編輯:關於Android編程
一 說明
這裡重要應用類 AutoTextView,這是一個自定義的類,繼承至TextSwitcher,下面臨 AutoTextView類做簡要說明:
1. 該類應用的重點,在於設置兩個動畫, setInAnimation(...) 和 setOutAnimation(...),分離是文字進入的動畫和文字退出的動畫;
2. 類中定義了一個外部類-Rotate3dAnimation,重要靠該類實現文字進出動畫,該外部類繼承至Animation。說來偶合,這個恰好是在apiDemo中看到了,自定義Animation我還是第一次應用,動畫邏輯均在void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t)中實現,代碼相當鋒利,我在原來的基礎上,更改了一下,實現了上述的效果,
二 代碼部分:
1.AutoTextView.java
復制代碼 代碼如下:
package com.example.animtextview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Camera;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.AccelerateInterpolator;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.Transformation;
import android.widget.TextSwitcher;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher;
public class AutoTextView extends TextSwitcher implements
ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory {
private float mHeight;
private Context mContext;
//mInUp,mOutUp分離構成向下翻頁的進出動畫
private Rotate3dAnimation mInUp;
private Rotate3dAnimation mOutUp;
//mInDown,mOutDown分離構成向下翻頁的進出動畫
private Rotate3dAnimation mInDown;
private Rotate3dAnimation mOutDown;
public AutoTextView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public AutoTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.auto3d);
mHeight = a.getDimension(R.styleable.auto3d_textSize, 36);
a.recycle();
mContext = context;
init();
}
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
setFactory(this);
mInUp = createAnim(-90, 0 , true, true);
mOutUp = createAnim(0, 90, false, true);
mInDown = createAnim(90, 0 , true , false);
mOutDown = createAnim(0, -90, false, false);
//TextSwitcher重要用於文件切換,比如 從文字A 切換到 文字 B,
//setInAnimation()後,A將執行inAnimation,
//setOutAnimation()後,B將執行OutAnimation
setInAnimation(mInUp);
setOutAnimation(mOutUp);
}
private Rotate3dAnimation createAnim(float start, float end, boolean turnIn, boolean turnUp){
final Rotate3dAnimation rotation = new Rotate3dAnimation(start, end, turnIn, turnUp);
rotation.setDuration(800);
rotation.setFillAfter(false);
rotation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
return rotation;
}
//這裡返回的TextView,就是我們看到的View
@Override
public View makeView() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
TextView t = new TextView(mContext);
t.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
t.setTextSize(mHeight);
t.setMaxLines(2);
return t;
}
//定義動作,向下滾動翻頁
public void previous(){
if(getInAnimation() != mInDown){
setInAnimation(mInDown);
}
if(getOutAnimation() != mOutDown){
setOutAnimation(mOutDown);
}
}
//定義動作,向上滾動翻頁
public void next(){
if(getInAnimation() != mInUp){
setInAnimation(mInUp);
}
if(getOutAnimation() != mOutUp){
setOutAnimation(mOutUp);
}
}
class Rotate3dAnimation extends Animation {
private final float mFromDegrees;
private final float mToDegrees;
private float mCenterX;
private float mCenterY;
private final boolean mTurnIn;
private final boolean mTurnUp;
private Camera mCamera;
public Rotate3dAnimation(float fromDegrees, float toDegrees, boolean turnIn, boolean turnUp) {
mFromDegrees = fromDegrees;
mToDegrees = toDegrees;
mTurnIn = turnIn;
mTurnUp = turnUp;
}
@Override
public void initialize(int width, int height, int parentWidth, int parentHeight) {
super.initialize(width, height, parentWidth, parentHeight);
mCamera = new Camera();
mCenterY = getHeight() / 2;
mCenterX = getWidth() / 2;
}
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) {
final float fromDegrees = mFromDegrees;
float degrees = fromDegrees + ((mToDegrees - fromDegrees) * interpolatedTime);
final float centerX = mCenterX ;
final float centerY = mCenterY ;
final Camera camera = mCamera;
final int derection = mTurnUp ? 1: -1;
final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix();
camera.save();
if (mTurnIn) {
camera.translate(0.0f, derection *mCenterY * (interpolatedTime - 1.0f), 0.0f);
} else {
camera.translate(0.0f, derection *mCenterY * (interpolatedTime), 0.0f);
}
camera.rotateX(degrees);
camera.getMatrix(matrix);
camera.restore();
matrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
matrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY);
}
}
}
2. MainActivity.java
復制代碼 代碼如下:
package com.example.animtextview;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button mBtnNext;
private Button mBtnPrev;
private AutoTextView mTextView02;
private static int sCount = 10;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mBtnNext = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next);
mBtnPrev = (Button) findViewById(R.id.prev);
mTextView02 = (AutoTextView) findViewById(R.id.switcher02);
mTextView02.setText("Hello world!");
mBtnPrev.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnNext.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch (arg0.getId()) {
case R.id.next:
mTextView02.next();
sCount++;
break;
case R.id.prev:
mTextView02.previous();
sCount--;
break;
}
mTextView02.setText(sCount%2==0 ?
sCount+"AAFirstAA" :
sCount+"BBBBBBB");
System.out.println("getH: ["+mTextView02.getHeight()+"]");
}
}
3. activity_main.xml
復制代碼 代碼如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:auto3d="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.animtextview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="@string/next" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/prev"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="@string/prev" />
</RelativeLayout>
<com.example.animtextview.AutoTextView
android:id="@+id/switcher02"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
auto3d:textSize="30sp" />
</LinearLayout>
代碼中沒寫太多注釋,不過結構還算清晰,應該不難看懂!
三 小結
我認為該控件實現的難點在於 動畫文件的編寫,即Rotate3dAnimation中applyTransformation(...)方法的實現,通過控制camara在Y方向上挪動和在X方向上的旋轉,從而造成上下翻滾的視覺感,然後將該值轉換到matrix上,從而改變了參數(..,Transformation t).有興致的朋友可以直接改寫該方法,便可失掉不同動畫效果的TextSwitcher.
 《Android源碼設計模式解析與實戰》讀書筆記(二十三)
《Android源碼設計模式解析與實戰》讀書筆記(二十三)
第二十三章、外觀模式 外觀模式是結構型設計模式之一,它在開發中的運用頻率非常高,是我們封裝API的常用手段。我們經常使用的三方SDK基本都使用的外觀模式,這樣可以對用戶屏
 Android新手入門2016(16)--畫圖
Android新手入門2016(16)--畫圖
畫圖設計到圖片的格式,有空可以看看圖片資源各種格式。了解一下圖片格式,對學習有用的。而且我面試別人的時候也很喜歡問這個問題,哈哈。先看個圖。直接看代碼吧,注釋很詳細了。a
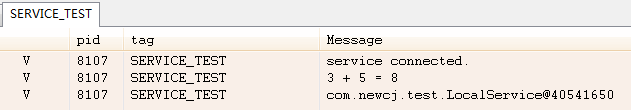 Android Service總結及詳細介紹
Android Service總結及詳細介紹
1、Service的種類按運行地點分類: 類別 區別 優點 缺點 應用
 安卓啟動流程
安卓啟動流程
看了很多相關博客,今天也來自己梳理以下~~~Android從Linux系統啟動 init進程啟動 Native服務啟動 System Server, Android 服務