編輯:關於Android編程
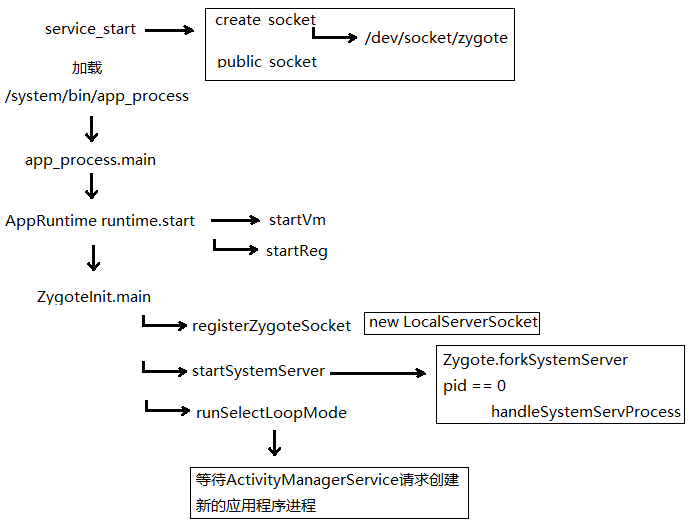
這張圖簡單說明了Zygote的啟動過程
下面重點解析這些函數,從app_process.main開始
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
...
// These are global variables in ProcessState.cpp
mArgC = argc;
mArgV = argv;
mArgLen = 0;
for (int i=0; i<argc; marglen="" appruntime="" const="" argv0="argv[0];" process="" command="" line="" arguments="" ignore="" everything="" up="" to="" or="" first="" non="" arg="" goes="" the="" vm="" int="" i="" parse="" runtime="" arguments.="" stop="" at="" unrecognized="" option.="" bool="" zygote="false;" startsystemserver="false;" application="false;" parentdir="NULL;" nicename="NULL;" classname="NULL;" while="" if="" else="" --nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName = arg + 12;
} else {
className = arg;
break;
}
}
if (niceName && *niceName) {
setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
set_process_name(niceName);
}
runtime.mParentDir = parentDir;
if (zygote) {
//這個start函數來自AppRuntime的父類
//AndroidRuntime
runtime.start(" :="" remainder="" of="" args="" get="" passed="" startup="" class="" runtime.mclassname="className;" runtime.margc="argc" -="" runtime.margv="argv" error:="" no="" name="" --zygote="" app_process:="" return="" pre="">
重點在start函數
這個函數在之前不止一次遇到過
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
{
...
/* start the virtual machine */
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
...
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}前面是創建第一個虛擬機實例並且注冊JNI函數,然後執行className.main函數
這個className是com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
registerZygoteSocket();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc();
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
// If requested, start system server directly from Zygote
if (argv.length != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
startSystemServer();
} else if (!argv[1].equals("")) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
runSelectLoop();
closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}主要內容有三個,registerZygoteSocket函數創建一個Server端Socket,用來接受AMS的創建進程請求
startSystemServer用來啟動System進程
runSelectLoopMode等待AMS請求創建進程
private static void registerZygoteSocket() {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
try {
//ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV = "ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote"
String env = System.getenv(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV);
//轉化為文件描述符
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(
createFileDescriptor(fileDesc));
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}sServerSocket是ZygoteInit的一個靜態成員,用於保存創建的server socket
成功之後繼續執行startSystemServer來啟動SystemServer
private static boolean startSystemServer()
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007",
"--capabilities=130104352,130104352",
"--runtime-init",
"--nice-name=system_server",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}這個SystemServer通過forkSystemServer創建,在SystemServer進程中執行的是handleSystemServerProcess
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
closeServerSocket();
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Libcore.os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
null, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
}
/* should never reach here */
}這個進程fork自Zygote,而根據Linux的fork原理可知,Zygote的ServerSocket也會被這個進程所共有,所以第一行
需要調用closeServerSocket將這個socket關閉
之後就調用RuntimeInit.zygoteInit
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
redirectLogStreams();
commonInit();//設置通用信息
nativeZygoteInit();//啟動一個Binder線程池
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv);
}繼續看調用的applicationInit
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args;
try {
args = new Arguments(argv);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());
// let the process exit
return;
}
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs);
}最後通過invokeStatic來啟動入口函數,由前面可知,這裡的args.startClass是com.android.server.SystemServer
啟動的就是它的main函數
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it
// shortly.
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
}
}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
}
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
init1(args);
}這段代碼除了一個很萌的more memory注釋之外,就是調用native層的init1函數
static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
system_init();
}我只想說這個函數很萌。。。
extern "C" status_t system_init()
{
ALOGI("Entered system_init()");
sp proc(ProcessState::self());
sp sm = defaultServiceManager();
ALOGI("ServiceManager: %p\n", sm.get());
sp grim = new GrimReaper();
sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim, grim.get(), 0);
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the SurfaceFlinger
SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
}
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the sensor service
SensorService::instantiate();
}
// And now start the Android runtime. We have to do this bit
// of nastiness because the Android runtime initialization requires
// some of the core system services to already be started.
// All other servers should just start the Android runtime at
// the beginning of their processes's main(), before calling
// the init function.
ALOGI("System server: starting Android runtime.\n");
AndroidRuntime* runtime = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
ALOGI("System server: starting Android services.\n");
JNIEnv* env = runtime->getJNIEnv();
if (env == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/android/server/SystemServer");
if (clazz == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "init2", "()V");
if (methodId == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId);
ALOGI("System server: entering thread pool.\n");
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
ALOGI("System server: exiting thread pool.\n");
return NO_ERROR;
}
GrimReaper用來接受Service Manager的死亡通知
啟動SurfaceFlinger、SensorServer,然後獲取前面的AndroidRuntime對象,之後通過這個對象調用com.android.server.SystemServer的init2函數
public static final void init2() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
Thread thr = new ServerThread();
thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
thr.start();
}又回到了Java層,創建一個ServerThread類型的Thread,然後啟動
ServerThread.run這個函數很長
首先會創建一個消息循環
Looper.prepareMainLooper();然後啟動關鍵服務,並將它們在Service Manager中注冊
最後進入到消息循環當中
Looper.loop();這當中具體的關鍵服務下次再說,不然就扯遠了
回到之前我們所說的三個重要函數,還有最後一個runSelectLoopMode
在4.3中這個函數已經改名為runSelectLoop,不過沒啥關系
private static void runSelectLoop() throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList fds = new ArrayList();
ArrayList peers = new ArrayList();
FileDescriptor[] fdArray = new FileDescriptor[4];
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
int loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
while (true) {
int index;
/*
* Call gc() before we block in select().
* It's work that has to be done anyway, and it's better
* to avoid making every child do it. It will also
* madvise() any free memory as a side-effect.
*
* Don't call it every time, because walking the entire
* heap is a lot of overhead to free a few hundred bytes.
*/
if (loopCount <= 0) {
gc();
loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
} else {
loopCount--;
}
try {
fdArray = fds.toArray(fdArray);
index = selectReadable(fdArray);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()", ex);
}
if (index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()");
} else if (index == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer();
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
boolean done;
done = peers.get(index).runOnce();
if (done) {
peers.remove(index);
fds.remove(index);
}
}
}
} 創建一個4個socket大小的fdArray,表示Zygote最多同時處理4個socket連接,將前面創建出來的用於等待AMS發送請求的
sServerSocket加入到fds中。然後循環等待
首先將fds中的socket文件描述符轉移到fdArray中,調用selectReadable檢查fdArray中是否有可讀的數據
如果index為0,表示AMS與sServerSocket建立了連接
如果大於0,表示AMS發送了一個創建進程的請求,會調用ZygoteConnection的runOnce函數來創建一個新的應用進程
 Android進階——Preference詳解之Preference系的基本應用(三)
Android進階——Preference詳解之Preference系的基本應用(三)
引言前面一篇文章介紹了二級Preference的使用和特點,接下來進入系統給我提供的底級Preference的使用CheckBox選擇項CheckBoxPreferenc
 Android Paint類介紹以及浮雕和陰影效果的設置
Android Paint類介紹以及浮雕和陰影效果的設置
Paint類介紹Paint即畫筆,在繪制文本和圖形用它來設置圖形顏色, 樣式等繪制信息。1.圖形繪制setARGB(int a,int r,int g,int b);設置
 從AIDL看Android跨進程通信
從AIDL看Android跨進程通信
AIDL是Android實現IPC的一種重要的方式,理解它的原理對理解Android進程間通信有很大的幫助。AIDL的定義,已經有很多介紹的文章了,這裡就不做詳解了。我們
 Android中如何搭建一個WebServer
Android中如何搭建一個WebServer
今天終於把老大交代的任務搞完了,感覺收獲挺多的,所以就寫一篇來記錄一下吧,首先還是來看一下,老大們的需求 需求: 希望移動端的用戶標識(IMEI)和HTML頁面的用戶