編輯:關於Android編程
**********************************************************************
android 實現圖片的翻轉
**********************************************************************
Resources res = this.getContext().getResources(); img = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, R.drawable.aa); Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); matrix.postRotate(180); /*翻轉180度*/ int width = img.getWidth(); int height = img.getHeight(); img_a = Bitmap.createBitmap(img, 0, 0, width, height, matrix, true);
然後可以直接把img_a draw到畫布上,canvas.drawBitmap(img_a, 10, 10, p);
Matrix 是一個處理翻轉、縮放等圖像效果的重要類,Matrix.postScale 可設置縮放比例,默認為1
**********************************************************************
android 實現圖片的旋轉
**********************************************************************
public class ex04_22 extends Activity{
private ImageView mImageView;
private Button btn1,btn2;
private TextView mTextView;
private AbsoluteLayout layout1;
private int ScaleTimes=1,ScaleAngle=1;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mImageView=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.myImageView);
final Bitmap bmp=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(this.getResources(),R.drawable.ex04_22_1);
final int widthOrig=bmp.getWidth();
final int heightOrig=bmp.getHeight();
mImageView.setImageBitmap(bmp);
btn1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton1);
btn1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
ScaleAngle--;
if(ScaleAngle<-60){
ScaleAngle=-60;
}
int newWidth=widthOrig*ScaleTimes;
int newHeight=heightOrig*ScaleTimes;
float scaleWidth=((float)newWidth)/widthOrig;
float scaleHeight=((float)newHeight)/heightOrig;
Matrix matrix=new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
matrix.setRotate(5*ScaleAngle);
Bitmap resizeBitmap=Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp, 0, 0, widthOrig, heightOrig, matrix, true);
BitmapDrawable myNewBitmapDrawable=new BitmapDrawable(resizeBitmap);
mImageView.setImageDrawable(myNewBitmapDrawable);
}
});
btn2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton2);
btn2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
ScaleAngle++;
if(ScaleAngle>60){
ScaleAngle=60;
}
int newWidth=widthOrig*ScaleTimes;
int newHeight=heightOrig*ScaleTimes;
float scaleWidth=((float)newWidth)/widthOrig;
float scaleHeight=((float)newHeight)/heightOrig;
Matrix matrix=new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
matrix.setRotate(5*ScaleAngle);
Bitmap resizeBitmap=Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp, 0, 0, widthOrig, heightOrig, matrix, true);
BitmapDrawable myNewBitmapDrawable=new BitmapDrawable(resizeBitmap);
mImageView.setImageDrawable(myNewBitmapDrawable);
}
});
}
**********************************************************************
實現畫面淡入淡出效果可以用 :setAlpha(alpha);
alpha從255,逐漸遞減!
**********************************************************************
如何實現屏幕的滾動效果,這裡有兩個關鍵點,一個是實現OnGestureListener,以便在觸摸事件發生的時候,被回調。包括按下,滾動等等,按照API文檔,需要分兩步來實現檢測手勢行為。
1)創建GestureDetector實例
2) 在onTouchEvent()方法中調用GestureDetector的onTouchEvent()方法。
另一個關鍵點是自己實現一個簡單的View,來繪制圖片。
代碼如下所示。由於,我們不需要使用layout定義,所以不需要提供xml文件。
直接在程序裡面setContentView()即可。
package com.j2medev;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.Resources;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.GestureDetector;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.GestureDetector.OnGestureListener;
public class HorizontalScroll extends Activity implements OnGestureListener {
private static final int X_MAX = 800;
private static final int Y_MAX = 600;
private int scrollX = 0;
private int scrollY = 0;
MyView main;
Bitmap bmp;
Bitmap adapt;
Resources res;
Paint paint;
GestureDetector gestureScanner;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
gestureScanner = new GestureDetector(this);
paint = new Paint();
res = getResources();
bmp = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, R.drawable.arc);
adapt = Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp);
main = new MyView(this);
setContentView(main, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(800, 600));
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent me) {
return gestureScanner.onTouchEvent(me);
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX,
float distanceY) {
main.handleScroll(distanceX, distanceY);
return true;
}
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
return true;
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
return true;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
}
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
return true;
}
// //////////////////
// /////////////////
// ////////////////
class MyView extends View {
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawBitmap(adapt, -scrollX, -scrollY, paint);
}
public void handleScroll(float distX, float distY) {
// X-Axis ////////////////////////////////
if (distX > 6.0) {
if (scrollX < 460) {
scrollX += 15;
}
} else if (distX < -6.0) {
if (scrollX >= 15) {
scrollX -= 15;
}
}
// //////////////////////////////////////////
// Y-AXIS //////////////////////////////////
if (distY > 6.0) {
if (scrollY < 100) {
scrollY += 15;
}
} else if (distY < -6.0) {
if (scrollY >= 15) {
scrollY -= 15;
}
}
// //////////////////////////////////////////
//
// if ((scrollX <= 480) && (scrollY <= 120)) {
// adapt = Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp, scrollX, scrollY, 320, 480);
// invalidate();
// }
invalidate();
}
}
}
**********************************************************************
教你在谷歌Android平台中處理圖片
**********************************************************************
操作圖像像素
現在你可以對單獨的像素進行處理了。通過使用android.graphics.Bitmap API中的getPixels,可以加載像素到一個整數數組中。
在本文例子中,你將按照一定規則對每一個像素實現著色。經過這個處理後,所有的像素將被轉化為一個范圍在0到255的字節碼。
android.graphics.Bitmap API中的setPixels則用來加載這個整數數組到一個圖像中。
最後一步是通過ImageView變量mIV來更新屏幕。以下是實現這個染色過程的代碼片段。
private void TintThePicture(int deg) {
int[] pix = new int[picw * pich];
mBitmap.getPixels(pix, 0, picw, 0, 0, picw, pich);
int RY, GY, BY, RYY, GYY, BYY, R, G, B, Y;
double angle = (3.14159d * (double)deg) / 180.0d;
int S = (int)(256.0d * Math.sin(angle));
int C = (int)(256.0d * Math.cos(angle));
for (int y = 0; y < pich; y++)
for (int x = 0; x < picw; x++)
{
int index = y * picw + x;
int r = (pix[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
int g = (pix[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
int b = pix[index] & 0xff;
RY = ( 70 * r - 59 * g - 11 * b) / 100;
GY = (-30 * r + 41 * g - 11 * b) / 100;
BY = (-30 * r - 59 * g + 89 * b) / 100;
Y = ( 30 * r + 59 * g + 11 * b) / 100;
RYY = (S * BY + C * RY) / 256;
BYY = (C * BY - S * RY) / 256;
GYY = (-51 * RYY - 19 * BYY) / 100;
R = Y + RYY;
R = (R < 0) ? 0 : ((R > 255) ? 255 : R);
G = Y + GYY;
G = (G < 0) ? 0 : ((G > 255) ? 255 : G);
B = Y + BYY;
B = (B < 0) ? 0 : ((B > 255) ? 255 : B);
pix[index] = 0xff000000 | (R << 16) | (G << 8) | B;
}
Bitmap bm = Bitmap.createBitmap(picw, pich, false);
bm.setPixels(pix, 0, picw, 0, 0, picw, pich);
// Put the updated bitmap into the main view
mIV.setImageBitmap(bm);
mIV.invalidate();
mBitmap = bm;
pix = null;
}
**********************************************************************
android 圖片的放大和縮小
**********************************************************************
public class ex04_22 extends Activity{
private ImageView mImageView;
private Button btn1,btn2;
private TextView mTextView;
private AbsoluteLayout layout1;
private Bitmap bmp;
private int id=0;
private int displayWidth,displayHeight;
private float scaleWidth=1,scaleHeight=1;
private final static String filename="/data/data/ex04_22.lcs/ex04_22_2.png";
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//取得屏幕分辨率
DisplayMetrics dm=new DisplayMetrics();
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm);
displayWidth=dm.widthPixels;
displayHeight=dm.heightPixels-80;
bmp=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(this.getResources(),R.drawable.ex04_22_1);
layout1=(AbsoluteLayout)findViewById(R.id.layout1);
mImageView=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.myImageView);
btn1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton1);
btn1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
small();
}
});
btn2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton2);
btn2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
big();
}
});
}
private void small(){
//獲得Bitmap的高和寬
int bmpWidth=bmp.getWidth();
int bmpHeight=bmp.getHeight();
//設置縮小比例
double scale=0.8;
//計算出這次要縮小的比例
scaleWidth=(float)(scaleWidth*scale);
scaleHeight=(float)(scaleHeight*scale);
//產生resize後的Bitmap對象
Matrix matrix=new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
Bitmap resizeBmp=Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp, 0, 0, bmpWidth, bmpHeight, matrix, true);
if(id==0){
layout1.removeView(mImageView);
}
else{
layout1.removeView((ImageView)findViewById(id));
}
id++;
ImageView imageView=new ImageView(this);
imageView.setId(id);
imageView.setImageBitmap(resizeBmp);
layout1.addView(imageView);
setContentView(layout1);
btn2.setEnabled(true);
}
private void big(){
//獲得Bitmap的高和寬
int bmpWidth=bmp.getWidth();
int bmpHeight=bmp.getHeight();
//設置縮小比例
double scale=1.25;
//計算出這次要縮小的比例
scaleWidth=(float)(scaleWidth*scale);
scaleHeight=(float)(scaleHeight*scale);
//產生resize後的Bitmap對象
Matrix matrix=new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
Bitmap resizeBmp=Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp, 0, 0, bmpWidth, bmpHeight, matrix, true);
if(id==0){
layout1.removeView(mImageView);
}
else{
layout1.removeView((ImageView)findViewById(id));
}
id++;
ImageView imageView=new ImageView(this);
imageView.setId(id);
imageView.setImageBitmap(resizeBmp);
layout1.addView(imageView);
setContentView(layout1);
if(scaleWidth*scale*bmpWidth>displayWidth||scaleHeight*scale*scaleHeight>displayHeight){
btn2.setEnabled(false);
}
}
}
xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <AbsoluteLayout android:id="@+id/layout1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/myImageView" android:layout_width="200px" android:layout_height="150px" android:src="@drawable/ex04_22_1" android:layout_x="0px" android:layout_y="0px" > </ImageView> <Button android:id="@+id/myButton1" android:layout_width="90px" android:layout_height="60px" android:text="縮小" android:textSize="18sp" android:layout_x="20px" android:layout_y="372px" > </Button> <Button android:id="@+id/myButton2" android:layout_width="90px" android:layout_height="60px" android:text="放大" android:textSize="18sp" android:layout_x="210px" android:layout_y="372px" > </Button> </AbsoluteLayout>
*********************************************************************
android 圖片透明度處理代碼
*********************************************************************
public static Bitmap setAlpha(Bitmap sourceImg, int number) {
int[] argb = new int[sourceImg.getWidth() * sourceImg.getHeight()];
sourceImg.getPixels(argb, 0, sourceImg.getWidth(), 0, 0,sourceImg.getWidth(), sourceImg.getHeight());// 獲得圖片的ARGB值
number = number * 255 / 100;
for (int i = 0; i < argb.length; i++) {
argb = (number << 24) | (argb & 0x00FFFFFF);// 修改最高2位的值
}
sourceImg = Bitmap.createBitmap(argb, sourceImg.getWidth(), sourceImg.getHeight(), Config.ARGB_8888);
return sourceImg;
}
以上就是涉及到了Android圖片處理的所有內容,包括android圖片反轉、android 圖片翻轉、android 圖片旋轉、實現畫面淡入淡出效果、android 圖片的放大和縮小以及教你在谷歌Android平台中處理圖片。
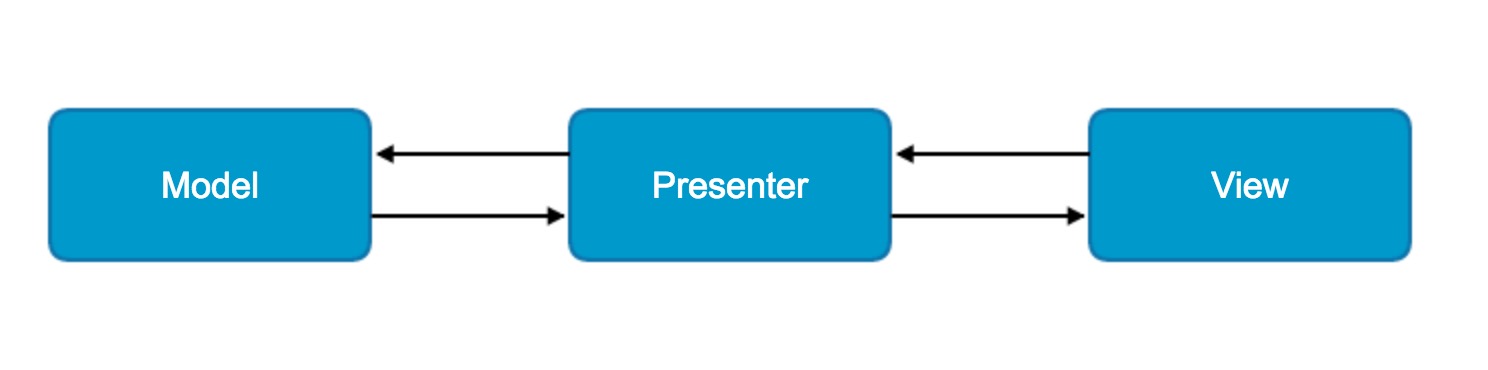 Android官方MVP架構解讀
Android官方MVP架構解讀
綜述對於MVP (Model View Presenter)架構是從著名的MVC(Model View Controller)架構演變而來的。而對於Android應用的開
 Android中TabLayout結合ViewPager實現頁面切換
Android中TabLayout結合ViewPager實現頁面切換
一、實現思路1、在build.gradle中添加依賴,例如:compile com.android.support:support-v4:23.4.0compile co
 Android使用WindowManager構造懸浮view
Android使用WindowManager構造懸浮view
一般在android顯示一個View都是通過Activity的setContentView設置的,但是還有一種方法,可以直接使用WindowManager在整個應用的最上
 安卓手機重置便攜式熱點密碼方法
安卓手機重置便攜式熱點密碼方法
安卓手機重置便攜式熱點密碼方法如何?小編就來演示一下。 開啟手機,進入手機設置界面; 選擇“無線和網絡”; 選擇&