編輯:關於Android編程
畫三角形是open GL ES中最簡單的入門項目,下面講解具體的流程,方便自己總結工具類,沒有別的意思。
為了使用OpenGL ES 2.0 API,需要添加如下聲明:
創建GLSurfaceViewGLSurfaceView是用來放置圖形view的容器。所有的東西都是繪制在GLSurfaceView上面的,就相當於畫布的概念,
這裡先實現一個GLSurfaceView。擴展自GLSurfaceView,實現自己的MyGLSurfaceView
public class MyGLSurfaceView extends GLSurfaceView {
private Context mContext;
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
}
創建RenderRenderer類(渲染器類),即 GLSurfaceView.Renderer的實現類,它控制了與它相關聯的 GLSurfaceView 上繪制什麼。
需要實現一下接口:
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
}
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
}
onSurfaceCreated()函數在surface創建的時候調用,所以初始化的工作在裡面完成。 onSurfaceChanged()函數在surface發生改變的時候調用; onDrawFrame()函數是完成surfaceview上面顯示內容的繪制,每一幀的繪制都會去調用。
基礎參數設置
//給shader中的變量傳參數時候用到的
private final int mStrideBytes = 7 * 4; //3 + 4 3表示坐標, 4表示顏色 一共7個float變量,每個變量4字節//一次性讀取 7 x 4個字節
private final int mPositionOffset = 0; //頂點坐標的偏移量
private final int mPositionDataSize = 3; //3個為一組,表示一個頂點坐標
private final int mColorOffset = 3; //顏色數據的變異量為3, 也就是每次讀取數據,從第三個開始是表示顏色的
private final int mColorDataSize = 4; //4個數據都是表示顏色的
mStrideBytes是指定buffer在讀取數據的時候一次讀取多少,7表示個數,7個數據, 4表示字節,7*4表示一次讀取多少字節的數據。
比如:
-0.5f, -0.25f, 0.0f, //point
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, //color
mPositionOffset表示頂點坐標的偏移量 mPositionDataSize表示頂底每個頂點坐標用多少個數據表示,三個:-0.5f, -0.25f, 0.0f, //point mColorOffset讀取顏色數據時的偏移量,因為頂點坐標用3個數據表示,所以偏移量為3 mColorDataSize表示多少個數據表示一個顏色,4個參數分別為ARGB
頂點坐標和顏色坐標
//數據
private final float vertexData[] = {
// X, Y, Z,
// R, G, B, A
-0.5f, -0.25f, 0.0f, //point
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, //color
0.5f, -0.25f, 0.0f, //point
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, //color
0.0f, 0.559016994f, 0.0f,//point
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f //color
};
可以看到,每組數據有7個,前面3個表示位置坐標,後面4個表示顏色值,可以結合前面的參數設置來理解。
這個數據是程序傳入openGL的數據。
創建Buffer存放數據
//數據的buffer
private FloatBuffer mShaderDateBuffer;
private FloatBuffer getVertexBuffer(float[] data) {
//先 創建內存地址
ByteBuffer vbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(data.length * 4); //每個float是4個字節
//ByteOrder.nativeOrder()返回本地jvm運行的硬件的字節順序.使用和硬件一致的字節順序可能使buffer更加有效.
vbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
FloatBuffer vertexBuffer = vbb.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(data);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
return vertexBuffer;
}
上面代碼中的注釋已經很清楚了,裡面的代碼大多數是固定的寫法。
Matrix的設置openGL 中有三個類型份額舉證,分別是:
* Model Matrix 模型矩陣
* View Matrix 視圖矩陣
* Projection Matrix 投影矩陣
由於這幾個概念很繞,是個人都要糊弄一會兒才能搞清楚,下面就這幾個矩陣,好好的糊弄糊弄。
所謂的坐標變換,就是將一個坐標系下的坐標,在另外一個坐標系中表示出來。
下圖中世界坐標系下的相機:

這個東西就是將坐標從世界坐標轉換到相機坐標的矩陣,那世界坐標的原點為例(0,0,0,1), 有

在opengl中,數據從用戶構建的局部坐標系,經過一系列的處理,最終渲染在屏幕上面,主要經過了一下過程:
Open gl中只定義了裁剪坐標系、規范化設備坐標系以及屏幕坐標系,而局部坐標系、世界坐標系和相機坐標系是為了
方便用戶的,用戶在OpenGL中的轉換如下:
從坐標來看,就是一下過程
下圖中茶壺在Model Matrix中的定義
世界坐標系下的茶壺:
從世界坐標系到相機坐標系

為什麼要將世界坐標系轉化到相機坐標系,我們最終看到的就是相機拍到的,而不是上帝視角下看到的一切(純屬個人理解,不喜勿噴)。
從相機坐標系到裁剪坐標系,通過投影完成的。分為正交投影和透視投影兩種。
最後讀下來還是感覺很暈,的確很暈。那這些東西和上面提到的三個矩陣有什麼關系呢?
基本上就是: Model Matrix是模型坐標系轉換到世界坐標系用,View Matrix就是視圖坐標系,用來轉換到相機坐標系用的,Projection Matrix轉化裁剪坐標系的。
ES中坐標系矩陣的計算計算模型矩陣,裡面調用了rotateM接口
private float[] mModelMatrix = new float[16]; //模型矩陣
private void initModelMatrix() {
// Do a complete rotation every 10 seconds.
long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 10000L;
float angleInDegrees = (360.0f / 10000.0f) * ((int) time);
// Draw the triangle facing straight on.
// 模型矩陣設為單位矩陣
Matrix.setIdentityM(mModelMatrix, 0);
// angleInDegrees是旋轉的角度,(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)是模型矩陣
Matrix.rotateM(mModelMatrix, 0, angleInDegrees, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
}
計算ViewMatrix,需要設置相機的位置,相機觀察的方向,以及相機的觀察正向向量
private float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16]; //視圖矩陣
private void initViewMatrix() {
//放置eye眼睛的位置
final float eyeX = 0.0f;
final float eyeY = 0.0f;
final float eyeZ = 1.5f;
//設置look方向
// look也成為center, center到eye所形成的向量,稱為視線方向,與真正的視線看過去的方向相反
final float lookX = 0.0f;
final float lookY = 0.0f;
final float lookZ = -5.0f;
//設置up坐標
//eye的位置本身只代表一個坐標而已,但是 look向量和up向量結合右手螺旋准則才能唯一的確定一個坐標系
//這個坐標系就是eye看到的坐標系,兩者垂直知識為了與常用的三位坐標系一樣
final float upX = 0.0f;
final float upY = 1.0f;
final float upZ = 0.0f;
//經過計算的到了 viewMatrix,
Matrix.setLookAtM(mViewMatrix, 0, eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ, lookX, lookY, lookZ, upX, upY, upZ);
}
投影矩陣,設置關於遠近 以及投影屏幕的大小等屬性。
private float[] mProjectionMatrix = new float[16]; //投射矩陣
private void initProjectionMatrix(int width, int height) {
// Set the OpenGL viewport to the same size as the surface.
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
// Create a new perspective projection matrix. The height will stay the same
// while the width will vary as per aspect ratio.
final float ratio = (float) width / height;
final float left = -ratio;
final float right = ratio;
final float bottom = -1.0f;
final float top = 1.0f;
final float near = 1.0f;
final float far = 10.0f;
Matrix.frustumM(mProjectionMatrix, 0, left, right, bottom, top, near, far);
}
Shader數據傳入使用工具類:
public static int compileShader(final int shaderType, final String shaderSource) {
// 創建shader句柄
int shaderHandle = GLES20.glCreateShader(shaderType);
if (shaderHandle != 0) {
// Pass in the shader source.
// 使用glShaderSource()分別將頂點著色程序的源代碼字符數組綁定到頂點著色器對象,將片段著色程序的源代碼字符數組綁定到片段著色器對象;
// 綁定作用
GLES20.glShaderSource(shaderHandle, shaderSource);
// Compile the shader.
// 編譯
GLES20.glCompileShader(shaderHandle);
// Get the compilation status.
// 得到計算結果
final int[] compileStatus = new int[1];
GLES20.glGetShaderiv(shaderHandle, GLES20.GL_COMPILE_STATUS, compileStatus, 0);
// If the compilation failed, delete the shader.
// 結果審查
if (compileStatus[0] == 0) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error compiling shader: " + GLES20.glGetShaderInfoLog(shaderHandle));
GLES20.glDeleteShader(shaderHandle);
shaderHandle = 0;
}
}
if (shaderHandle == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error creating shader.");
}
return shaderHandle;
}
shaderType為兩種,一種是GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER,一種是GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER。最終返回的是shader的句柄,後面要用到這個句柄傳入參數,
計算。
鏈接程序
vertexShader
uniform mat4 u_MVPMatrix; //應用程序傳入的變換矩陣 ,MVP 是modle view projection的意思,通過這個來計算最終的坐標
attribute vec4 a_Position; //應用程序傳入的 頂點的坐標
attribute vec4 a_Color; //應用程序傳入的 頂點顏色的坐標
varying vec4 v_Color; //這個變量會傳到 fragment shader中處理
void main() {
v_Color = a_Color;
gl_Position = u_MVPMatrix * a_Position;
}
fragmentShader
precision mediump float; //精度
varying vec4 v_Color; //這個名字一定要和在 vertex shader中聲明的一樣
void main() {
gl_FragColor = v_Color;
}
變量,這些變量是在shader中定義的,這裡的名稱和c語言中定義的名稱一致。通過這個個名稱獲取變量,傳入參數
private String[] mAttributes = {
"u_MVPMatrix",
"a_Position",
"a_Color"
};
public static int createAndLinkProgram(final int vertexShaderHandle, final int fragmentShaderHandle, final String[] attributes) {
// 創建程序句柄
int programHandle = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
if (programHandle != 0) {
// Bind the vertex shader to the program.
// 綁定shader到program
GLES20.glAttachShader(programHandle, vertexShaderHandle);
// Bind the fragment shader to the program.
GLES20.glAttachShader(programHandle, fragmentShaderHandle);
// Bind attributes
// 綁定參數到program
if (attributes != null) {
final int size = attributes.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
GLES20.glBindAttribLocation(programHandle, i, attributes[i]);
}
}
// Link the two shaders together into a program.
GLES20.glLinkProgram(programHandle);
// Get the link status.
final int[] linkStatus = new int[1];
GLES20.glGetProgramiv(programHandle, GLES20.GL_LINK_STATUS, linkStatus, 0);
// If the link failed, delete the program.
if (linkStatus[0] == 0) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error compiling program: " + GLES20.glGetProgramInfoLog(programHandle));
GLES20.glDeleteProgram(programHandle);
programHandle = 0;
}
}
if (programHandle == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error creating program.");
}
return programHandle;
}
最後一步,繪制圖形onSurfaceCreated函數主要是做初始化用的。
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
//清屏指令
GLES20.glClearColor(0f, 0f, 0f, 0f);
//初始化相機的位置
initViewMatrix();
initShader();
}
private void initShader() {
int vertexShaderHandle = ShaderHelper.compileShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, TextResourceReader.readTextFileFromResource(mContext, R.raw.vertex_shader));
int fragmentShaderHandle = ShaderHelper.compileShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, TextResourceReader.readTextFileFromResource(mContext, R.raw.fragment_shader));
int programHandle = ShaderHelper.createAndLinkProgram(vertexShaderHandle, fragmentShaderHandle, mAttributes);
//者三個變量是我們在glsl文件中定義的三個變量,現在鏈接程序之後把他們取出來用,是為了後面賦值
mMVPMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(programHandle, "u_MVPMatrix");
mPositionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programHandle, "a_Position");
mColorHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programHandle, "a_Color");
GLES20.glUseProgram(programHandle);
}
onSurfaceChanged()函數
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
initProjectionMatrix(width, height);
}
onDrawFrame()繪制
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
initModelMatrix();
drawFrame(mShaderDateBuffer);
}
private void drawFrame(final FloatBuffer frameBuffer) {
//移動到 表示坐標的起始位置
frameBuffer.position(mPositionOffset);
//glVertexAttribPointer(positionSlot, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, stride, pCoords);
/* 為頂點著色器位置信息賦值,
1.positionSlot表示頂點著色器位置屬性(即,Position);就是在glsl文件中聲明的attribute變量
2.表示每一個頂點信息由幾個值組成,這個值必須位1,2,3或4;
3.GL_FLOAT表示頂點信息的數據類型;
4.GL_FALSE表示不要將數據類型標准化(即fixed-point);
5.stride表示數組中每個元素的長度;pCoords表示數組的首地址
*/
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mPositionHandle, mPositionDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false,
mStrideBytes, frameBuffer);
//開啟頂點屬性數組
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle);
//定位到color數據首地址
frameBuffer.position(mColorOffset);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mColorHandle, mColorDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false,
mStrideBytes, frameBuffer);
//開啟頂點屬性數組
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mColorHandle);
Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix, 0, mViewMatrix, 0, mModelMatrix, 0);
// This multiplies the modelview matrix by the projection matrix, and stores the result in the MVP matrix
// (which now contains model * view * projection).
Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix, 0, mProjectionMatrix, 0, mMVPMatrix, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mMVPMatrixHandle, 1, false, mMVPMatrix, 0);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
}
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mPositionHandle, mPositionDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false,
mStrideBytes, frameBuffer);
mPositionHandle是GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programHandle, "a_Position");綁定的變量,mPositionDataSize表示position坐標的數據個數,
也就是多少個數據表示一個坐標,mStrideBytes表示每次讀取多少字節數據。
同樣地,GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mColorHandle, mColorDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false,mStrideBytes, frameBuffer);
是傳入color數據。
Matrix.multiplyMM是計算MVP矩陣。
glDrawArrays參數詳解在OpenGl中所有的圖形都是通過分解成三角形的方式進行繪制。
繪制圖形通過GL10類中的glDrawArrays方法實現,
該方法原型:
glDrawArrays(int mode, int first,int count)
*參數1:有三種取值
1.GL_TRIANGLES:每三個頂之間繪制三角形,之間不連接
2.GL_TRIANGLE_FAN:以V0V1V2,V0V2V3,V0V3V4,……的形式繪制三角形
3.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP:順序在每三個頂點之間均繪制三角形。這個方法可以保證從相同的方向上所有三角形均被繪制。以V0V1V2,V1V2V3,V2V3V4……的形式繪制三角形
*參數2:從數組緩存中的哪一位開始繪制,一般都定義為0
*參數3:頂點的數量
MainActivityMainActivity中增加opengl版本支持相關代碼。
//GLSurfaceView
private MyGLSurfaceView mGLSurfaceView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
initGL();
final ActivityManager activityManager = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final ConfigurationInfo configurationInfo = activityManager.getDeviceConfigurationInfo();
final boolean supportsEs2 = configurationInfo.reqGlEsVersion >= 0x20000;
if (supportsEs2)
{
// Request an OpenGL ES 2.0 compatible context.
mGLSurfaceView.setEGLContextClientVersion(2);
// Set the renderer to our demo renderer, defined below.
mGLSurfaceView.setRenderer(new MyRender(this));
}
else
{
// This is where you could create an OpenGL ES 1.x compatible
// renderer if you wanted to support both ES 1 and ES 2.
return;
}
setContentView(mGLSurfaceView);
}
//初始化 opengl相關
private void initGL() {
mGLSurfaceView = new MyGLSurfaceView(this);
}
//在下面的兩個方法中,必須有對 GLSurfaceView的處理,當Activity暫停時,在onPause中處理
//同樣在onResume中有相應的恢復處理
//下面是最長見的處理方法
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mGLSurfaceView.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mGLSurfaceView.onResume();
}
總結畫一個三角形和寫一個Hello World一樣難!!!
Referencesopen GL空間坐標系的理解
 Android 5.0中CoordinatorLayout的使用技巧
Android 5.0中CoordinatorLayout的使用技巧
CoordinatorLayout 實現了多種Material Design中提到的滾動效果。目前這個框架提供了幾種不用寫動畫代碼就能工作的方法,這些效果包括: *讓浮動
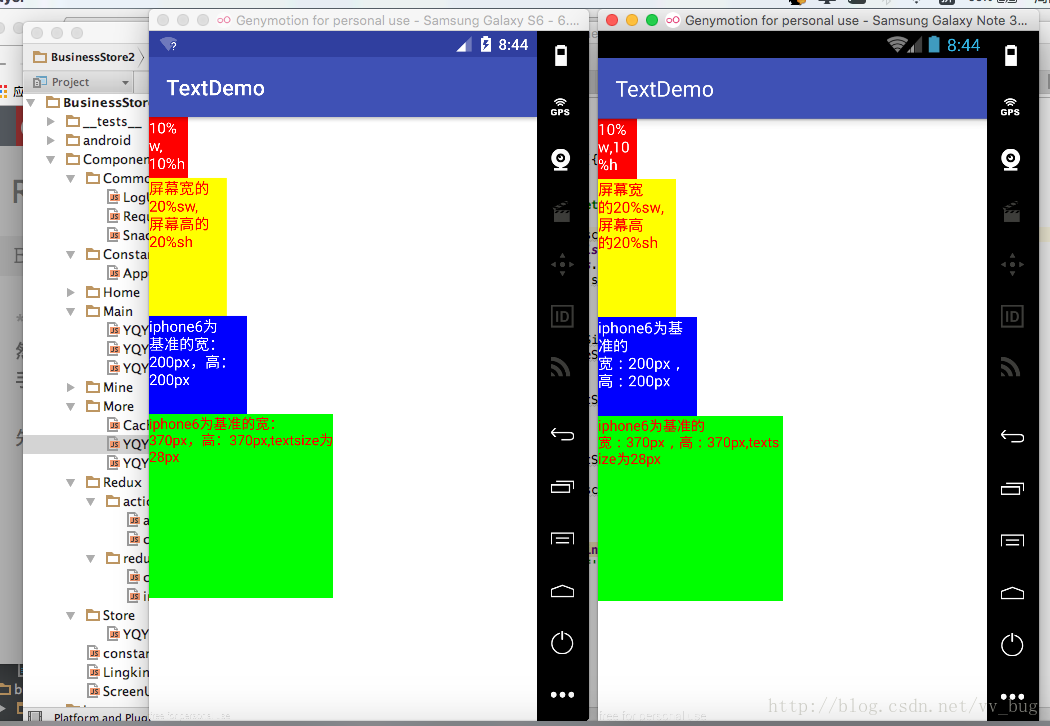 ReactNative與Android中的屏幕適配
ReactNative與Android中的屏幕適配
前言:從開始接觸rn到現在終於能寫出點東西了,的確得為自己好好地點個贊 ,不管咋樣,學習還是得繼續啊,廢話少說了,在rn中我們也需要對屏幕進行適配,但是rn中的適配貌似比
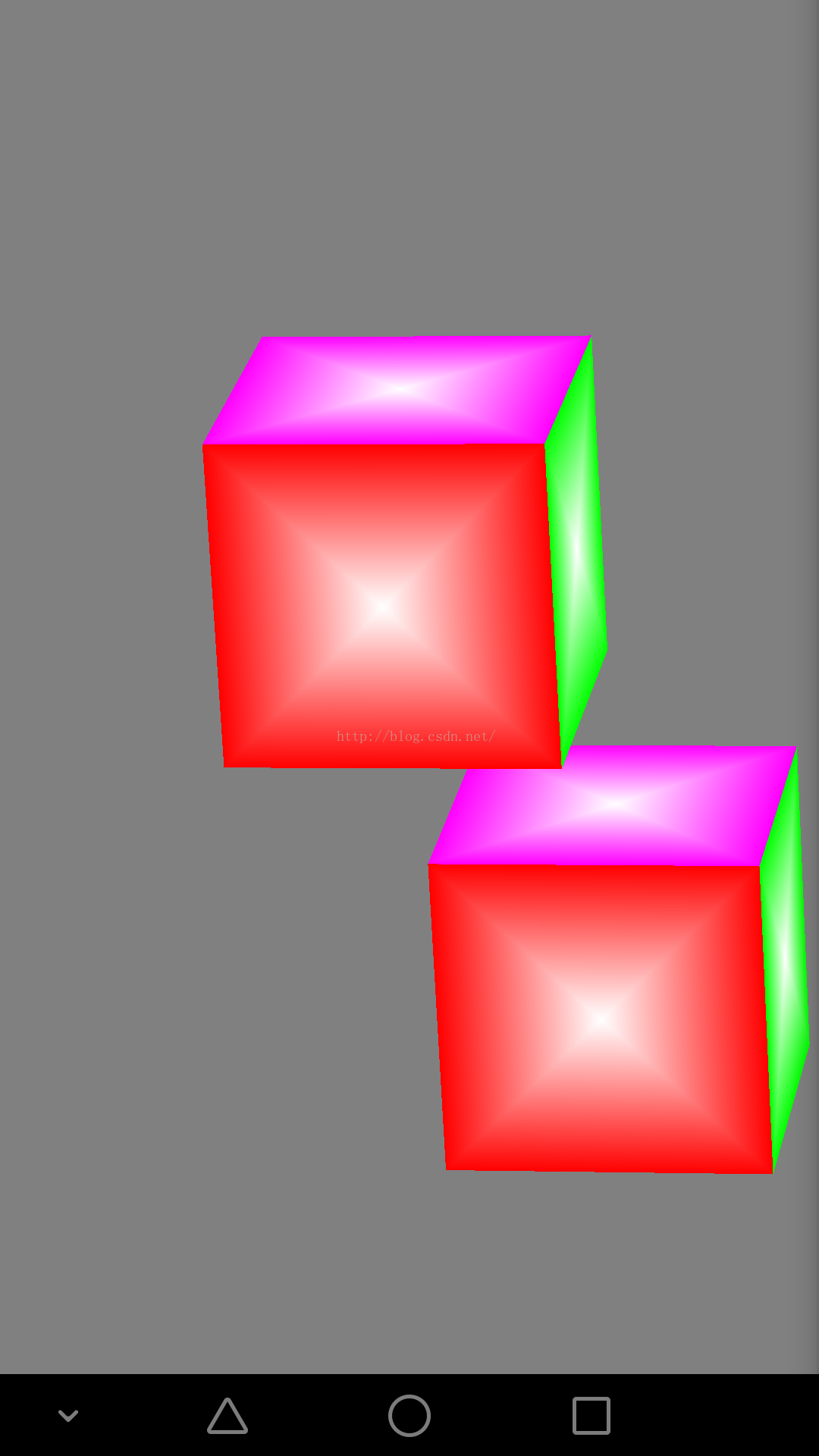 opengles繪制立方體
opengles繪制立方體
本人比較懶,不說廢話,直接貼代碼,代碼後附有完整項目package test.com.opengles5_3;import android.opengl.GLES20;i
 Android中WebView無法後退和js注入漏洞的解決方案
Android中WebView無法後退和js注入漏洞的解決方案
因重定向無法正常goBack()解決方案首先說下問題,初始頁面為A,點擊某個鏈接跳轉到B(http://xxx.com.cn/),B頁面重定向到C頁面(http://xx