編輯:關於Android編程
Android的ion(二):今天來看一下kernel裡面的ion的實現,首先知道的是system/libion下的實現都是通過ion_ioctl系統調用進入kernel裡面的,下面來看一下系統調用進入kernel裡面的處理流程。
static long ion_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct ion_client *client = filp->private_data;
struct ion_device *dev = client->dev;
struct ion_handle *cleanup_handle = NULL;
int ret = 0;
unsigned int dir;
union {
struct ion_fd_data fd;
struct ion_allocation_data allocation;
struct ion_handle_data handle;
struct ion_custom_data custom;
} data;
dir = ion_ioctl_dir(cmd);
if (_IOC_SIZE(cmd) > sizeof(data))
return -EINVAL;
if (dir & _IOC_WRITE)
if (copy_from_user(&data, (void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd)))
return -EFAULT;
switch (cmd) {
case ION_IOC_ALLOC:
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
handle = ion_alloc(client, data.allocation.len,
data.allocation.align,
data.allocation.heap_id_mask,
data.allocation.flags);
if (IS_ERR(handle))
return PTR_ERR(handle);
data.allocation.handle = handle->id;
cleanup_handle = handle;
break;
}
case ION_IOC_FREE:
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
handle = ion_handle_get_by_id(client, data.handle.handle);
if (IS_ERR(handle))
return PTR_ERR(handle);
ion_free(client, handle);
ion_handle_put(handle);
break;
}
case ION_IOC_SHARE:
case ION_IOC_MAP:
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
handle = ion_handle_get_by_id(client, data.handle.handle);
if (IS_ERR(handle))
return PTR_ERR(handle);
data.fd.fd = ion_share_dma_buf_fd(client, handle);
ion_handle_put(handle);
if (data.fd.fd < 0)
ret = data.fd.fd;
break;
}
case ION_IOC_IMPORT:
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
handle = ion_import_dma_buf(client, data.fd.fd);
if (IS_ERR(handle))
ret = PTR_ERR(handle);
else
data.handle.handle = handle->id;
break;
}
case ION_IOC_SYNC:
{
ret = ion_sync_for_device(client, data.fd.fd);
break;
}
case ION_IOC_CUSTOM:
{
if (!dev->custom_ioctl)
return -ENOTTY;
ret = dev->custom_ioctl(client, data.custom.cmd,
data.custom.arg);
break;
}
case ION_IOC_CLEAN_CACHES:
return client->dev->custom_ioctl(client,
ION_IOC_CLEAN_CACHES, arg);
case ION_IOC_INV_CACHES:
return client->dev->custom_ioctl(client,
ION_IOC_INV_CACHES, arg);
case ION_IOC_CLEAN_INV_CACHES:
return client->dev->custom_ioctl(client,
ION_IOC_CLEAN_INV_CACHES, arg);
default:
return -ENOTTY;
}
if (dir & _IOC_READ) {
if (copy_to_user((void __user *)arg, &data, _IOC_SIZE(cmd))) {
if (cleanup_handle)
ion_free(client, cleanup_handle);
return -EFAULT;
}
}
return ret;
}
首先通過copy_from_user將用戶空間的數據轉遞到kernel裡面,然後根據cmd分別進行處理。
首先來看cmd為ION_IOC_ALLOC的,此cmd為分配內存的,詳見源碼:
case ION_IOC_ALLOC:
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
handle = ion_alloc(client, data.allocation.len,
data.allocation.align,
data.allocation.heap_id_mask,
data.allocation.flags);
if (IS_ERR(handle))
return PTR_ERR(handle);
data.allocation.handle = handle->id;
cleanup_handle = handle;
break;
}
可以看到的是通過ion_alloc來分配內存,
struct ion_handle *ion_alloc(struct ion_client *client, size_t len,
size_t align, unsigned int heap_id_mask,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
struct ion_device *dev = client->dev;
struct ion_buffer *buffer = NULL;
struct ion_heap *heap;
int ret;
unsigned long secure_allocation = flags & ION_FLAG_SECURE;
const unsigned int MAX_DBG_STR_LEN = 64;
char dbg_str[MAX_DBG_STR_LEN];
unsigned int dbg_str_idx = 0;
dbg_str[0] = '\0';
/*
* For now, we don't want to fault in pages individually since
* clients are already doing manual cache maintenance. In
* other words, the implicit caching infrastructure is in
* place (in code) but should not be used.
*/
flags |= ION_FLAG_CACHED_NEEDS_SYNC;
pr_debug("%s: len %zu align %zu heap_id_mask %u flags %x\n", __func__,
len, align, heap_id_mask, flags);
/*
* traverse the list of heaps available in this system in priority
* order. If the heap type is supported by the client, and matches the
* request of the caller allocate from it. Repeat until allocate has
* succeeded or all heaps have been tried
*/
len = PAGE_ALIGN(len);
if (!len)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
down_read(&dev->lock);
plist_for_each_entry(heap, &dev->heaps, node) {
/* if the caller didn't specify this heap id */
if (!((1 << heap->id) & heap_id_mask))
continue;
/* Do not allow un-secure heap if secure is specified */
if (secure_allocation &&
!ion_heap_allow_secure_allocation(heap->type))
continue;
trace_ion_alloc_buffer_start(client->name, heap->name, len,
heap_id_mask, flags);
buffer = ion_buffer_create(heap, dev, len, align, flags);
trace_ion_alloc_buffer_end(client->name, heap->name, len,
heap_id_mask, flags);
if (!IS_ERR(buffer))
break;
trace_ion_alloc_buffer_fallback(client->name, heap->name, len,
heap_id_mask, flags,
PTR_ERR(buffer));
if (dbg_str_idx < MAX_DBG_STR_LEN) {
unsigned int len_left = MAX_DBG_STR_LEN-dbg_str_idx-1;
int ret_value = snprintf(&dbg_str[dbg_str_idx],
len_left, "%s ", heap->name);
if (ret_value >= len_left) {
/* overflow */
dbg_str[MAX_DBG_STR_LEN-1] = '\0';
dbg_str_idx = MAX_DBG_STR_LEN;
} else if (ret_value >= 0) {
dbg_str_idx += ret_value;
} else {
/* error */
dbg_str[MAX_DBG_STR_LEN-1] = '\0';
}
}
}
up_read(&dev->lock);
if (buffer == NULL) {
trace_ion_alloc_buffer_fail(client->name, dbg_str, len,
heap_id_mask, flags, -ENODEV);
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
}
if (IS_ERR(buffer)) {
trace_ion_alloc_buffer_fail(client->name, dbg_str, len,
heap_id_mask, flags,
PTR_ERR(buffer));
pr_debug("ION is unable to allocate 0x%zx bytes (alignment: 0x%zx) from heap(s) %sfor client %s\n",
len, align, dbg_str, client->name);
return ERR_PTR(PTR_ERR(buffer));
}
handle = ion_handle_create(client, buffer);
/*
* ion_buffer_create will create a buffer with a ref_cnt of 1,
* and ion_handle_create will take a second reference, drop one here
*/
ion_buffer_put(buffer);
if (IS_ERR(handle))
return handle;
mutex_lock(&client->lock);
ret = ion_handle_add(client, handle);
mutex_unlock(&client->lock);
if (ret) {
ion_handle_put(handle);
handle = ERR_PTR(ret);
}
return handle;
}
主要的工作是先是遍歷heap鏈表,然後符合條件的才會去通過ion_buffer_create創建buffer,然後通過ion_handle_create來創建對應的handle來管理buffer。
首先可以看到是通過ion_buffer_create來創建buffer的:
/* this function should only be called while dev->lock is held */
static struct ion_buffer *ion_buffer_create(struct ion_heap *heap,
struct ion_device *dev,
unsigned long len,
unsigned long align,
unsigned long flags)
{
struct ion_buffer *buffer;
struct sg_table *table;
struct scatterlist *sg;
int i, ret;
buffer = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ion_buffer), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!buffer)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
buffer->heap = heap;
buffer->flags = flags;
kref_init(&buffer->ref);
ret = heap->ops->allocate(heap, buffer, len, align, flags);
if (ret) {
if (!(heap->flags & ION_HEAP_FLAG_DEFER_FREE))
goto err2;
ion_heap_freelist_drain(heap, 0);
ret = heap->ops->allocate(heap, buffer, len, align,
flags);
if (ret)
goto err2;
}
buffer->dev = dev;
buffer->size = len;
buffer->flags = flags;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&buffer->vmas);
table = heap->ops->map_dma(heap, buffer);
if (WARN_ONCE(table == NULL,
"heap->ops->map_dma should return ERR_PTR on error"))
table = ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if (IS_ERR(table)) {
heap->ops->free(buffer);
kfree(buffer);
return ERR_PTR(PTR_ERR(table));
}
buffer->sg_table = table;
if (ion_buffer_fault_user_mappings(buffer)) {
int num_pages = PAGE_ALIGN(buffer->size) / PAGE_SIZE;
struct scatterlist *sg;
int i, j, k = 0;
buffer->pages = vmalloc(sizeof(struct page *) * num_pages);
if (!buffer->pages) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err1;
}
for_each_sg(table->sgl, sg, table->nents, i) {
struct page *page = sg_page(sg);
for (j = 0; j < sg->length / PAGE_SIZE; j++)
buffer->pages[k++] = page++;
}
if (ret)
goto err;
}
mutex_init(&buffer->lock);
/* this will set up dma addresses for the sglist -- it is not
technically correct as per the dma api -- a specific
device isn't really taking ownership here. However, in practice on
our systems the only dma_address space is physical addresses.
Additionally, we can't afford the overhead of invalidating every
allocation via dma_map_sg. The implicit contract here is that
memory comming from the heaps is ready for dma, ie if it has a
cached mapping that mapping has been invalidated */
for_each_sg(buffer->sg_table->sgl, sg, buffer->sg_table->nents, i) {
if (sg_dma_address(sg) == 0)
sg_dma_address(sg) = sg_phys(sg);
}
mutex_lock(&dev->buffer_lock);
ion_buffer_add(dev, buffer);
mutex_unlock(&dev->buffer_lock);
atomic_add(len, &heap->total_allocated);
return buffer;
err:
heap->ops->unmap_dma(heap, buffer);
heap->ops->free(buffer);
err1:
if (buffer->pages)
vfree(buffer->pages);
err2:
kfree(buffer);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
在ion_buffer_create中可以看到的是首先調用kzalloc來申請一個內存,然後會發現其所申請的內存都被初始化過,在接下來根據不同的heap來調用其allocate方法,最後將申請到的buffer都放到設備數下進行管理。
接著使用ion_handle_create來創建一個handle,然後將client和buffer都和handle綁定起來。
static struct ion_handle *ion_handle_create(struct ion_client *client,
struct ion_buffer *buffer)
{
struct ion_handle *handle;
handle = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ion_handle), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!handle)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
kref_init(&handle->ref);
RB_CLEAR_NODE(&handle->node);
handle->client = client;
ion_buffer_get(buffer);
ion_buffer_add_to_handle(buffer);
handle->buffer = buffer;
return handle;
}
具體分配內存的工作是放在對應的heap對應的allocate中的:
static int ion_carveout_heap_allocate(struct ion_heap *heap,
struct ion_buffer *buffer,
unsigned long size, unsigned long align,
unsigned long flags)
{
buffer->priv_phys = ion_carveout_allocate(heap, size, align);
return buffer->priv_phys == ION_CARVEOUT_ALLOCATE_FAIL ? -ENOMEM : 0;
}
ion_carveout_heap_allocate還是通過調用ion_carveout_allocate來實現的:
ion_phys_addr_t ion_carveout_allocate(struct ion_heap *heap,
unsigned long size,
unsigned long align)
{
struct ion_carveout_heap *carveout_heap =
container_of(heap, struct ion_carveout_heap, heap);
unsigned long offset = gen_pool_alloc_aligned(carveout_heap->pool,
size, ilog2(align));
if (!offset) {
if ((carveout_heap->total_size -
carveout_heap->allocated_bytes) >= size)
pr_debug("%s: heap %s has enough memory (%lx) but"
" the allocation of size %lx still failed."
" Memory is probably fragmented.",
__func__, heap->name,
carveout_heap->total_size -
carveout_heap->allocated_bytes, size);
return ION_CARVEOUT_ALLOCATE_FAIL;
}
carveout_heap->allocated_bytes += size;
return offset;
}
這裡可以看出,其實buffer之前已經預留了一塊,只要上去取出buffer來就行,然後還要將取出的buffer記錄一下。
 Android Studio 1.5.1 JNI 編程
Android Studio 1.5.1 JNI 編程
1. 新建project MyJNI,使用默認設置即可。2. 新建Test類:右鍵com.example.myjni新建java類3. 在Test類中編寫如下代碼,loa
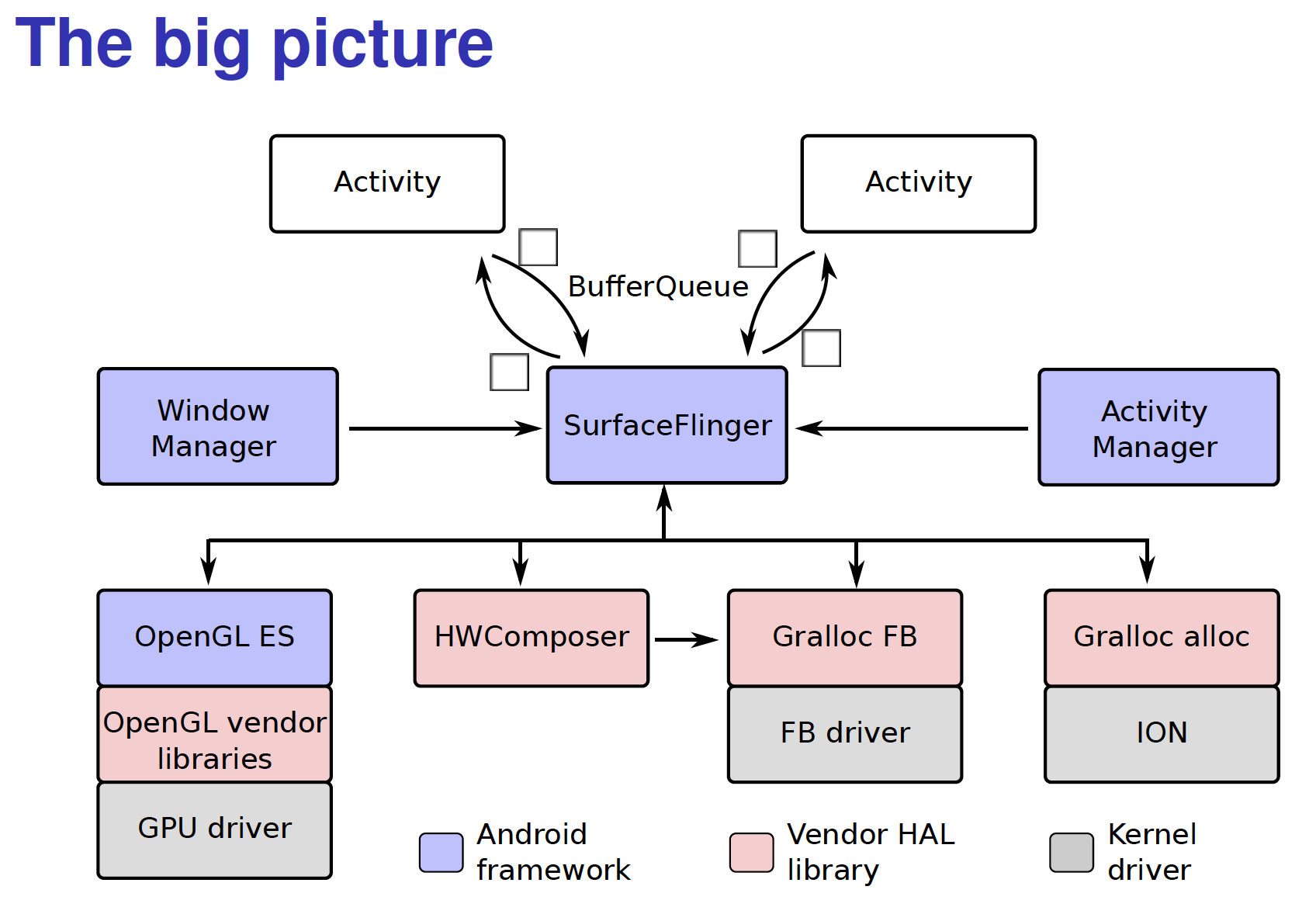 Android graphic path
Android graphic path
UI的畫圖流程中,先不管怎麼填充要畫的數據的,只是來看一下需要畫到屏幕上的數據是通過怎樣的流程最終傳遞到屏幕上的。這個流程都是UI獲取並創建Surface並利用Cavan
 Android開發中利用imeOptions屬性將鍵盤回車鍵改成搜索等功能鍵
Android開發中利用imeOptions屬性將鍵盤回車鍵改成搜索等功能鍵
Android中鍵盤輸入是用戶輸入交互的最常用最直接的手段,關於鍵盤輸入,有幾點可以提高用戶使用體驗。第一:彈出鍵盤整體頁面上移,使鍵盤不遮擋控件,需要在AndroidM
 android 視頻錄制 保存到本地
android 視頻錄制 保存到本地
下面貼一下 主要的代碼 詳細/************************************************************ * * Ease