編輯:關於Android編程
VR即Virtual Reality虛擬現實。虛擬現實技術是一種可以創建和體驗虛擬世界的計算機仿真系統它利用計算機生成一種模擬環境是一種多源信息融合的交互式的三維動態視景和實體行為的系統仿真使用戶沉浸到該環境中。
那麼,如何在Android中去開發VR功能的APP呢?我們利用谷歌提供的開源SDK去實現一個360°全景游戲的功能。接下來主要是針對谷歌提供的開發VR的SDK中的游戲例子進行翻譯。
CardBoard:卡紙板,google早期推出的VR 開發集合,封裝修改了Activity,GLSurfaceView 以及 Render等標准類的一層API,其中具體細致的實現封在so庫中,用戶使用CardBoard提供的jar包以及so,按照API的規則使用OPENGL實現特定函數即可開發VR程序
DayDream:白日夢,在CardBoard基礎上的專業版,實現了更多的VR特性功能,如3D音效,全景視圖,全景視頻播放,控制器,封裝的API和so也相應的增多,API更加有結構模塊化。
TreasureHunt游戲場景包括一個平面接地網格和一個浮動 “寶藏”多維數據集。 當用戶觀看立方體時,立方體將變成金色。 用戶可以直接激活Cardboard觸發器在其Cardboard查看器上使用觸摸觸發器,或使用白日夢基於控制器的觸發器仿真。 然後激活觸發器,點擊尋找寶藏,寶藏消失後隨機重新定位立方體。
minSdkVersion 19 targetSdkVersion 25
/**
* 將視圖設置為我們的GvrView並初始化我們將用於渲染我們的場景的轉換矩陣。
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
initializeGvrView();
modelCube = new float[16];
camera = new float[16];
view = new float[16];
modelViewProjection = new float[16];
modelView = new float[16];
modelFloor = new float[16];
tempPosition = new float[4];
// Model first appears directly in front of user.
modelPosition = new float[]{0.0f, 0.0f, -MAX_MODEL_DISTANCE / 2.0f};
headRotation = new float[4];
headView = new float[16];
vibrator = (Vibrator) getSystemService(Context.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
// Initialize 3D audio engine.
gvrAudioEngine = new GvrAudioEngine(this, GvrAudioEngine.RenderingMode.BINAURAL_HIGH_QUALITY);
}
/**
* 初始化VR顯示界面
*/
public void initializeGvrView() {
setContentView(R.layout.common_ui);
GvrView gvrView = (GvrView) findViewById(R.id.gvr_view);
gvrView.setEGLConfigChooser(8, 8, 8, 8, 16, 8);
/**設置渲染器**/
gvrView.setRenderer(this);
gvrView.setTransitionViewEnabled(true);
/**使用Daydream耳機啟用Cardboard觸發反饋。
* 這是一種使用現有Cardboard觸發器API支持Daydream控制器輸入進行基本交互的簡單方法。**/
gvrView.enableCardboardTriggerEmulation();
if (gvrView.setAsyncReprojectionEnabled(true)) {
/**異步投影,沉浸式,性能模式**/
AndroidCompat.setSustainedPerformanceMode(this, true);
}
setGvrView(gvrView);
}
@Override
public void onPause() {
gvrAudioEngine.pause();
super.onPause();
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
gvrAudioEngine.resume();
}
@Override
public void onRendererShutdown() {
Log.i(TAG, "onRendererShutdown");
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(int width, int height) {
Log.i(TAG, "onSurfaceChanged");
}
/**
* 創建用於存儲有關3D界面的信息的緩沖區。
* <p>
* </p><p>OpenGL不使用Java數組,而是需要可以理解的格式的數據。 因此我們使用ByteBuffers。
*
* @param config The EGL configuration used when creating the surface.
*/
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(EGLConfig config) {
Log.i(TAG, "onSurfaceCreated");
GLES20.glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 0.5f); // Dark background so text shows up well.
ByteBuffer bbVertices = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COORDS.length * 4);
bbVertices.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeVertices = bbVertices.asFloatBuffer();
cubeVertices.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COORDS);
cubeVertices.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbColors = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COLORS.length * 4);
bbColors.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeColors = bbColors.asFloatBuffer();
cubeColors.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COLORS);
cubeColors.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbFoundColors =
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_FOUND_COLORS.length * 4);
bbFoundColors.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeFoundColors = bbFoundColors.asFloatBuffer();
cubeFoundColors.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_FOUND_COLORS);
cubeFoundColors.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbNormals = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_NORMALS.length * 4);
bbNormals.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeNormals = bbNormals.asFloatBuffer();
cubeNormals.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_NORMALS);
cubeNormals.position(0);
// make a floor
ByteBuffer bbFloorVertices = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COORDS.length * 4);
bbFloorVertices.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
floorVertices = bbFloorVertices.asFloatBuffer();
floorVertices.put(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COORDS);
floorVertices.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbFloorNormals = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_NORMALS.length * 4);
bbFloorNormals.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
floorNormals = bbFloorNormals.asFloatBuffer();
floorNormals.put(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_NORMALS);
floorNormals.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbFloorColors = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COLORS.length * 4);
bbFloorColors.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
floorColors = bbFloorColors.asFloatBuffer();
floorColors.put(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COLORS);
floorColors.position(0);
int vertexShader = loadGLShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, R.raw.light_vertex);
int gridShader = loadGLShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, R.raw.grid_fragment);
int passthroughShader = loadGLShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, R.raw.passthrough_fragment);
cubeProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(cubeProgram, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(cubeProgram, passthroughShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(cubeProgram);
GLES20.glUseProgram(cubeProgram);
checkGLError("Cube program");
cubePositionParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(cubeProgram, "a_Position");
cubeNormalParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(cubeProgram, "a_Normal");
cubeColorParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(cubeProgram, "a_Color");
cubeModelParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_Model");
cubeModelViewParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_MVMatrix");
cubeModelViewProjectionParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_MVP");
cubeLightPosParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_LightPos");
checkGLError("Cube program params");
floorProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(floorProgram, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(floorProgram, gridShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(floorProgram);
GLES20.glUseProgram(floorProgram);
checkGLError("Floor program");
floorModelParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_Model");
floorModelViewParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_MVMatrix");
floorModelViewProjectionParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_MVP");
floorLightPosParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_LightPos");
floorPositionParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(floorProgram, "a_Position");
floorNormalParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(floorProgram, "a_Normal");
floorColorParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(floorProgram, "a_Color");
checkGLError("Floor program params");
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelFloor, 0);
Matrix.translateM(modelFloor, 0, 0, -floorDepth, 0); // Floor appears below user.
// Avoid any delays during start-up due to decoding of sound files.
new Thread(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Start spatial audio playback of OBJECT_SOUND_FILE at the model position. The
// returned sourceId handle is stored and allows for repositioning the sound object
// whenever the cube position changes.
gvrAudioEngine.preloadSoundFile(OBJECT_SOUND_FILE);
sourceId = gvrAudioEngine.createSoundObject(OBJECT_SOUND_FILE);
gvrAudioEngine.setSoundObjectPosition(
sourceId, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
gvrAudioEngine.playSound(sourceId, true /* looped playback */);
// Preload an unspatialized sound to be played on a successful trigger on the cube.
gvrAudioEngine.preloadSoundFile(SUCCESS_SOUND_FILE);
}
})
.start();
updateModelPosition();
checkGLError("onSurfaceCreated");
}
/**
* 將保存為資源的原始文本文件轉換為OpenGL ES著色器。
*
* @param type The type of shader we will be creating.
* @param resId The resource ID of the raw text file about to be turned into a shader.
* @return The shader object handler.
*/
private int loadGLShader(int type, int resId) {
String code = readRawTextFile(resId);
int shader = GLES20.glCreateShader(type);
GLES20.glShaderSource(shader, code);
GLES20.glCompileShader(shader);
// Get the compilation status.
final int[] compileStatus = new int[1];
GLES20.glGetShaderiv(shader, GLES20.GL_COMPILE_STATUS, compileStatus, 0);
// If the compilation failed, delete the shader.
if (compileStatus[0] == 0) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error compiling shader: " + GLES20.glGetShaderInfoLog(shader));
GLES20.glDeleteShader(shader);
shader = 0;
}
if (shader == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error creating shader.");
}
return shader;
}
/**
* 檢查我們在OpenGL ES中是否有錯誤,如果有錯誤查看錯誤。
*
* @param label Label to report in case of error.
*/
private static void checkGLError(String label) {
int error;
while ((error = GLES20.glGetError()) != GLES20.GL_NO_ERROR) {
Log.e(TAG, label + ": glError " + error);
throw new RuntimeException(label + ": glError " + error);
}
}
/**
* 更新立方體的位置。
*/
protected void updateModelPosition() {
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelCube, 0);
Matrix.translateM(modelCube, 0, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
// Update the sound location to match it with the new cube position.
if (sourceId != GvrAudioEngine.INVALID_ID) {
gvrAudioEngine.setSoundObjectPosition(
sourceId, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
}
checkGLError("updateCubePosition");
}
/**
* 將原始文本文件轉換為字符串。
*
* @param resId 要轉換為著色器的原始文本文件的資源ID。
* @return 文本文件的上下文,或者在出現錯誤的情況下為null。
*/
private String readRawTextFile(int resId) {
InputStream inputStream = getResources().openRawResource(resId);
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line).append("\n");
}
reader.close();
return sb.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 在繪制視圖之前准備OpenGL ES。
*
* @param headTransform 新幀中的頭變換。
*/
@Override
public void onNewFrame(HeadTransform headTransform) {
setCubeRotation();
// Build the camera matrix and apply it to the ModelView.
Matrix.setLookAtM(camera, 0, 0.0f, 0.0f, CAMERA_Z, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
headTransform.getHeadView(headView, 0);
// Update the 3d audio engine with the most recent head rotation.
headTransform.getQuaternion(headRotation, 0);
gvrAudioEngine.setHeadRotation(
headRotation[0], headRotation[1], headRotation[2], headRotation[3]);
// Regular update call to GVR audio engine.
gvrAudioEngine.update();
checkGLError("onReadyToDraw");
}
/**
* 設置立方體旋轉矩陣
*/
protected void setCubeRotation() {
Matrix.rotateM(modelCube, 0, TIME_DELTA, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f);
}
/**
* 為我們的視野畫每一幀圖。
*
* @param eye 視圖呈現。 包括所有必需的轉換。
*/
@Override
public void onDrawEye(Eye eye) {
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
checkGLError("colorParam");
// Apply the eye transformation to the camera.
Matrix.multiplyMM(view, 0, eye.getEyeView(), 0, camera, 0);
// Set the position of the light
Matrix.multiplyMV(lightPosInEyeSpace, 0, view, 0, LIGHT_POS_IN_WORLD_SPACE, 0);
// Build the ModelView and ModelViewProjection matrices
// for calculating cube position and light.
float[] perspective = eye.getPerspective(Z_NEAR, Z_FAR);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelView, 0, view, 0, modelCube, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjection, 0, perspective, 0, modelView, 0);
drawCube();
// Set modelView for the floor, so we draw floor in the correct location
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelView, 0, view, 0, modelFloor, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjection, 0, perspective, 0, modelView, 0);
drawFloor();
}
@Override
public void onFinishFrame(Viewport viewport) {
}
/**
* 繪制立方體。
* </p><p>
* </p><p>設置了所有的轉換矩陣。簡單地將它們傳遞給著色器。
*/
public void drawCube() {
GLES20.glUseProgram(cubeProgram);
GLES20.glUniform3fv(cubeLightPosParam, 1, lightPosInEyeSpace, 0);
// Set the Model in the shader, used to calculate lighting
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(cubeModelParam, 1, false, modelCube, 0);
// Set the ModelView in the shader, used to calculate lighting
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(cubeModelViewParam, 1, false, modelView, 0);
// Set the position of the cube
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
cubePositionParam, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, cubeVertices);
// Set the ModelViewProjection matrix in the shader.
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(cubeModelViewProjectionParam, 1, false, modelViewProjection, 0);
// Set the normal positions of the cube, again for shading
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(cubeNormalParam, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, cubeNormals);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(cubeColorParam, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0,
isLookingAtObject() ? cubeFoundColors : cubeColors);
// Enable vertex arrays
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(cubePositionParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(cubeNormalParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(cubeColorParam);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
// Disable vertex arrays
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(cubePositionParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(cubeNormalParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(cubeColorParam);
checkGLError("Drawing cube");
}
/**
* 畫地板。
* </p><p>
* </p><p>這將底層的數據饋入著色器。 注意,這不會輸入關於燈的位置的數據,因此,如果我們重寫我們的代碼來繪制地板,照明可能
* 看起來很奇怪。
*/
public void drawFloor() {
GLES20.glUseProgram(floorProgram);
// Set ModelView, MVP, position, normals, and color.
GLES20.glUniform3fv(floorLightPosParam, 1, lightPosInEyeSpace, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(floorModelParam, 1, false, modelFloor, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(floorModelViewParam, 1, false, modelView, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(floorModelViewProjectionParam, 1, false, modelViewProjection, 0);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
floorPositionParam, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, floorVertices);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(floorNormalParam, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, floorNormals);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(floorColorParam, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, floorColors);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(floorPositionParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(floorNormalParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(floorColorParam);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 24);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(floorPositionParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(floorNormalParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(floorColorParam);
checkGLError("drawing floor");
}
/**
* 當點擊或拉動Cardboard觸發器時調用。
*/
@Override
public void onCardboardTrigger() {
Log.i(TAG, "onCardboardTrigger");
if (isLookingAtObject()) {
successSourceId = gvrAudioEngine.createStereoSound(SUCCESS_SOUND_FILE);
gvrAudioEngine.playSound(successSourceId, false /* looping disabled */);
hideObject();
}
// Always give user feedback.
vibrator.vibrate(50);
}
/**
* 方法作用:隱藏物體即為對象找到一個新的隨機位置。
* </p><p>
* 方法說明:我們將圍繞Y軸旋轉它,使它看不見,然後向上或向下一點點。
*/
protected void hideObject() {
float[] rotationMatrix = new float[16];
float[] posVec = new float[4];
// First rotate in XZ plane, between 90 and 270 deg away, and scale so that we vary
// the object's distance from the user.
float angleXZ = (float) Math.random() * 180 + 90;
Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, angleXZ, 0f, 1f, 0f);
float oldObjectDistance = objectDistance;
objectDistance =
(float) Math.random() * (MAX_MODEL_DISTANCE - MIN_MODEL_DISTANCE) + MIN_MODEL_DISTANCE;
float objectScalingFactor = objectDistance / oldObjectDistance;
Matrix.scaleM(rotationMatrix, 0, objectScalingFactor, objectScalingFactor, objectScalingFactor);
Matrix.multiplyMV(posVec, 0, rotationMatrix, 0, modelCube, 12);
float angleY = (float) Math.random() * 80 - 40; // Angle in Y plane, between -40 and 40.
angleY = (float) Math.toRadians(angleY);
float newY = (float) Math.tan(angleY) * objectDistance;
modelPosition[0] = posVec[0];
modelPosition[1] = newY;
modelPosition[2] = posVec[2];
updateModelPosition();
}
/**
* 通過計算對象在眼睛空間中的位置來檢查用戶是否正在查看對象。
*
* @return 如果用戶正在查看對象,則為true。
*/
private boolean isLookingAtObject() {
// Convert object space to camera space. Use the headView from onNewFrame.
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelView, 0, headView, 0, modelCube, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMV(tempPosition, 0, modelView, 0, POS_MATRIX_MULTIPLY_VEC, 0);
float pitch = (float) Math.atan2(tempPosition[1], -tempPosition[2]);
float yaw = (float) Math.atan2(tempPosition[0], -tempPosition[2]);
return Math.abs(pitch) < PITCH_LIMIT && Math.abs(yaw) < YAW_LIMIT;
}</p>
 Android編程實現ActionBar的home圖標動畫切換效果
Android編程實現ActionBar的home圖標動畫切換效果
本文實例講述了Android編程實現ActionBar的home圖標動畫切換效果。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:Material Design中一個重要特性是側滑菜單
 Android程序開發之ListView實現橫向滾動(帶表頭與固定列)
Android程序開發之ListView實現橫向滾動(帶表頭與固定列)
問題背景:在做圖表展示的時候,ListView可以上下左右滑動,但最左邊一列在向右滑動時,保持不變,表頭在向下滑動時保持不變。有用兩個ListView實現的,但測試過,好
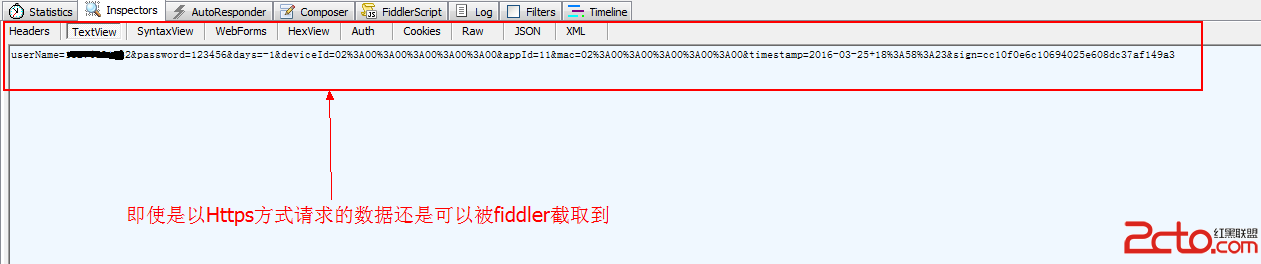 我的Android進階之旅------)Android采用AES+RSA的加密機制對http請求進行加密
我的Android進階之旅------)Android采用AES+RSA的加密機制對http請求進行加密
前言 最近維護公司APP應用的登錄模塊,由於測試人員用Fiddler抓包工具抓取到了公司關於登錄時候的明文登錄信息。雖然使用的是HTTPS的方式進行http請求的,但還是
 詳解Android中Service服務的基礎知識及編寫方法
詳解Android中Service服務的基礎知識及編寫方法
首先,讓我們確認下什麼是service? service就是android系統中的服務