編輯:關於Android編程
最近作圖片的顯示,遇到了些問題,簡單總結
1)可以用ImageSwicher和ImageView結合在來做,這樣會用到setFectory(),華而不實
最要命的是如果圖片的大小超過屏幕,實現比較困難,目前是沒有找到方法
2)最簡單的方法是用ImageView,圖片直接FIT_CENTER,android會根據圖片的大小自動調節
保持圖片的比例。如果圖片分辨率超過屏幕,android也會自動的調整到屏幕能放下整張的圖片
在放大圖片的時候,可以用ImageView的SetFrame() 和setScale()方法,可以把圖片放大
到超過屏幕,原理就是ImageView放大,圖片跟著放大。同時也是可以添加各種animation.
大致如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(Main.this, R.anim.my_scale_action);
imageView.setLayoutParams(new Gallery.LayoutParams(206, 206));
imageView.startAnimation(animation);
寫一個自己的MyImageView類,代碼如下,可以直接用
復制代碼 代碼如下:
package com.practice.imageviewpic;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.*;
import android.graphics.drawable.BitmapDrawable;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ImageView.ScaleType;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
//創建一個自己的ImageView類
class MyImageView extends ImageView {
private float scale = 0.1f;
//兩點觸屏後之間的長度
private float beforeLenght;
private float afterLenght;
//單點移動的前後坐標值
private float afterX,afterY;
private float beforeX,beforeY;
public MyImageView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
//用來設置ImageView的位置
private void setLocation(int x,int y) {
this.setFrame(this.getLeft()+x, this.getTop()+y, this.getRight()+x, this.getBottom()+y);
}
/*
* 用來放大縮小ImageView
* 因為圖片是填充ImageView的,所以也就有放大縮小圖片的效果
* flag為0是放大圖片,為1是小於圖片
*/
public void setScale(float temp,int flag) {
if(flag==0) {
this.setFrame(this.getLeft()-(int)(temp*this.getWidth()),
this.getTop()-(int)(temp*this.getHeight()),
this.getRight()+(int)(temp*this.getWidth()),
this.getBottom()+(int)(temp*this.getHeight()));
}else {
this.setFrame(this.getLeft()+(int)(temp*this.getWidth()),
this.getTop()+(int)(temp*this.getHeight()),
this.getRight()-(int)(temp*this.getWidth()),
this.getBottom()-(int)(temp*this.getHeight()));
}
}
//繪制邊框
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Rect rec=canvas.getClipBounds();
rec.left++;
rec.top++;
rec.bottom--;
rec.right--;
Paint paint=new Paint();
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
canvas.drawRect(rec, paint);
}
/* 讓圖片跟隨手指觸屏的位置移動
* beforeX、Y是用來保存前一位置的坐標
* afterX、Y是用來保存當前位置的坐標
* 它們的差值就是ImageView各坐標的增加或減少值
*/
public void moveWithFinger(MotionEvent event) {
switch(event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
//Log.d(TAG, "down ..");
beforeX = event.getX();
beforeY = event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//Log.d(TAG, "move ..");
afterX = event.getX();
afterY = event.getY();
this.setLocation((int)(afterX-beforeX),(int)(afterY-beforeY));
beforeX = afterX;
beforeY = afterY;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
//Log.d(TAG, "up ..");
break;
}
}
/*
* 通過多點觸屏放大或縮小圖像
* beforeLenght用來保存前一時間兩點之間的距離
* afterLenght用來保存當前時間兩點之間的距離
*/
public void scaleWithFinger(MotionEvent event) {
float moveX = event.getX(1) - event.getX(0);
float moveY = event.getY(1) - event.getY(0);
switch(event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
beforeLenght = (float) Math.sqrt( (moveX*moveX) + (moveY*moveY) );
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//得到兩個點之間的長度
afterLenght = (float) Math.sqrt( (moveX*moveX) + (moveY*moveY) );
float gapLenght = afterLenght - beforeLenght;
if(gapLenght == 0) {
break;
}
//如果當前時間兩點距離大於前一時間兩點距離,則傳0,否則傳1
if(gapLenght>0) {
this.setScale(scale,0);
}else {
this.setScale(scale,1);
}
beforeLenght = afterLenght;
break;
}
}
//這裡來監聽屏幕觸控時間
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
/*
* 判定用戶是否觸摸到了圖片
* 如果是單點觸摸則調用控制圖片移動的方法
* 如果是2點觸控則調用控制圖片大小的方法
*/
if(event.getY() > this.getTop() && event.getY() < this.getBottom()
&& event.getX() > this.getLeft() && event.getX() < this.getRight()) {
if(event.getPointerCount() == 2) {
this.scaleWithFinger(event);
}else if(event.getPointerCount() == 1) {
this.moveWithFinger(event);
}
}
return true;
}
}
 android動畫-布局動畫(3)
android動畫-布局動畫(3)
這一篇我們來學點新的東西。做項目的時候應該碰到這種問題:根據不同條件顯示或者隱藏一個控件或者布局,我們能想到的第一個方法就是 調用View.setVisibility()
 Android-屏幕適配需要注意的地方總結
Android-屏幕適配需要注意的地方總結
1.盡量使用線性布局(LinearLayout)和相對布局(RelativeLayout),不要使用絕對布局。 2.盡量使用dip和sp,不要使用px。 3.為不同的分辨
 Android app開發中Retrofit框架的初步上手使用
Android app開發中Retrofit框架的初步上手使用
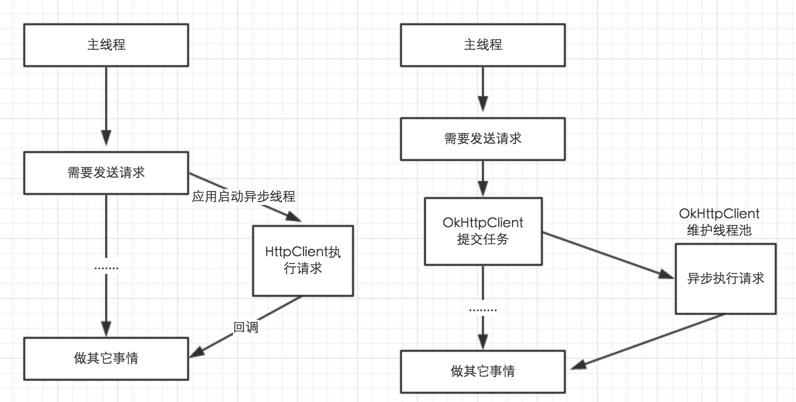
Retrofit 2.0先來說一下Retrofit 2.0版本中一些引人注意的地方。在Retrofit 2.0中,最大的改動莫過於減小庫的體積,首先,Retrofit 2
 百度地圖API提示230 錯誤app scode碼校驗失敗的解決辦法
百度地圖API提示230 錯誤app scode碼校驗失敗的解決辦法
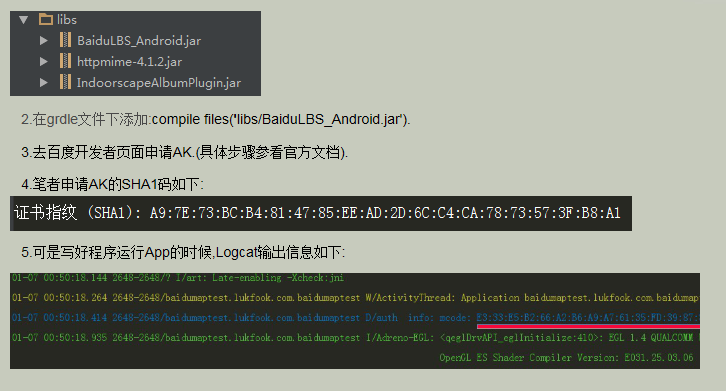
筆者近2天在 Android Studio上玩了一下百度地圖,碰到了常見的230錯誤 APP Scode校驗失敗,下面我來介紹一下具體的解決辦法. 1.在andriod