編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述了Android編程實現的超炫圖片浏覽器。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
使用過Android自帶的gallery組件的人都知道,gallery實現的效果就是拖動浏覽一組圖片,相比iphone裡也是用於拖動浏覽圖片的coverflow,顯然遜色不少。實際上,可以通過擴展gallery,通過偽3D變換可以基本實現coverflow的效果。本文通過源代碼解析這一功能的實現。具體代碼作用可參照注釋。
最終實現效果如下:
要使用gallery,我們必須首先給其指定一個adapter。在這裡,我們實現了一個自定義的ImageAdapter,為圖片制作倒影效果。
傳入參數為context和程序內drawable中的圖片ID數組。之後調用其中的createReflectedImages()方法分別創造每一個圖像的倒影效果,生成對應的ImageView數組,最後在getView()中返回。
Copyright (C) 2010 Neil Davies
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* [url]http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0[/url]
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
* This code is base on the Android Gallery widget and was Created
* by Neil Davies neild001 'at' gmail dot com to be a Coverflow widget
*
* @author Neil Davies
*/
public class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
int mGalleryItemBackground;
private Context mContext;
private Integer[] mImageIds ;
private ImageView[] mImages;
public ImageAdapter(Context c, int[] ImageIds) {
mContext = c;
mImageIds = ImageIds;
mImages = new ImageView[mImageIds.length];
}
public boolean createReflectedImages() {
// The gap we want between the reflection and the original image
final int reflectionGap = 4;
int index = 0;
for (int imageId : mImageIds) {
Bitmap originalImage = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(
mContext.getResources(), imageId);
int width = originalImage.getWidth();
int height = originalImage.getHeight();
// This will not scale but will flip on the Y axis
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.preScale(1, -1);
// Create a Bitmap with the flip matrix applied to it.
// We only want the bottom half of the image
Bitmap reflectionImage = Bitmap.createBitmap(originalImage, 0,
height / 2, width, height / 2, matrix, false);
// Create a new bitmap with same width but taller to fit
// reflection
Bitmap bitmapWithReflection = Bitmap.createBitmap(width,
(height + height / 2), Config.ARGB_8888);
// Create a new Canvas with the bitmap that's big enough for
// the image plus gap plus reflection
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmapWithReflection);
// Draw in the original image
canvas.drawBitmap(originalImage, 0, 0, null);
// Draw in the gap
Paint deafaultPaint = new Paint();
canvas.drawRect(0, height, width, height + reflectionGap,
deafaultPaint);
// Draw in the reflection
canvas.drawBitmap(reflectionImage, 0, height + reflectionGap,
null);
// Create a shader that is a linear gradient that covers the
// reflection
Paint paint = new Paint();
LinearGradient shader = new LinearGradient(0,
originalImage.getHeight(), 0,
bitmapWithReflection.getHeight() + reflectionGap,
0x70ffffff, 0x00ffffff, TileMode.CLAMP);
// Set the paint to use this shader (linear gradient)
paint.setShader(shader);
// Set the Transfer mode to be porter duff and destination in
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(Mode.DST_IN));
// Draw a rectangle using the paint with our linear gradient
canvas.drawRect(0, height, width,
bitmapWithReflection.getHeight() + reflectionGap, paint);
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(mContext);
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmapWithReflection);
imageView
.setLayoutParams(new GalleryFlow.LayoutParams(160, 240));
// imageView.setScaleType(ScaleType.MATRIX);
mImages[index++] = imageView;
}
return true;
}
public int getCount() {
return mImageIds.length;
}
public Object getItem(int position) {
return position;
}
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// Use this code if you want to load from resources
/*
* ImageView i = new ImageView(mContext);
* i.setImageResource(mImageIds[position]); i.setLayoutParams(new
* CoverFlow.LayoutParams(350,350));
* i.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE);
*
* //Make sure we set anti-aliasing otherwise we get jaggies
* BitmapDrawable drawable = (BitmapDrawable) i.getDrawable();
* drawable.setAntiAlias(true); return i;
*/
return mImages[position];
}
/**
* Returns the size (0.0f to 1.0f) of the views depending on the
* 'offset' to the center.
*/
public float getScale(boolean focused, int offset) {
/* Formula: 1 / (2 ^ offset) */
returnMath.max(0,1.0f / (float) Math.pow(2, Math.abs(offset)));
}
}
}
僅僅實現了圖片的倒影效果還不夠,因為在coverflow中圖片切換是有旋轉和縮放效果的,而自帶的gallery中並沒有實現。因此,我們擴展自帶的gallery,實現自己的galleryflow。在原gallery類中,提供了一個方法getChildStaticTransformation()以實現對圖片的變換。我們通過覆寫這個方法並在其中調用自定義的transformImageBitmap(“每個圖片與gallery中心的距離”)方法,,即可實現每個圖片做相應的旋轉和縮放。其中使用了camera和matrix用於視圖變換。具體可參考代碼注釋。
public class GalleryFlow extendsGallery {
/**
* Graphics Camera used for transforming the matrix of ImageViews
*/
privateCamera mCamera = newCamera();
/**
* The maximum angle the Child ImageView will be rotated by
*/
privateint mMaxRotationAngle =60;
/**
* The maximum zoom on the centre Child
*/
privateint mMaxZoom = -120;
/**
* The Centre of the Coverflow
*/
privateint mCoveflowCenter;
publicGalleryFlow(Context context) {
super(context);
this.setStaticTransformationsEnabled(true);
}
publicGalleryFlow(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
this.setStaticTransformationsEnabled(true);
}
publicGalleryFlow(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
this.setStaticTransformationsEnabled(true);
}
/**
* Get the max rotational angle of the image
*
* @return the mMaxRotationAngle
*/
publicint getMaxRotationAngle() {
returnmMaxRotationAngle;
}
/**
* Set the max rotational angle of each image
*
* @param maxRotationAngle
* the mMaxRotationAngle to set
*/
publicvoid setMaxRotationAngle(intmaxRotationAngle) {
mMaxRotationAngle = maxRotationAngle;
}
/**
* Get the Max zoom of the centre image
*
* @return the mMaxZoom
*/
publicint getMaxZoom() {
returnmMaxZoom;
}
/**
* Set the max zoom of the centre image
*
* @param maxZoom
* the mMaxZoom to set
*/
publicvoid setMaxZoom(intmaxZoom) {
mMaxZoom = maxZoom;
}
/**
* Get the Centre of the Coverflow
*
* @return The centre of this Coverflow.
*/
privateint getCenterOfCoverflow() {
return(getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) / 2
+ getPaddingLeft();
}
/**
* Get the Centre of the View
*
* @return The centre of the given view.
*/
privatestatic int getCenterOfView(View view) {
returnview.getLeft() + view.getWidth() / 2;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @see #setStaticTransformationsEnabled(boolean)
*/
protectedboolean getChildStaticTransformation(View child, Transformation t) {
finalint childCenter = getCenterOfView(child);
finalint childWidth = child.getWidth();
introtationAngle = 0;
t.clear();
t.setTransformationType(Transformation.TYPE_MATRIX);
if(childCenter == mCoveflowCenter) {
transformImageBitmap((ImageView) child, t,0);
}else {
rotationAngle = (int) (((float) (mCoveflowCenter - childCenter) / childWidth) * mMaxRotationAngle);
if(Math.abs(rotationAngle) > mMaxRotationAngle) {
rotationAngle = (rotationAngle <0) ? -mMaxRotationAngle
: mMaxRotationAngle;
}
transformImageBitmap((ImageView) child, t, rotationAngle);
}
returntrue;
}
/**
* This is called during layout when the size of this view has changed. If
* you were just added to the view hierarchy, you're called with the old
* values of 0.
*
* @param w
* Current width of this view.
* @param h
* Current height of this view.
* @param oldw
* Old width of this view.
* @param oldh
* Old height of this view.
*/
protectedvoid onSizeChanged(intw, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
mCoveflowCenter = getCenterOfCoverflow();
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
}
/**
* Transform the Image Bitmap by the Angle passed
*
* @param imageView
* ImageView the ImageView whose bitmap we want to rotate
* @param t
* transformation
* @param rotationAngle
* the Angle by which to rotate the Bitmap
*/
privatevoid transformImageBitmap(ImageView child, Transformation t,
introtationAngle) {
mCamera.save();
finalMatrix imageMatrix = t.getMatrix();
finalint imageHeight = child.getLayoutParams().height;
finalint imageWidth = child.getLayoutParams().width;
finalint rotation = Math.abs(rotationAngle);
// 在Z軸上正向移動camera的視角,實際效果為放大圖片。
// 如果在Y軸上移動,則圖片上下移動;X軸上對應圖片左右移動。
mCamera.translate(0.0f,0.0f, 100.0f);
// As the angle of the view gets less, zoom in
if(rotation < mMaxRotationAngle) {
floatzoomAmount = (float) (mMaxZoom + (rotation *1.5));
mCamera.translate(0.0f,0.0f, zoomAmount);
}
// 在Y軸上旋轉,對應圖片豎向向裡翻轉。
// 如果在X軸上旋轉,則對應圖片橫向向裡翻轉。
mCamera.rotateY(rotationAngle);
mCamera.getMatrix(imageMatrix);
imageMatrix.preTranslate(-(imageWidth /2), -(imageHeight /2));
imageMatrix.postTranslate((imageWidth /2), (imageHeight /2));
mCamera.restore();
}
}
代碼到這裡就結束了。有興趣的話可以自行調整裡面的參數來實現更多更炫的效果。
下面是調用的示例:
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_gallery);
Integer[] images = { R.drawable.img0001, R.drawable.img0030,
R.drawable.img0100, R.drawable.img0130, R.drawable.img0200,
R.drawable.img0230, R.drawable.img0300, R.drawable.img0330,
R.drawable.img0354 };
ImageAdapter adapter =new ImageAdapter(this, images);
adapter.createReflectedImages();
GalleryFlow galleryFlow = (GalleryFlow) findViewById(R.id.gallery_flow);
galleryFlow.setAdapter(adapter);
}
PS1:
可以看出來這樣實現的gallery鋸齒問題比較嚴重。可以在createReflectedImages()使用以下代碼:
BitmapDrawable bd = new BitmapDrawable(bitmapWithReflection); bd.setAntiAlias(true);
然後用iv.setImageDrawable(bd);
代替iv.setImageBitmap(bitmapWithReflection);
即可基本消除鋸齒。
PS2:
ImageAdapter有待確定的MemoryLeak問題,貌似的Bitmap的decode方法會造成ML,使用ImageAdapter時多次旋轉屏幕後會出現OOM。目前可以通過將使用完畢的bimap調用recycle()方法和設置null並及時調用system.gc()得到一些改善,但是問題並不明顯。
慶祝精華和推薦,增加3個PS~
PS3 ON PS1:
為什麼開啟抗鋸齒後不明顯。答案是,鋸齒不可能完全消除,但開啟抗鋸齒後會有很大改善。
另外還說到為什麼android不默認開啟鋸齒,以下是我的一點想法:
插值是我現在所知道的抗鋸齒的算法,也就是計算像素間的相關度對其間插入中間像素以達到平滑圖像邊緣的效果。但這無疑會耗費了大量的運算。
雖然我沒有經過測試,但是我猜測,使用antialias後圖形性能至少會下降30%。
當然,在這裡沒有涉及到復雜的圖形運算,所以開啟抗鋸齒不會有很明顯的性能影響,但如果你在模擬器或者低端機型上測試就會發現一點問題。
PS4:
有人問到transformImageBitmap()中這倆句話是什麼意思:
imageMatrix.preTranslate(-(imageWidth / 2), -(imageHeight / 2)); imageMatrix.postTranslate((imageWidth / 2), (imageHeight / 2));
個人的理解如下:
preTranslate相當於在對圖像進行任何矩陣變換前先進行preTranslate,postTranslate相反,進行所有變換後再執行postTranlate。
這倆句的意思是:在做任何變換前,先將整個圖像從圖像的中心點移動到原點((0,0)點),執行變換完畢後再將圖像從原點移動到之前的中心點。
如果不加這倆句,任何變換將以圖像的原點為變換中心點,加了之後,任何變換都將以圖像的中心點為變換中心點。
舉個例子,對圖像進行旋轉,需要倆個參數:一個是旋轉的角度,另一個是旋轉中心的坐標。旋轉中心的坐標影響旋轉的效果。這個能明白嗎?你拿一根棍子,拿著棍子的一端進行旋轉和拿在棍子中間旋轉,是不一樣的。preTranslate和postTranslate執行後對圖像本身不會有影響,影響的是對圖像進行變換時的旋轉軸。
說了這麼多有點繞,其實就是矩陣變換的知識。
PS5 ON PS2:
這個問題在google group下有過很充分的討論,貌似一般只在debug模式下存在。現在我使用這段代碼沒有出現OOM問題了
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
 Android組件:Fragment切換後保存狀態
Android組件:Fragment切換後保存狀態
之前寫的第一篇Fragment實例,和大多數人一開始學的一樣,都是通過FragmentTransaction的replace方法來實現,replace方法相
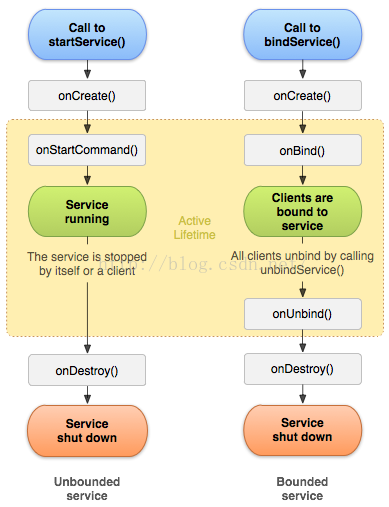 Android Service詳解
Android Service詳解
來自:https://developer.android.com/guide/components/services.htmlService是一個可以在後台執行長時間運行
 android自定義View之仿通訊錄側邊欄滑動,實現A-Z字母檢索
android自定義View之仿通訊錄側邊欄滑動,實現A-Z字母檢索
我們的手機通訊錄一般都有這樣的效果,如下圖:OK,這種效果大家都見得多了,基本上所有的android手機通訊錄都有這樣的效果。那我們今天就來看看這個效果該怎麼實現。一.概
 小米4如何刷Win10操作系統?小米4刷Win10教程
小米4如何刷Win10操作系統?小米4刷Win10教程
小米4絕對是小米的一個神機:至少是安卓手機中稍有的可以刷雙系統的,為發燒而生。微軟教程不是人看的!官方就放了句話,然後死都不給教程!坑死人不償命!!!!首先