編輯:關於Android編程
在之前的Android超精准計步器開發-Dylan計步中的首頁用到了一個自定義控件,和QQ運動的界面有點類似,還有動畫效果,下面就來講一下這個View是如何繪制的。
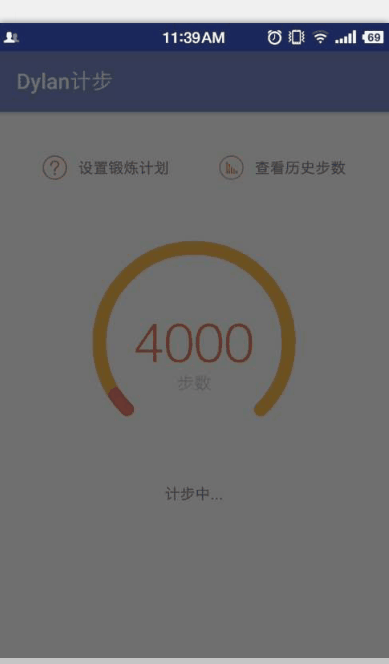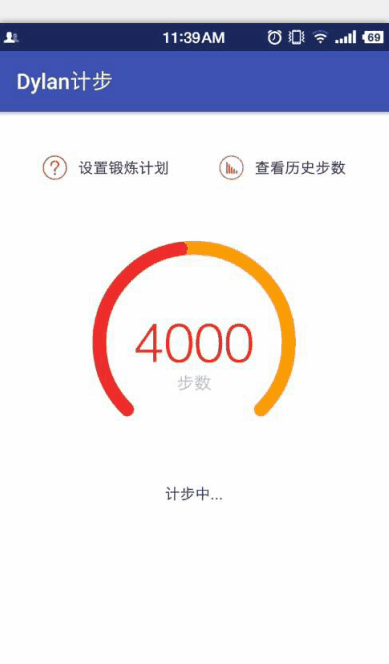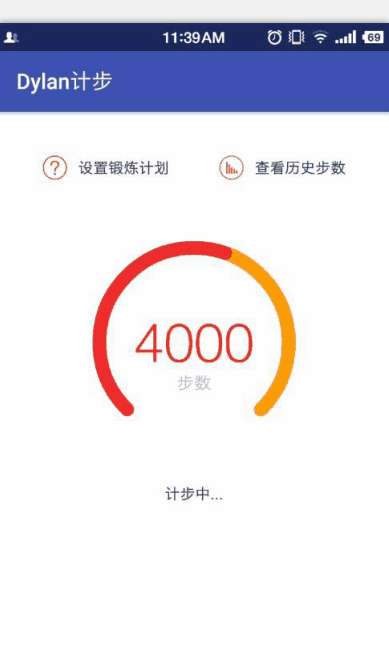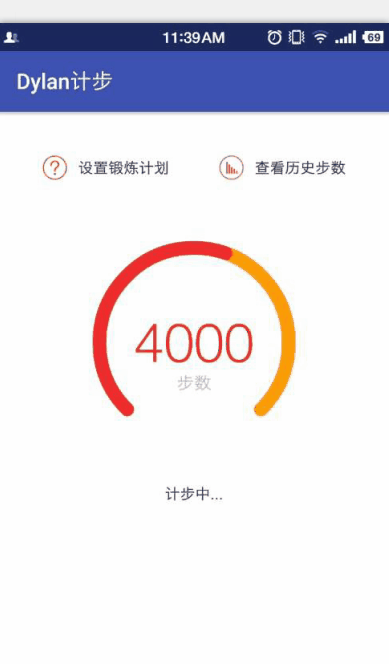
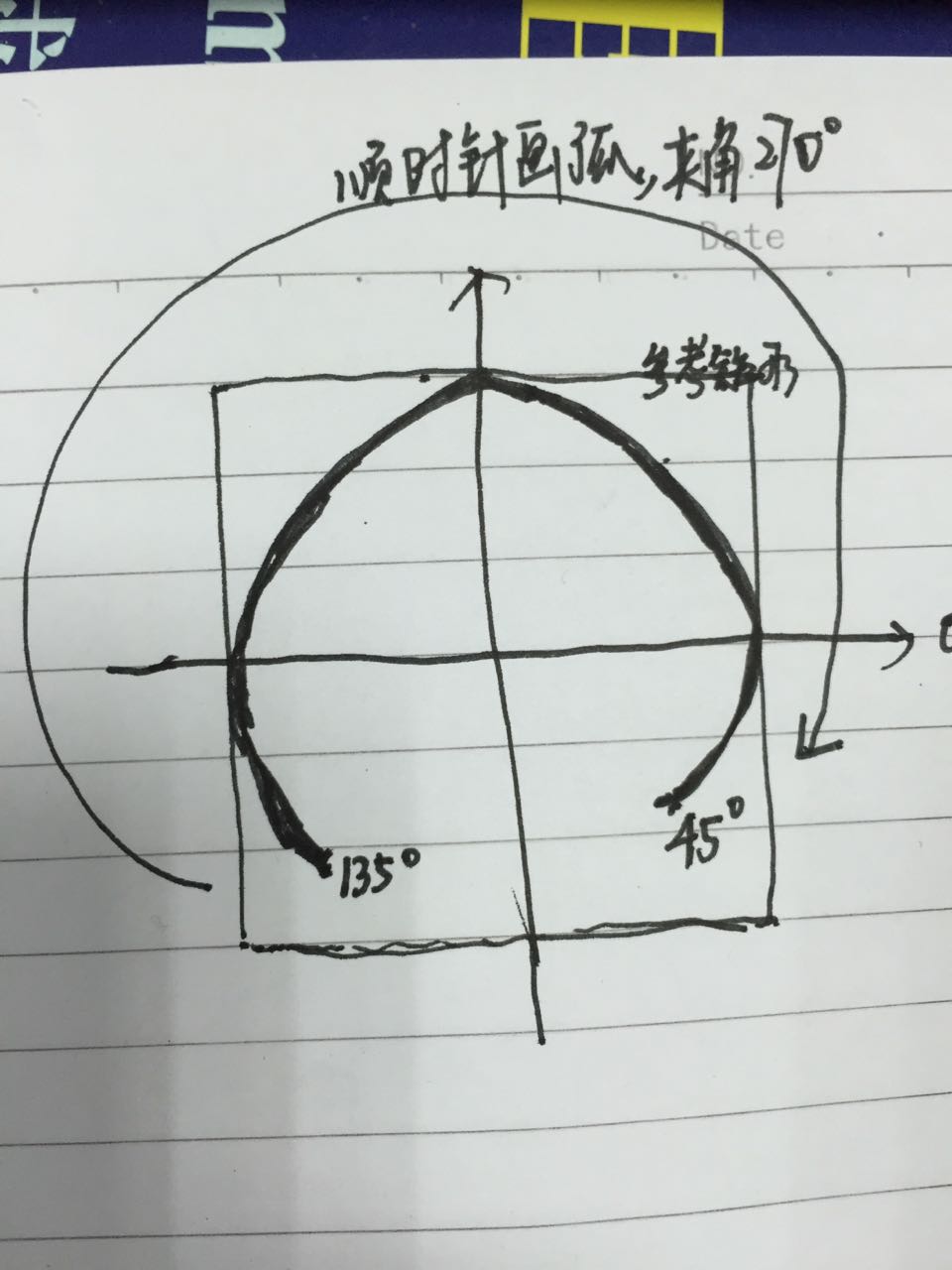
在Canvas中有一個畫圓弧的方法
drawArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean useCenter, Paint paint)//畫弧,
參數一是RectF對象,一個矩形區域橢圓形的界限用於定義在形狀、大小、電弧,
參數二是起始角(度)在電弧的開始,圓弧起始角度,單位為度。
參數三圓弧掃過的角度,順時針方向,單位為度,從右中間開始為零度。
參數四是如果是true(真)的話,在繪制圓弧時將圓心包括在內,通常用來繪制扇形;如果是false(假)這將是一個弧線。
參數五是Paint對象;
對於這個方法,大家可以看一下我手繪的草圖,比較爛,表達一下這幾個參數的意思和繪制過程,畫得不好望大家見諒!
/**中心點的x坐標*/ float centerX = (getWidth()) / 2;
/**指定圓弧的外輪廓矩形區域*/ RectF rectF = new RectF(0 + borderWidth, borderWidth, 2 * centerX - borderWidth, 2 * centerX - borderWidth);
/**
* 1.繪制總步數的黃色圓弧
*
* @param canvas 畫筆
* @param rectF 參考的矩形
*/
private void drawArcYellow(Canvas canvas, RectF rectF) {
Paint paint = new Paint();
/** 默認畫筆顏色,黃色 */
paint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.yellow));
/** 結合處為圓弧*/
paint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
/** 設置畫筆的樣式 Paint.Cap.Round ,Cap.SQUARE等分別為圓形、方形*/
paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
/** 設置畫筆的填充樣式 Paint.Style.FILL :填充內部;Paint.Style.FILL_AND_STROKE :填充內部和描邊; Paint.Style.STROKE :僅描邊*/
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
/**抗鋸齒功能*/
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
/**設置畫筆寬度*/
paint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
/**繪制圓弧的方法
* drawArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean useCenter, Paint paint)//畫弧,
參數一是RectF對象,一個矩形區域橢圓形的界限用於定義在形狀、大小、電弧,
參數二是起始角(度)在電弧的開始,圓弧起始角度,單位為度。
參數三圓弧掃過的角度,順時針方向,單位為度,從右中間開始為零度。
參數四是如果這是true(真)的話,在繪制圓弧時將圓心包括在內,通常用來繪制扇形;如果它是false(假)這將是一個弧線,
參數五是Paint對象;
*/
canvas.drawArc(rectF, startAngle, angleLength, false, paint);
}
/**
* 2.繪制當前步數的紅色圓弧
*/
private void drawArcRed(Canvas canvas, RectF rectF) {
Paint paintCurrent = new Paint();
paintCurrent.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
paintCurrent.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);//圓角弧度
paintCurrent.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//設置填充樣式
paintCurrent.setAntiAlias(true);//抗鋸齒功能
paintCurrent.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);//設置畫筆寬度
paintCurrent.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.red));//設置畫筆顏色
canvas.drawArc(rectF, startAngle, currentAngleLength, false, paintCurrent);
}
/**
* 3.圓環中心的步數
*/
private void drawTextNumber(Canvas canvas, float centerX) {
Paint vTextPaint = new Paint();
vTextPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
vTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//抗鋸齒功能
vTextPaint.setTextSize(numberTextSize);
Typeface font = Typeface.create(Typeface.SANS_SERIF, Typeface.NORMAL);
vTextPaint.setTypeface(font);//字體風格
vTextPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.red));
Rect bounds_Number = new Rect();
vTextPaint.getTextBounds(stepNumber, 0, stepNumber.length(), bounds_Number);
canvas.drawText(stepNumber, centerX, getHeight() / 2 + bounds_Number.height() / 2, vTextPaint);
}
/**
* 4.圓環中心[步數]的文字
*/
private void drawTextStepString(Canvas canvas, float centerX) {
Paint vTextPaint = new Paint();
vTextPaint.setTextSize(dipToPx(16));
vTextPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
vTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//抗鋸齒功能
vTextPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.grey));
String stepString = "步數";
Rect bounds = new Rect();
vTextPaint.getTextBounds(stepString, 0, stepString.length(), bounds);
canvas.drawText(stepString, centerX, getHeight() / 2 + bounds.height() + getFontHeight(numberTextSize), vTextPaint);
}
ValueAnimator是整個屬性動畫機制當中最核心的一個類,屬性動畫的運行機制是通過不斷地對值進行操作來實現的,而初始值和結束值之間的動畫過渡就是由ValueAnimator這個類來負責計算的。它的內部使用一種時間循環的機制來計算值與值之間的動畫過渡, 我們只需要將初始值和結束值提供給ValueAnimator,並且告訴它動畫所需運行的時長,那麼ValueAnimator就會自動幫我們完成從初始值平滑地過渡到結束值這樣的效果。
/*為進度設置動畫
* @param start 初始值
* @param current 結束值
* @param length 動畫時長
*/
private void setAnimation(float start, float current, int length) {
ValueAnimator progressAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(start, current);
progressAnimator.setDuration(length);
progressAnimator.setTarget(currentAngleLength);
progressAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
/**每次在初始值和結束值之間產生的一個平滑過渡的值,逐步去更新進度*/
currentAngleLength = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
progressAnimator.start();
}
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.RectF;
import android.graphics.Typeface;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import cn.bluemobi.dylan.step.R;
/**
* Created by DylanAndroid on 2016/5/26.
* 顯示步數的圓弧
*/
public class StepArcView extends View {
/**
* 圓弧的寬度
*/
private float borderWidth = 38f;
/**
* 畫步數的數值的字體大小
*/
private float numberTextSize = 0;
/**
* 步數
*/
private String stepNumber = "0";
/**
* 開始繪制圓弧的角度
*/
private float startAngle = 135;
/**
* 終點對應的角度和起始點對應的角度的夾角
*/
private float angleLength = 270;
/**
* 所要繪制的當前步數的紅色圓弧終點到起點的夾角
*/
private float currentAngleLength = 0;
/**
* 動畫時長
*/
private int animationLength = 3000;
public StepArcView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public StepArcView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public StepArcView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
/**中心點的x坐標*/
float centerX = (getWidth()) / 2;
/**指定圓弧的外輪廓矩形區域*/
RectF rectF = new RectF(0 + borderWidth, borderWidth, 2 * centerX - borderWidth, 2 * centerX - borderWidth);
/**【第一步】繪制整體的黃色圓弧*/
drawArcYellow(canvas, rectF);
/**【第二步】繪制當前進度的紅色圓弧*/
drawArcRed(canvas, rectF);
/**【第三步】繪制當前進度的紅色數字*/
drawTextNumber(canvas, centerX);
/**【第四步】繪制"步數"的紅色數字*/
drawTextStepString(canvas, centerX);
}
/**
* 1.繪制總步數的黃色圓弧
*
* @param canvas 畫筆
* @param rectF 參考的矩形
*/
private void drawArcYellow(Canvas canvas, RectF rectF) {
Paint paint = new Paint();
/** 默認畫筆顏色,黃色 */
paint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.yellow));
/** 結合處為圓弧*/
paint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
/** 設置畫筆的樣式 Paint.Cap.Round ,Cap.SQUARE等分別為圓形、方形*/
paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
/** 設置畫筆的填充樣式 Paint.Style.FILL :填充內部;Paint.Style.FILL_AND_STROKE :填充內部和描邊; Paint.Style.STROKE :僅描邊*/
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
/**抗鋸齒功能*/
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
/**設置畫筆寬度*/
paint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
/**繪制圓弧的方法
* drawArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean useCenter, Paint paint)//畫弧,
參數一是RectF對象,一個矩形區域橢圓形的界限用於定義在形狀、大小、電弧,
參數二是起始角(度)在電弧的開始,圓弧起始角度,單位為度。
參數三圓弧掃過的角度,順時針方向,單位為度,從右中間開始為零度。
參數四是如果這是true(真)的話,在繪制圓弧時將圓心包括在內,通常用來繪制扇形;如果它是false(假)這將是一個弧線,
參數五是Paint對象;
*/
canvas.drawArc(rectF, startAngle, angleLength, false, paint);
}
/**
* 2.繪制當前步數的紅色圓弧
*/
private void drawArcRed(Canvas canvas, RectF rectF) {
Paint paintCurrent = new Paint();
paintCurrent.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
paintCurrent.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);//圓角弧度
paintCurrent.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//設置填充樣式
paintCurrent.setAntiAlias(true);//抗鋸齒功能
paintCurrent.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);//設置畫筆寬度
paintCurrent.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.red));//設置畫筆顏色
canvas.drawArc(rectF, startAngle, currentAngleLength, false, paintCurrent);
}
/**
* 3.圓環中心的步數
*/
private void drawTextNumber(Canvas canvas, float centerX) {
Paint vTextPaint = new Paint();
vTextPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
vTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//抗鋸齒功能
vTextPaint.setTextSize(numberTextSize);
Typeface font = Typeface.create(Typeface.SANS_SERIF, Typeface.NORMAL);
vTextPaint.setTypeface(font);//字體風格
vTextPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.red));
Rect bounds_Number = new Rect();
vTextPaint.getTextBounds(stepNumber, 0, stepNumber.length(), bounds_Number);
canvas.drawText(stepNumber, centerX, getHeight() / 2 + bounds_Number.height() / 2, vTextPaint);
}
/**
* 4.圓環中心[步數]的文字
*/
private void drawTextStepString(Canvas canvas, float centerX) {
Paint vTextPaint = new Paint();
vTextPaint.setTextSize(dipToPx(16));
vTextPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
vTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//抗鋸齒功能
vTextPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.grey));
String stepString = "步數";
Rect bounds = new Rect();
vTextPaint.getTextBounds(stepString, 0, stepString.length(), bounds);
canvas.drawText(stepString, centerX, getHeight() / 2 + bounds.height() + getFontHeight(numberTextSize), vTextPaint);
}
/**
* 獲取當前步數的數字的高度
*
* @param fontSize 字體大小
* @return 字體高度
*/
public int getFontHeight(float fontSize) {
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setTextSize(fontSize);
Rect bounds_Number = new Rect();
paint.getTextBounds(stepNumber, 0, stepNumber.length(), bounds_Number);
return bounds_Number.height();
}
/**
* dip 轉換成px
*
* @param dip
* @return
*/
private int dipToPx(float dip) {
float density = getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dip * density + 0.5f * (dip >= 0 ? 1 : -1));
}
/**
* 所走的步數進度
*
* @param totalStepNum 設置的步數
* @param currentCounts 所走步數
*/
public void setCurrentCount(int totalStepNum, int currentCounts) {
stepNumber = currentCounts + "";
setTextSize(currentCounts);
/**如果當前走的步數超過總步數則圓弧還是270度,不能成為園*/
if (currentCounts > totalStepNum) {
currentCounts = totalStepNum;
}
/**所走步數占用總共步數的百分比*/
float scale = (float) currentCounts / totalStepNum;
/**換算成弧度最後要到達的角度的長度-->弧長*/
float currentAngleLength = scale * angleLength;
/**開始執行動畫*/
setAnimation(0, currentAngleLength, animationLength);
}
/**
* 為進度設置動畫
* ValueAnimator是整個屬性動畫機制當中最核心的一個類,屬性動畫的運行機制是通過不斷地對值進行操作來實現的,
* 而初始值和結束值之間的動畫過渡就是由ValueAnimator這個類來負責計算的。
* 它的內部使用一種時間循環的機制來計算值與值之間的動畫過渡,
* 我們只需要將初始值和結束值提供給ValueAnimator,並且告訴它動畫所需運行的時長,
* 那麼ValueAnimator就會自動幫我們完成從初始值平滑地過渡到結束值這樣的效果。
*
* @param last
* @param current
*/
private void setAnimation(float last, float current, int length) {
ValueAnimator progressAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(last, current);
progressAnimator.setDuration(length);
progressAnimator.setTarget(currentAngleLength);
progressAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
currentAngleLength = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
progressAnimator.start();
}
/**
* 設置文本大小,防止步數特別大之後放不下,將字體大小動態設置
*
* @param num
*/
public void setTextSize(int num) {
String s = String.valueOf(num);
int length = s.length();
if (length <= 4) {
numberTextSize = dipToPx(50);
} else if (length > 4 && length <= 6) {
numberTextSize = dipToPx(40);
} else if (length > 6 && length <= 8) {
numberTextSize = dipToPx(30);
} else if (length > 8) {
numberTextSize = dipToPx(25);
}
}
}
Activity中
StepArcView sv = (StepArcView) findViewById(R.id.sv); sv.setCurrentCount(7000, 1000);
 Android中子線程真的不能更新UI嗎?
Android中子線程真的不能更新UI嗎?
Android的UI訪問是沒有加鎖的,這樣在多個線程訪問UI是不安全的。所以Android中規定只能在UI線程中訪問UI。但是有沒有極端的情況?使得我們在子線程中訪問UI
 Android中的Telephony學習筆記(2)
Android中的Telephony學習筆記(2)
上一篇文章中學習了android.provider中Telephony類。這一篇文章學習android.telephony包中的類,這些類是android提供給上層調用的
 Android Developer:Heap Viewer演示
Android Developer:Heap Viewer演示
這個演示展示了Heap Viewer工具的基本用法。Heap Viewer實時報告你的應用程序已經分配了什麼類型的對象,多少個,和它們在堆內存中的大小。它的優勢:獲取你的
 自定義ImageView實現局部截圖功能
自定義ImageView實現局部截圖功能
1、前言最近在做一個能夠自選區域進行局部截圖的功能,接下來,會給大家講解,整個截圖的實現過程。筆者這邊實現的自選區域的形狀是矩形,讀者如果有需要,可以根據我給大家講解的思