編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述了Android短信發送器實現方法。分享給大家供大家參考。具體如下:
這裡模擬android短信發送器的實現
AndroidManifest.xml清單文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.ljq.sms" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/> </manifest>
main.xml布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:layout_width="115dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="請輸入手機號" android:id="@+id/mobilelabel" /> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/mobilelabel" android:text="5556" android:id="@+id/mobile" /> </RelativeLayout> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="請輸入短信內容" /> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:minLines="3" android:text="I am a teacher!" android:id="@+id/content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="發送" android:id="@+id/button" /> </LinearLayout>
MainActivity類:
package com.ljq.sms;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.telephony.SmsManager;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private EditText mobileText=null;
private EditText contentText=null;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mobileText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.mobile);
contentText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.content);
Button button=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
String mobile=mobileText.getText().toString();
String content=contentText.getText().toString();
//取得android系統中默認的短信管理器
SmsManager manager=SmsManager.getDefault();
//如果短信內容過長時,則對短信內容進行拆分
ArrayList<String> texts=manager.divideMessage(content);
for(String text:texts){
//第一個參數:對方手機號碼
//第二個參數:短信中心號碼,一般設置為空
//第三個參數:短信內容
//第四個參數:sentIntent判斷短信是否發送成功,如果你沒有SIM卡,或者網絡中斷,則可以通過這個intent來判斷。
//注意強調的是“發送”的動作是否成功。那麼至於對於對方是否收到,另當別論
//第五個參數:當短信發送到收件人時,會收到這個deliveryIntent。即強調了“發送”後的結果
//就是說是在"短信發送成功"和"對方收到此短信"才會激活sentIntent和deliveryIntent這兩個Intent。這也相當於是延遲執行了Intent
manager.sendTextMessage(mobile, null, text, null, null);
}
//Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "發送成功", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "發送成功", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
}
運行結果:
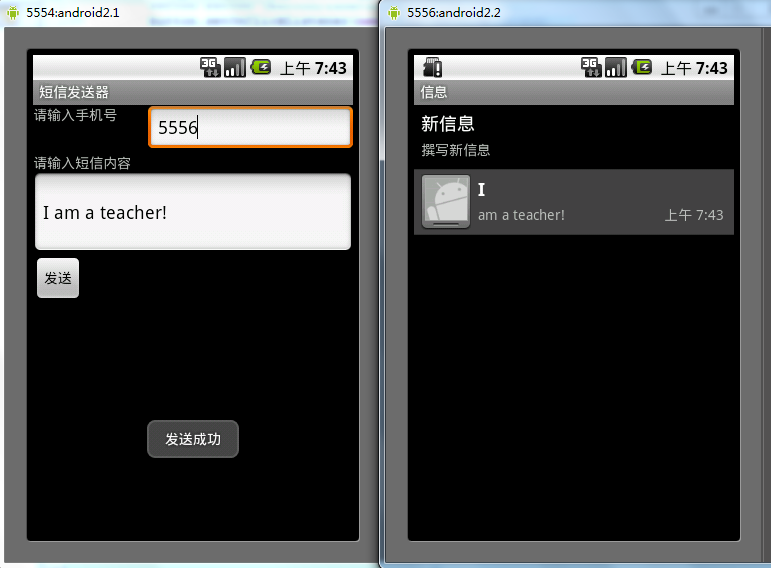
希望本文所述對大家的Android程序設計有所幫助。
 Android自定義SwipeRefreshLayout高仿微信朋友圈下拉刷新
Android自定義SwipeRefreshLayout高仿微信朋友圈下拉刷新
上一篇文章裡把SwipeRefreshLayout的原理簡單過了一下,大致了解了其工作原理,不熟悉的可以去看一下:http://www.jb51.net/article/
 Android - ToDoList(定制ArrayAdapter)
Android - ToDoList(定制ArrayAdapter)
ToDoList(定制ArrayAdapter) 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/
 Android界面坐標圖示和Rect(矩形)簡介
Android界面坐標圖示和Rect(矩形)簡介
Android界面的坐標是以左上角為起始點,平行的為X軸,垂直的為Y軸,數值都是遞增的。如下圖所示: Android的Rect類是形成一個矩形的區域,區域
 UC-Android逆向工程師面試第2題分析
UC-Android逆向工程師面試第2題分析
一、簡介這個題目是別人面試UC優視集團Android逆向工程師一職位的面試題,相比較前面的面試題1,增加了一些難度。 二、題目分析1.使