編輯:關於Android編程
前面文章介紹了Activity以及Intent的使用,本文就來介紹Service。如果把Activity比喻為前台程序,那麼Service就是後台程序,Service的整個生命周期都只會在後台執行。Service跟Activity一樣也由Intent調用。在工程裡想要添加一個Service,先新建繼承Service的類,然後到AndroidManifest.xml -> Application ->Application Nodes中的Service標簽中添加。
Service要由Activity通過startService 或者 bindService來啟動,Intent負責傳遞參數。
先貼出本文程序運行截圖如下:
本文主要講解Service的調用,以及其生命周期。
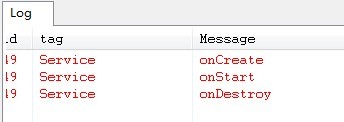
上圖是startService之後再stopService的Service狀態變化。
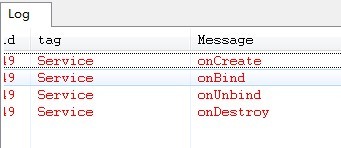
上圖是bindService之後再unbindService的Service狀態變化。
startService與bindService都可以啟動Service,那麼它們之間有什麼區別呢?它們兩者的區別就是使Service的周期改變。由startService啟動的Service必須要有stopService來結束Service,不調用stopService則會造成Activity結束了而Service還運行著。bindService啟動的Service可以由unbindService來結束,也可以在Activity結束之後(onDestroy)自動結束。
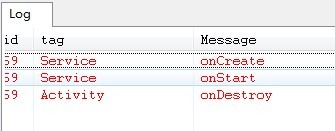
上圖是startService之後再Activity.finish()的Service狀態變化,Service還在跑著。
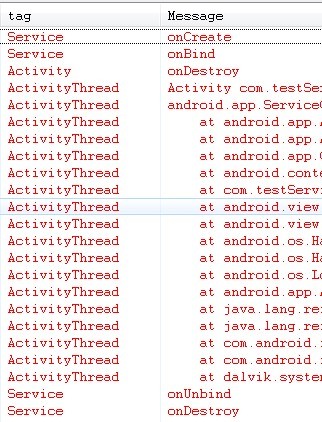
上圖是bindService之後再Activity.finish()的Service狀態變化,Service最後自動unbindService。
main.xml代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/btnStartMyService" android:text="StartMyService"></Button> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/btnStopMyService" android:text="StopMyService"></Button> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/btnBindMyService" android:text="BindMyService"></Button> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/btnUnbindMyService" android:text="UnbindMyService"></Button> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/btnExit" android:text="退出程序"></Button> </LinearLayout>
testService.java的源碼如下:
package com.testService;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class testService extends Activity {
Button btnStartMyService,btnStopMyService,btnBindMyService,btnUnbindMyService,btnExit;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnStartMyService=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnStartMyService);
btnStartMyService.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnStopMyService=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnStopMyService);
btnStopMyService.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnBindMyService=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnBindMyService);
btnBindMyService.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnUnbindMyService=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnUnbindMyService);
btnUnbindMyService.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnExit=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnExit);
btnExit.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
}
@Override
public void onDestroy()
{
super.onDestroy();
Log.e("Activity","onDestroy");
}
private ServiceConnection _connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName arg0, IBinder arg1) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
class ClickEvent implements View.OnClickListener{
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(testService.this,MyService.class);
if(v==btnStartMyService){
testService.this.startService(intent);
}
else if(v==btnStopMyService){
testService.this.stopService(intent);
}
else if(v==btnBindMyService){
testService.this.bindService(intent, _connection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
else if(v==btnUnbindMyService){
if(MyService.ServiceState=="onBind")//Service綁定了之後才能解綁
testService.this.unbindService(_connection);
}
else if(v==btnExit)
{
testService.this.finish();
}
}
}
}
MyService.java的源碼如下:
package com.testService;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
static public String ServiceState="";
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
Log.e("Service", "onBind");
ServiceState="onBind";
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent){
super.onUnbind(intent);
Log.e("Service", "onUnbind");
ServiceState="onUnbind";
return false;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(){
super.onCreate();
Log.e("Service", "onCreate");
ServiceState="onCreate";
}
@Override
public void onDestroy(){
super.onDestroy();
Log.e("Service", "onDestroy");
ServiceState="onDestroy";
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent,int startid){
super.onStart(intent, startid);
Log.e("Service", "onStart");
ServiceState="onStart";
}
}
 Android Notification通知欄消息
Android Notification通知欄消息
Activity:package com.wkk.app8;import android.annotation.TargetApi;import android.app.
 Android中使用AsyncTask實現文件下載以及進度更新提示
Android中使用AsyncTask實現文件下載以及進度更新提示
Android提供了一個工具類:AsyncTask,它使創建需要與用戶界面交互的長時間運行的任務變得更簡單。相對Handler來說AsyncTask更輕量級一些,適用於簡
 Android之Http通信——1.初識Http協議
Android之Http通信——1.初識Http協議
Android之Http通信——1.初識Http協議Android之Http通信1初識Http協議 引言 正文 Http是什麼鬼 名詞解析 Htt
 手把手帶你畫一個 時尚儀表盤 Android 自定義View
手把手帶你畫一個 時尚儀表盤 Android 自定義View
拿到美工效果圖,咱們程序員就得畫得一模一樣。 為了不被老板噴,只能多練啊。聽說你覺得前面幾篇都so easy,那今天就帶你做個相對比較復雜的。今天的效果圖如下(左邊是ui