編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述的是AlertDialog,這種對話框會經常遇到。AlertDialog跟WIN32開發中的Dialog不一樣,AlertDialog是非阻塞的,而阻塞的對話框用的是PopupWindow。
先貼出該程序運行的截圖:
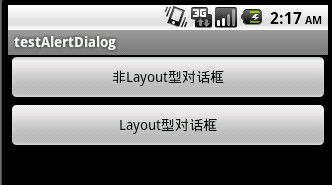
main.xml的源碼:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <Button android:id="@+id/Button01" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="非Layout型對話框" android:layout_width="fill_parent"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/Button02" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Layout型對話框" android:layout_width="fill_parent"></Button><View android:id="@+id/View01" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></View> </LinearLayout>
下圖是非Layout型對話框,直接使用AlertDialog
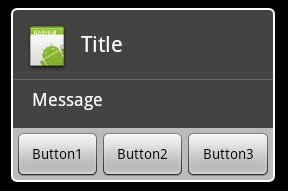
下圖是使用了Layout的對話框,可以自定義控件,實現更復雜的對話框

dialoglayout.xml的源碼:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_marginLeft="20dip" android:layout_marginRight="20dip" android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" android:id="@+id/edtInput"/> </LinearLayout>
程序源碼:
package com.testAlertDialog;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.PopupWindow;
public class testAlertDialog extends Activity {
Button btnShowDialog;
Button btnShowDialog_Layout;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//定義按鈕
btnShowDialog=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button01);
btnShowDialog.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnShowDialog_Layout=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button02);
btnShowDialog_Layout.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
}
//統一處理按鍵事件
class ClickEvent implements OnClickListener{
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v==btnShowDialog)
showDialog(testAlertDialog.this);
else if(v==btnShowDialog_Layout)
showDialog_Layout(testAlertDialog.this);
}
}
//顯示基本的AlertDialog
private void showDialog(Context context) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
builder.setTitle("Title");
builder.setMessage("Message");
builder.setPositiveButton("Button1",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("點擊了對話框上的Button1");
}
});
builder.setNeutralButton("Button2",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("點擊了對話框上的Button2");
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("Button3",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("點擊了對話框上的Button3");
}
});
builder.show();
}
//顯示基於Layout的AlertDialog
private void showDialog_Layout(Context context) {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
final View textEntryView = inflater.inflate(
R.layout.dialoglayout, null);
final EditText edtInput=(EditText)textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.edtInput);
final AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
builder.setCancelable(false);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
builder.setTitle("Title");
builder.setView(textEntryView);
builder.setPositiveButton("確認",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle(edtInput.getText());
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("");
}
});
builder.show();
}
}
 Android工程的目錄結構詳解
Android工程的目錄結構詳解
在搭建Android開發環境及簡單地建立一個HelloWorld項目後,本篇將通過HelloWorld項目來介紹Android項目的目錄結構。本文的主要主題如下: 1、H
 Android開發中Activity創建跳轉及傳值的方法
Android開發中Activity創建跳轉及傳值的方法
在Android系統的江湖中有四大組件:活動(Activity), 服務(Service), 廣播接收器(Broadcast Reciver)和內容提供者(Content
 Android開源框架Image-Loader詳解
Android開源框架Image-Loader詳解
如果說評價一下哪個圖片開源庫最被廣泛使用的話,我想應該可以說是Universal-Image-Loader,在主流的應用中如果你隨便去反編譯幾個,基本都能看到他的身影,它
 Android基於google Zxing實現各類二維碼掃描效果
Android基於google Zxing實現各類二維碼掃描效果
隨著微信的到來,二維碼越來越火爆,隨處能看到二維碼,比如商城裡面,肯德基,餐廳等等,對於二維碼掃描我們使用的是google的開源框架Zxing,我們可以去http://c