編輯:關於Android編程
1.首先下載一個libserial_port.so,新建目錄libs/armeabi,將so文件放到該目錄下。
2.定義串口類,在類的構建函數中修改權限,打開設備,創建輸入流和輸出流,通過native接口訪問串口打開關閉函數
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public class SerialPort {
/*Do not remove or rename the field mFd: it is used by native method close();*/
public SerialPort(File device, int baudrate, int flags) throws SecurityException, IOException, InvalidParameterException{
//如果串口權限不夠,改變權限
/* Check access permission */
if (!device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
try {
/* Missing read/write permission, trying to chmod the file */
Process su;
su = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("/system/bin/su");
String cmd = "chmod 666 " + device.getAbsolutePath() + "\n"
+ "exit\n";
su.getOutputStream().write(cmd.getBytes());
if ((su.waitFor() != 0) || !device.canRead()
|| !device.canWrite()) {
throw new SecurityException();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new SecurityException();
}
}
mFd = open(device.getAbsolutePath(), baudrate, flags);//打開串口
if (mFd == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "native open returns null");
throw new IOException();
}
mFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(mFd);//串口輸入流
mFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(mFd);//串口輸出流
}
// Getters and setters
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return mFileInputStream;
}
public OutputStream getOutputStream() {
return mFileOutputStream;
}
// JNI
private native static FileDescriptor open(String path, int baudrate, int flags);//c文件中的串口open()函數
public native void close();//c文件中的串口close()函數
static {
System.loadLibrary("serial_port");//加載串口庫
}
}
}
3.定義抽象類ServerData
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public abstract class ServerData {
protected SerialPort mSerialPort;
protected OutputStream mOutputStream;
private InputStream mInputStream;
private ReadThread mReadThread;
private class ReadThread extends Thread {
@Override
//在線程中讀取數據並處理數據
public void run() {
super.run();
byte[] buffer = new byte[128];
int size;
while(true) {
try {
if (mInputStream == null) return;
size = mInputStream.read(buffer);//讀取數據
if (size > 0) {
onDataReceived(buffer, size);//處理數據
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
}
}
4.實例化串口類,輸出流和輸入流,實例化讀取線程並開始執行該線程
[code]
public ServerData(String path, int baudrate){
try {
mSerialPort = new SerialPort(new File(path), baudrate, 0);
mOutputStream = mSerialPort.getOutputStream();
mInputStream = mSerialPort.getInputStream();
/* Create a receiving thread */
mReadThread = new ReadThread();
mReadThread.start();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
} catch (IOException e) {
} catch (InvalidParameterException e) {
}
}
protected abstract void onDataReceived(final byte[] buffer, final int size);
}
[/code]
5.然後再新建一個類,在新建的類中實現上面的抽象函數,並寫一個函數返回讀取到的數據。
復制代碼 代碼如下:
package View;
//導入R類,所在包不同,不能直接飲用,需要導入才可以使用
import android_serialport_api.sample.R;
/* EtcView類,Etc界面管理 */
public class SerialView {
private Activity context = null;
private Serial mEtcServer = null;
/* Etc界面構造函數 */
public SerialView(Activity context) {
this.context = context;
}
public void EtcInitView() {
//這樣才可以找到android_serialport_api.sample包下的id
TextView mytext=(TextView)context.findViewById(R.id.mytext);
mEtcServer = new Serial("/dev/s3c2410_serial3", 9600);
}
public void EtcRefresh() {
//返回串口線程讀取的數據
byte[] buffer = mEtcServer.getdata();
String recString=new String(buffer);//將byte[]的數組轉換成字符串string
mytext.setText(recString);//設置字符文本
buffer = null;
}
}
 Android導出jar包後的資源使用問題
Android導出jar包後的資源使用問題
我們經常遇到一個需求,就是給別人使用我們工程的時候,為了能夠屏蔽代碼,把代碼封裝成jar包提供給第三方使用,但是這樣我們的資源文件怎麼給對方用呢? 網上有很多方法,有用C
 詳解關鍵字static,const,volatile
詳解關鍵字static,const,volatile
static修飾局部變量static修飾局部變量用於修改變量的存儲位置,從自動變量修改為靜態變量(在靜態區開辟空間,不在棧上開辟),但變量的鏈接屬性和作用域不受影響。st
 Android打包簽名那點事
Android打包簽名那點事
接觸android開發也有一段時間了,對打包簽名有所了解,但都是皮毛,一點不深入。今天結合網絡上的資料和自己的實踐,盤點下相關內容,打消自己的一些疑問,順便做一下總結。
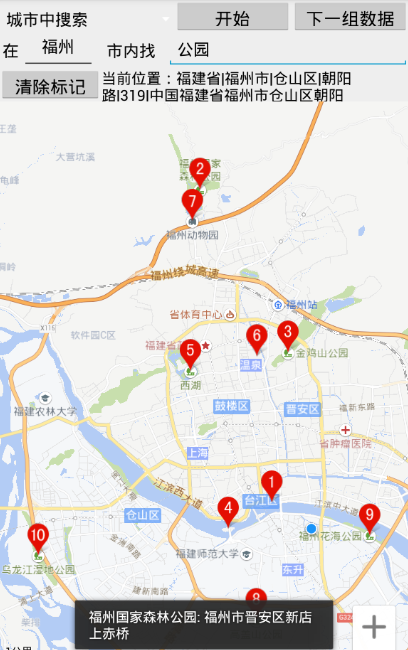 百度地圖
百度地圖
顯示地圖和定位對於一個地圖SDK來說,首先要顯示地圖,然後定位到當前城市。這方面百度地圖和高德地圖的處理代碼差不多,下面是兩種地圖sdk顯示並定位的代碼例子:百度地圖//