編輯:關於Android編程
關於 android 常用布局,利用 XML 文件實現已經有很多的實例了。但如何利用代碼實現呢?當然利用代碼實現沒有太大的必要,也是不提倡的,但我覺得利用代碼實現這些布局,可以更好的了解 SDK API ,所以在此也整理一些,和大家分享一下。
首先看一下,布局所對應的類的 API 繼承圖:
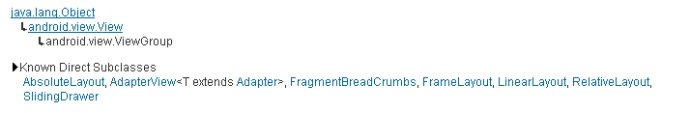
android常用布局的代碼實現所有的布局都會對應相關的類,這些類都是繼承自 android.view.ViewGroup 類的。而 LinearLayout,RelativeLayout 都是在 android.widget 包裡的。另外,TableLayout 是繼承自 LinearLayout.
下面直接貼代碼了。
// 利用代碼設置 線性布局
private void setLinearLayout(){
LinearLayout llayout = new LinearLayout(this);
llayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL); // 設置線性布局的排列方式
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setText("代碼實現的線性布局");
textView.setTextColor(Color.RED);
textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER); // 設置文本內容的對齊方式
LinearLayout.LayoutParams ll_lpara = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(MP,WC);
// ll_lpara.gravity = Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL; // 設置控件在布局中的對齊方式
llayout.addView(textView,ll_lpara);
Button btn = new Button(this);
btn.setText("按鈕");
llayout.addView(btn,ll_lpara); // 按指定屬性添加控件
setContentView(llayout);
}
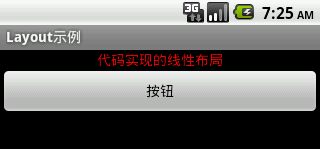
實現效果圖:
=========================================================================
// 利用代碼設置 相對布局
private void setRelativeLayout(){
RelativeLayout rlayout = new RelativeLayout(this);
rlayout.setPadding(10, 10, 10, 10); // 單位: pixels
int textViewID = 100;
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setId(textViewID);
textView.setText("請輸入:");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara1 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(MP, WC);
rlayout.addView(textView, rl_lpara1);
int editTextID = 200;
EditText editText = new EditText(this);
editText.setId(editTextID);
editText.setBackgroundResource(android.R.drawable.editbox_background); // 設置背景 , 同android:backgroumd
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara2 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(MP, WC);
rl_lpara2.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW,textViewID); // 設置相對屬性,需先指定相對控件的ID
rlayout.addView(editText, rl_lpara2);
int backBtnID = 300;
Button backBtn = new Button(this);
backBtn.setId(backBtnID);
backBtn.setText("返回");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara3 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(WC, WC);
rl_lpara3.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW, editTextID);
rl_lpara3.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT); // 設置與父控件的相對屬性
rlayout.addView(backBtn, rl_lpara3);
Button okBtn = new Button(this);
okBtn.setText("確定");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara4 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(WC, WC);
rl_lpara4.addRule(RelativeLayout.LEFT_OF, backBtnID);
rl_lpara4.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_TOP,backBtnID);
rlayout.addView(okBtn, rl_lpara4);
setContentView(rlayout);
}
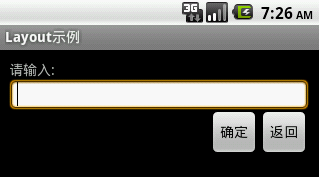
實現效果圖:
=========================================================================
// 利用代碼設置 表格布局
private void setTableLayout(){
TableLayout tlayout = new TableLayout(this);
tlayout.setColumnStretchable(2, true); // 拉長索引從0開始的第2列
TableLayout.LayoutParams tl_lpara = new TableLayout.LayoutParams(MP,WC);
// 1. TableRow 不需要設置 layout_width, layout_height
// 2. TableRow 中的控件不能設置 layout_span 屬性
TableRow tr1 = new TableRow(this);
TextView textView0 = new TextView(this);
textView0.setText("第0列");
tr1.addView(textView0);
TextView textView1 = new TextView(this);
textView1.setText("第1列");
tr1.addView(textView1);
TextView textView2 = new TextView(this);
textView2.setText("第2列");
textView2.setBackgroundColor(Color.CYAN);
tr1.addView(textView2);
tlayout.addView(tr1, tl_lpara);
TableRow tr2 = new TableRow(this);
Button btn0 = new Button(this);
btn0.setText("按鈕0");
tr2.addView(btn0);
Button btn1 = new Button(this);
btn1.setText("按鈕1");
tr2.addView(btn1);
Button btn2 = new Button(this);
btn2.setText("按鈕2");
tr2.addView(btn2);
Button btn3 = new Button(this);
btn3.setText("按鈕3");
tr2.addView(btn3);
tlayout.addView(tr2, tl_lpara);
setContentView(tlayout);
}
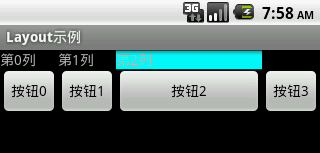
實現效果圖:
 Kotlin在Android工程中的應用
Kotlin在Android工程中的應用
Kotlin在Android工程中的應用 @author ASCE1885的 Github 簡書 微博 CSDN 原文鏈接簡介Kotlin是由JetBrains設計的開放
 re管理器是什麼 re管理器在哪
re管理器是什麼 re管理器在哪
re管理器是玩轉安卓的一個必不可少的神器之一,基於強大的文件管理功能,可以查看系統system分區文件,配合root授權使用,簡直就是可以發揮安卓的極致。r
 android項目 之 記事本(10) ----- 手寫功能之設置畫筆大小和畫筆顏色
android項目 之 記事本(10) ----- 手寫功能之設置畫筆大小和畫筆顏色
上一節,實現了畫板的所有功能,包括設置畫筆大小,設置畫筆顏色,橡皮擦等功能,而手寫,也可以添加設置筆跡大小和顏色的功能,這節就順勢實現手寫的調整筆跡大小和調整筆跡的顏色。
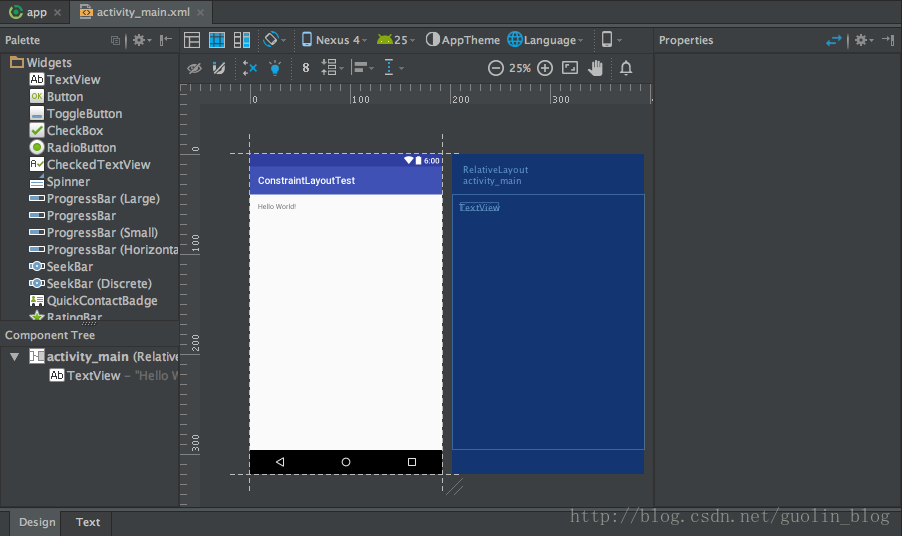 Android新特性介紹,ConstraintLayout完全解析
Android新特性介紹,ConstraintLayout完全解析
今天給大家帶來2017年的第一篇文章,這裡先祝大家新年好。本篇文章的主題是ConstraintLayout。其實ConstraintLayout是AndroidStudi