編輯:關於Android編程
本文從源碼的角度,來展開對動畫的深入解析,關於動畫基本用法,可查看Android動畫之入門篇(一),Android動畫之入門篇(二)。
關於動畫有兩個非常重要的類,那就是插值器(Interpolators)與 估值器(Evaluators),下面將詳細講解。
時間插值器,定義了一個時間的函數:y = f(t),其中t=elapsed time / duration.
每個插值器的源碼流程都相同,下面以AccelerateInterpolator為例,說明插值器的內部原理:
//系統自帶的所有插值器都繼承了BaseInterpolator
public class AccelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mFactor;
private final double mDoubleFactor;
//無參數的構造方法, factor默認為1
public AccelerateInterpolator() {
mFactor = 1.0f;
mDoubleFactor = 2.0;
}
//有參數的構造方法
public AccelerateInterpolator(float factor) {
mFactor = factor;
mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor;
}
//構造方法,通過資源文件獲取參數
public AccelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context.getResources(), context.getTheme(), attrs);
}
/** @hide 隱藏方法,真正用來解析資源文件的方法*/
public AccelerateInterpolator(Resources res, Theme theme, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray a;
if (theme != null) {
a = theme.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator, 0, 0);
} else {
a = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator);
}
//資源文件未定義factor時,默認為1.0f
mFactor = a.getFloat(R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator_factor, 1.0f);
mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor;
setChangingConfiguration(a.getChangingConfigurations());
// 回收TypedArray,釋放相應的內存資源
a.recycle();
}
//插值計算的核心方法,定義了插值的映射關系
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
if (mFactor == 1.0f) {
return input * input;
} else {
return (float)Math.pow(input, mDoubleFactor);
}
}
/** @hide */
@Override
public long createNativeInterpolator() {
return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createAccelerateInterpolator(mFactor);
}
}
其中 BaseInterpolaor實現了Interpolator接口,而Interpolator接口並沒有定義任何方法和屬性,只是單純地繼承了TimeInterpolator
abstract public class BaseInterpolator implements Interpolator {
private int mChangingConfiguration;
/**
* @hide
*/
public int getChangingConfiguration() {
return mChangingConfiguration;
}
/**
* @hide
*/
void setChangingConfiguration(int changingConfiguration) {
mChangingConfiguration = changingConfiguration;
}
}
TimeInterpolator接口自定義了一個方法getInterpolation,這就是所有插值器最為核心的方法。
public interface TimeInterpolator {
/*
* @param input 代表動畫的已執行的時間,∈[0,1]
* @return 插值轉換後的值
*/
float getInterpolation(float input);
}
通過分析每一個插值器的插值方法的源碼,下面總結了所有插值器的插值函數:
public LinearInterpolator(); //沒有任何可調參數y=t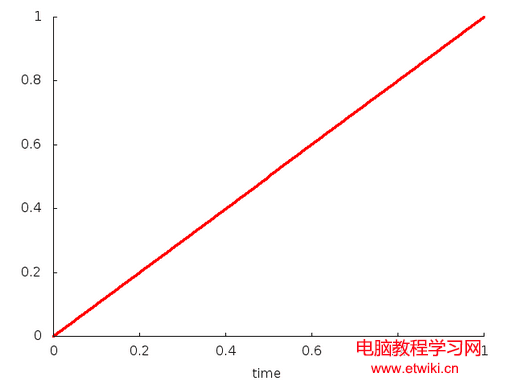
public AccelerateInterpolator();//默認factor=1public AccelerateInterpolator(float factor);public AccelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs); //通過資源文件獲取factor值,默認為1。y=t^(2f)y=t^2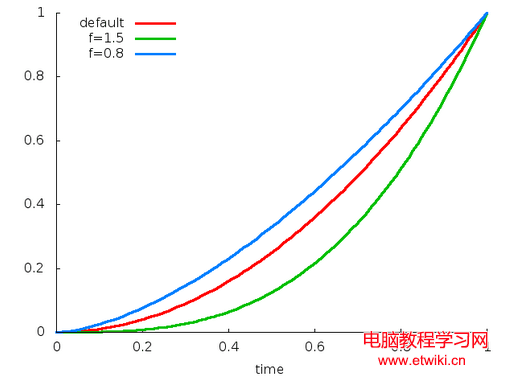
public AccelerateInterpolator();//默認factor=1public AccelerateInterpolator(float factor);public AccelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs); //通過資源文件獲取factor值,默認為1。y= 1-(1-t)^(2f),y= 2t-t^2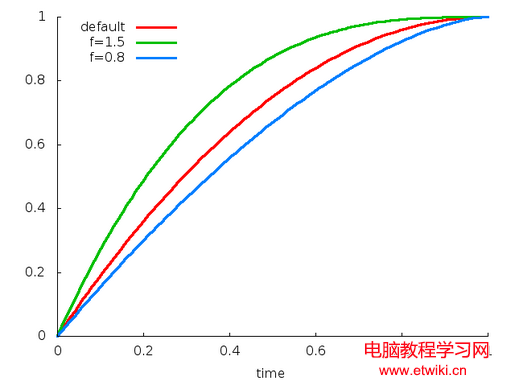
public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator(); //沒有任何可調參數 資源文件獲取factor值。y = 0.5cos((t+1)π)+0.5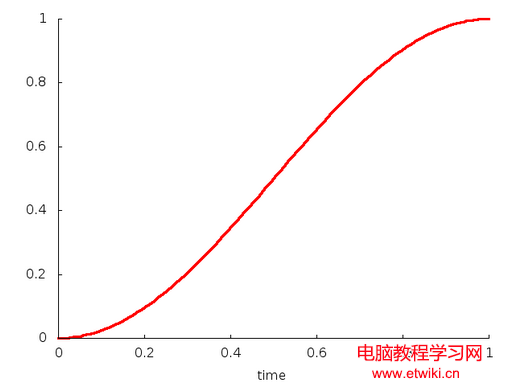
public AnticipateInterpolator();//默認tension=2public AnticipateInterpolator(float tension);public AnticipateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs); //通過資源文件獲取tension值。y = t*t*((s+1)t-s),y = t*t*(3t-2)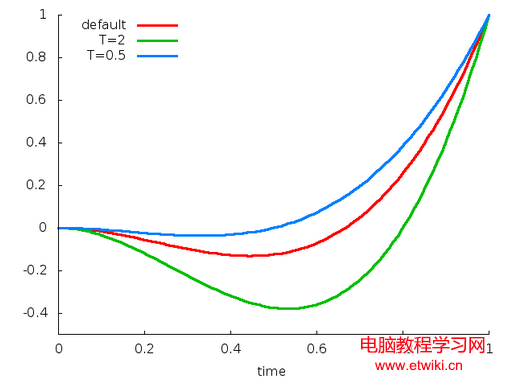
public OvershootInterpolator();//默認tension=2public OvershootInterpolator(float tension);public OvershootInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs); //通過資源文件獲取tension值。y = (t-1)(t-1)((s+1)(t-1)+s) + 1,y = (t-1)(t-1)(3t-1) + 1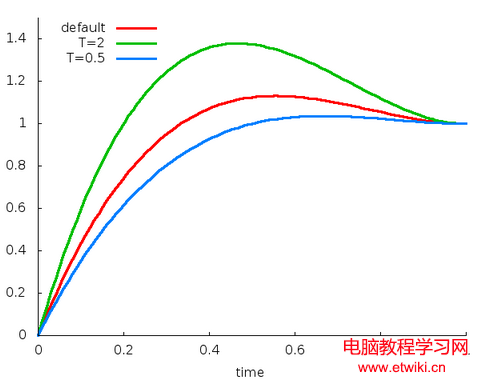
public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator();//默認tension=3public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(float tension); //tension = 1.5*tensionpublic AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(float tension, float extraTension); //tension = tension * extraTensionpublic AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs); //通過資源文件獲取tension值。y = 2t*t*(2t*s+2t-s), 當t < 0.5時,y = 2(t-1)(t-1)(2(s+1)(t-1)+s) + 1 , 當t >= 0.5時,y = 2t*t*(8t-3), 當t < 0.5時,y = 2(t-1)(t-1)(8t-5) + 1 , 當t >= 0.5時,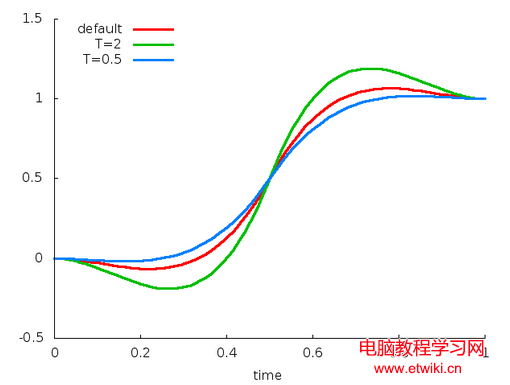
public BounceInterpolator();//沒有任何可調參數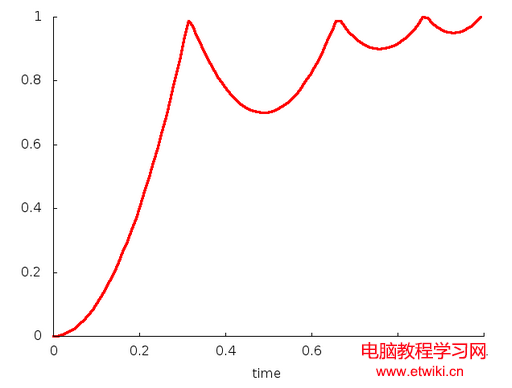
public CycleInterpolator(float cycles);public CycleInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs); //通過資源文件獲取cycles值,默認為1。y = sin(2*c*t*π),y = sin(2*t*π)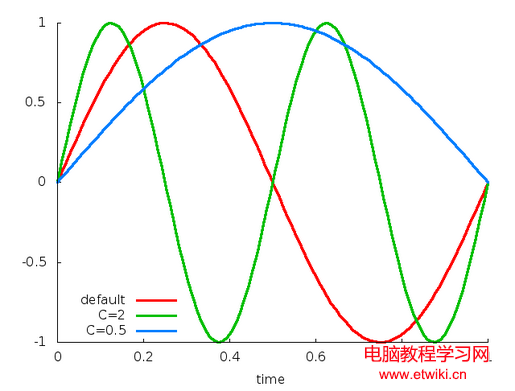
估值器,用於計算屬性動畫的給定屬性的取值,與屬性的起始值,結束值,fraction三個值相關。
每個估值器的源碼流程都相似,所有的估值器都實現了TypeEvaluator接口,接口采用泛型,可自定義各種類型的估值器,只需實現如下接口即可:
public interface TypeEvaluator<T> {
/*
*
* @param fraction 插值器計算轉換後的值
* @param startValue 屬性起始值
* @param endValue 屬性結束值
* @return 轉換後的值
*/
public T evaluate(float fraction, T startValue, T endValue);
}
用於評估Integer型的屬性值,起始值與結束值,以及evaluate返回值都是Integer類型。評估的返回值與fraction成一次函數,即線性關系。
public class IntEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<Integer> {
/**
* 函數關系:result = x0 + t * (x1 - x0)
*
* @param fraction
* @param startValue 屬性起始值,Integer類型
* @param endValue 屬性結束值,Integer類型
* @return 與fraction成線性關系。
*/
public Integer evaluate(float fraction, Integer startValue, Integer endValue) {
int startInt = startValue;
return (int)(startInt + fraction * (endValue - startInt));
}
}
用於評估Float型的屬性值,起始值與結束值,以及evaluate返回值都是Float類型,同樣也是線程關系。
public class FloatEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<Number> {
/**
* @param fraction
* @param startValue 屬性起始值,float類型
* @param endValue 屬性結束值,float類型
* @return 與fraction成線性關系。
*/
public Float evaluate(float fraction, Number startValue, Number endValue) {
float startFloat = startValue.floatValue();
return startFloat + fraction * (endValue.floatValue() - startFloat);
}
}
用於評估顏色的屬性值,采用16進制。將ARGB四個量,同步進行動畫漸變,同樣也是采用線性的。
public class ArgbEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator {
private static final ArgbEvaluator sInstance = new ArgbEvaluator();
/*
* @hide
* 貌似采用單例的方式,可該方法確實@hide隱藏方法,同時並沒有將構造方法定義為private。
* 意味著單例對於上層開發者來說是不可見的,這樣單例就沒有起效果,google難道只是為了framework
* 的單例使用,很詭異的設計。
*/
public static ArgbEvaluator getInstance() {
return sInstance;
}
public Object evaluate(float fraction, Object startValue, Object endValue) {
int startInt = (Integer) startValue;
int startA = (startInt >> 24) & 0xff;
int startR = (startInt >> 16) & 0xff;
int startG = (startInt >> 8) & 0xff;
int startB = startInt & 0xff;
int endInt = (Integer) endValue;
int endA = (endInt >> 24) & 0xff;
int endR = (endInt >> 16) & 0xff;
int endG = (endInt >> 8) & 0xff;
int endB = endInt & 0xff;
return (int)((startA + (int)(fraction * (endA - startA))) << 24) |
(int)((startR + (int)(fraction * (endR - startR))) << 16) |
(int)((startG + (int)(fraction * (endG - startG))) << 8) |
(int)((startB + (int)(fraction * (endB - startB))));
}
}
本文主要分兩部分,插值器與估值器。通過源碼方式概括性分析插值器的代碼實現方式;再從數學角度,逐一進行剖析系統自帶的9種插值器的插值函數以及其插值曲線。對於3種Evaluators,通過分析源碼,其方式較為簡單,需要注意的一點是evaluate中的fraction是插值器轉換後的值,而不是elapsed time。
 Android程序加入代碼混淆器
Android程序加入代碼混淆器
加入代碼混淆器,主要是加入proguard-project.txt文件的規則進行混淆,之前新建Android程序是proguard.cfg文件 可以看一下我采用的通用規則
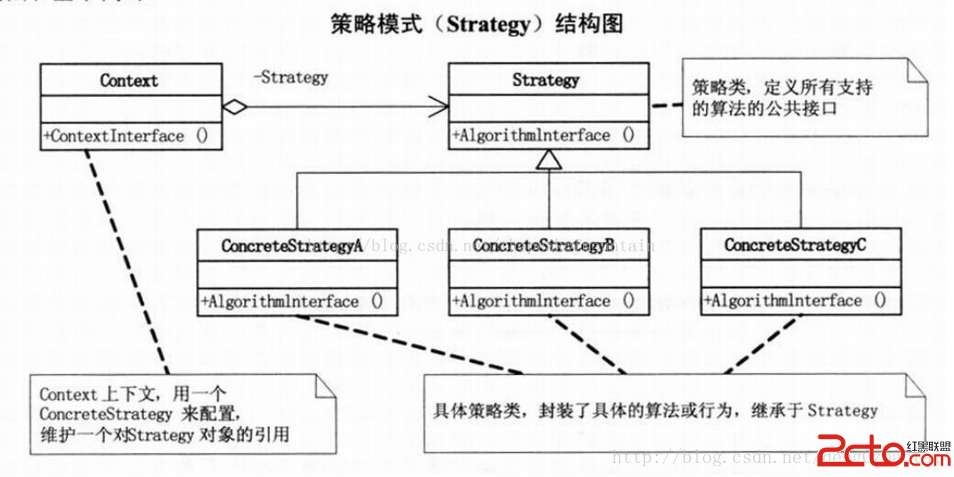 Android 設計模式之策略模式
Android 設計模式之策略模式
策略模式的定義:定義算法族,分別封裝起來,讓它們之間可以互相替換,此模式讓算法的變化獨立於使用算法的客戶。本質:分離算法,選擇實現 面向對象設計原則: 封裝變化 多用組合
 android studio中斷開SVN連接,並徹底清理項目中的.svn文件
android studio中斷開SVN連接,並徹底清理項目中的.svn文件
android studio中斷開SVN連接,並徹底清理項目中的.svn文件。如何斷開SVN的連接。在使用SVN過程中,我們會發現當我們第一次share到subversi
 緩存之 ACache
緩存之 ACache
1.android緩存的介紹Android開發本質上就是手機和互聯網中的web服務器之間進行通信,就必然需要從服務端獲取數據,而反復通過網絡獲取數據是比較耗時的,特別是訪