeft + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int cBottom = cTop + child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 進行子View進行布局
child.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cBottom);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin
+ lp.rightMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 父控件傳進來的寬度和高度以及對應的測量模式
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果當前ViewGroup的寬高為wrap_content的情況
int width = 0;// 自己測量的 寬度
int height = 0;// 自己測量的高度
// 記錄每一行的寬度和高度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 獲取子view的個數
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 測量子View的寬和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
// 子View占據的寬度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin
+ params.rightMargin;
// 子View占據的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.bottomMargin
+ params.topMargin;
// 換行時候
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth) {
// 對比得到最大的寬度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
// 重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
// 記錄行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
// 不換行情況
// 疊加行寬
lineWidth += childWidth;
// 得到最大行高
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
// 處理最後一個子View的情況
if (i == childCount - 1) {
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth
: width, modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight
: height);
}
/**
* 與當前ViewGroup對應的LayoutParams
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
}
希望本文所述對大家學習Android實現熱門標簽的流式布局有所幫助。
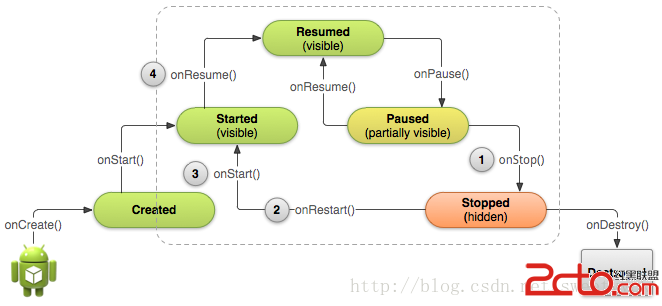 Android學習路線(十四)Activity生命周期——停止和重啟(Stopping and Restarting)一個Activity
Android學習路線(十四)Activity生命周期——停止和重啟(Stopping and Restarting)一個Activity
先占個位置,下次翻譯~ :p Properly stopping and restarting your activity is an important proce
 Android實現button居中的方法
Android實現button居中的方法
本文實例講述了Android實現button居中的方法。分享給大家供大家參考。具體如下:通過在main.xml 或者其他xml 布局文件中布局Button的時候,選擇An
 Android編程實現為應用添加菜單的方法
Android編程實現為應用添加菜單的方法
本文實例講述了Android編程實現為應用添加菜單的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:添加菜單的方法有很多,一般推薦用xml創建菜單。建立menu步驟:在res下建立
 手機相冊太多太亂?利用時間牆管理這些圖片!
手機相冊太多太亂?利用時間牆管理這些圖片!
如今的人們幾乎每天都會用手機拍攝無數張照片,但是照片一多管理就是一件麻煩事。一般來說,用戶管理照片不是系統的圖庫就是快圖應用,後者雖然浏覽速度快但管理功能卻