編輯:關於Android編程
在Android開發旅途中,經常會遇到系統控件無法滿足我們的視覺,交互效果,這個時候我們常常需要自己自定義控件來滿足我們的需求。在這個開發探索過程中,我們不可避免得遇到View要保存狀態信息這樣的問題。剛開始接觸控件自定義開發的時候,我自己也搞不懂要怎樣保存當前數據,如果沒有對當前狀態數據進行保存,那麼如果一不小心旋轉一下手機屏幕或者按下back,那麼控件又回到初始化狀態,之前所有的輸入都已經不存在。比如TextView文本顯示,EditText輸入內容,Switch選中狀態等等。當然也不要擔心,安卓系統通常會自動保存這些View的狀態(一般是系統控件),但是如果是我們自定義的控件,那麼就不起作用了,這就需要我們自己去保存我們自己自定義的控件的狀態。這些是後話,我們先來分析Android系統是怎麼保存系統控件的狀態的。
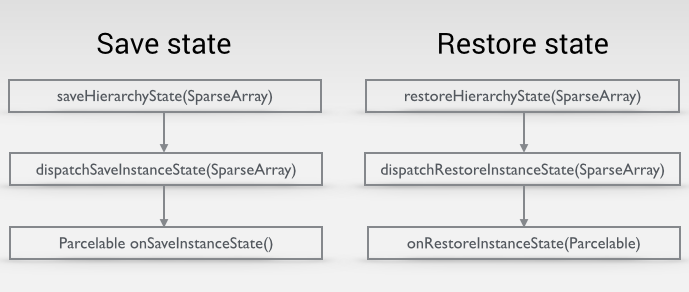
我們先來分析保存狀態的過程:
1、saveHierarchyState(SparseArray Container)
/**
* Store this view hierarchy's frozen state into the given container.
*
* @param container The SparseArray in which to save the view's state.
*
* @see #restoreHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #dispatchSaveInstanceState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #onSaveInstanceState()
*/
public void saveHierarchyState(SparseArray container) {
dispatchSaveInstanceState(container);
}
源碼上已經注釋很清楚了,saveHierarchyState(SparseArrayContainer)這個方法主要是將視圖層次結構凍結狀態儲存到給定的容器中。接著我們繼續一步步進入它的方法調用棧中看看具體的保存過程。
2、dispatchSaveInstanceState(SparseArray container)
被saveHierarchyState()調用。 在其內部調用onSaveInstanceState(),並且返回一個代表當前狀態的Parcelable。這個Parcelable被保存在container參數中,container參數是一個鍵值對的map集合。View的ID是加鍵,Parcelable是值。如果這是一個ViewGroup,還需要遍歷其子view,保存子View的狀態。
/**
* Called by {@link #saveHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)} to store the state for
* this view and its children. May be overridden to modify how freezing happens to a
* view's children; for example, some views may want to not store state for their children.
*
* @param container The SparseArray in which to save the view's state.
*
* @see #dispatchRestoreInstanceState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #saveHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #onSaveInstanceState()
*/
protected void dispatchSaveInstanceState(SparseArray container) {
if (mID != NO_ID && (mViewFlags & SAVE_DISABLED_MASK) == 0) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED;
Parcelable state = onSaveInstanceState();
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED) == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Derived class did not call super.onSaveInstanceState()");
}
if (state != null) {
// Log.i("View", "Freezing #" + Integer.toHexString(mID)
// + ": " + state);
container.put(mID, state);
}
}
}
從上面的源碼上我們可以看到dispatchSaveInstanceState(SparseArraycontainer)主要是調用onSaveInstanceState()方法返回當前狀態的Parcelable,利用Map集合器,把當前View的ID當作鍵,把Parcelable當作值保存到container這個Map容器中。
3、Parcelable onSaveInstanceState()
被 dispatchSaveInstanceState()調用。這個方法應該在View的實現中被重寫以返回實際的View狀態。
restoreHierarchyState(SparseArray container)
在需要恢復View狀態的時候被Android調用,作為傳入的SparseArray參數,包含了在保存過程中的所有view狀態。
/**
* Hook allowing a view to generate a representation of its internal state
* that can later be used to create a new instance with that same state.
* This state should only contain information that is not persistent or can
* not be reconstructed later. For example, you will never store your
* current position on screen because that will be computed again when a
* new instance of the view is placed in its view hierarchy.
*
* Some examples of things you may store here: the current cursor position * in a text view (but usually not the text itself since that is stored in a * content provider or other persistent storage), the currently selected * item in a list view. * * @return Returns a Parcelable object containing the view's current dynamic * state, or null if there is nothing interesting to save. The * default implementation returns null. * @see #onRestoreInstanceState(android.os.Parcelable) * @see #saveHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray) * @see #dispatchSaveInstanceState(android.util.SparseArray) * @see #setSaveEnabled(boolean) */ @CallSuper protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED; if (mStartActivityRequestWho != null) { BaseSavedState state = new BaseSavedState(AbsSavedState.EMPTY_STATE); state.mStartActivityRequestWhoSaved = mStartActivityRequestWho; return state; } return BaseSavedState.EMPTY_STATE; }
允許一個視圖來生成它的內部狀態的表示的鉤子,可以用來創建一個相同的狀態的新實例。此狀態只包含不持久的或無法重建的信息。例如,您將永遠不會在屏幕上存儲當前的位置,因為當視圖層次結構中的一個新實例放置在視圖中時,將再次計算您的當前位置。看到沒有,在onSaveInstanceState()中,創建了一個BaseSavedState的對象,看到這個對象的出現我想應該知道View的數據保存跟恢復是怎麼回事了吧。如果你還不是很清楚,沒關系,我們繼續看看BaseSavedState到底是個什麼鬼。
/**
* Constructor called by derived classes when creating their SavedState objects
*
* @param superState The state of the superclass of this view
*/
public BaseSavedState(Parcelable superState) {
super(superState);
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
super.writeToParcel(out, flags);
out.writeString(mStartActivityRequestWhoSaved);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR =
new Parcelable.Creator() {
public BaseSavedState createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new BaseSavedState(in);
}
public BaseSavedState[] newArray(int size) {
return new BaseSavedState[size];
}
};
}
構造函數調用派生類創建對象時傳入他們的savedstate,其實就是一個序列化數據的寫入,恢復數據無非就是從這個序列裡面讀取出剛剛寫入的數據。好了,我們再來分析數據恢復的過程。
從上面那張圖中,我們不難看出數據的恢復首先會調用restoreHierarchyState(SparseArray container)這個方法,然後再調dispatchRestoreInstanceState(SparseArray container),最後調onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state)。所以我們接下一步步往下看。
4、restoreHierarchyState(SparseArray container)
在需要恢復View狀態的時候被Android調用,作為傳入的SparseArray參數,包含了在保存過程中的所有view狀態。
/**
* Restore this view hierarchy's frozen state from the given container.
*
* @param container The SparseArray which holds previously frozen states.
*
* @see #saveHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #dispatchRestoreInstanceState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #onRestoreInstanceState(android.os.Parcelable)
*/
public void restoreHierarchyState(SparseArray container) {
dispatchRestoreInstanceState(container);
}
即從給定容器中恢復此視圖層次結構的凍結狀態。跟剛剛保存數據是一個相反的過程。
5、dispatchRestoreInstanceState(SparseArray container)
被restoreHierarchyState()調用。根據View的ID找出相應的Parcelable,同時傳遞給onRestoreInstanceState()。如果這是一個ViewGroup,還要恢復其子View的數據。
/**
* Called by {@link #restoreHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)} to retrieve the
* state for this view and its children. May be overridden to modify how restoring
* happens to a view's children; for example, some views may want to not store state
* for their children.
*
* @param container The SparseArray which holds previously saved state.
*
* @see #dispatchSaveInstanceState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #restoreHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #onRestoreInstanceState(android.os.Parcelable)
*/
protected void dispatchRestoreInstanceState(SparseArray container) {
if (mID != NO_ID) {
Parcelable state = container.get(mID);
if (state != null) {
// Log.i("View", "Restoreing #" + Integer.toHexString(mID)
// + ": " + state);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED;
onRestoreInstanceState(state);
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED) == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Derived class did not call super.onRestoreInstanceState()");
}
}
}
}
還記得保存數據的時候安卓是怎麼干的嗎?嘿嘿,把當前view的ID當作鍵,把Parcelable當作值,保存到給定的container Map容器裡面。那麼現在是恢復我們之前保存的數據,那當然是要從Map容器裡面把數據讀取出來。即根據當前view的ID找出相應的Parcelable值,然後一次同時,把這個Parcelable值傳給onRestoreInstanceState()。那麼我們順著往下看onRestoreInstanceState()到底干了啥。
6、onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state)
/**
* Hook allowing a view to re-apply a representation of its internal state that had previously
* been generated by {@link #onSaveInstanceState}. This function will never be called with a
* null state.
*
* @param state The frozen state that had previously been returned by
* {@link #onSaveInstanceState}.
*
* @see #onSaveInstanceState()
* @see #restoreHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray)
* @see #dispatchRestoreInstanceState(android.util.SparseArray)
*/
@CallSuper
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED;
if (state != null && !(state instanceof AbsSavedState)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong state class, expecting View State but "
+ "received " + state.getClass().toString() + " instead. This usually happens "
+ "when two views of different type have the same id in the same hierarchy. "
+ "This view's id is " + ViewDebug.resolveId(mContext, getId()) + ". Make sure "
+ "other views do not use the same id.");
}
if (state != null && state instanceof BaseSavedState) {
mStartActivityRequestWho = ((BaseSavedState) state).mStartActivityRequestWhoSaved;
}
}
看到沒,這個過程就是從BaseSavedState裡把之前寫進去的帶有數據屬性的變量給讀取出來。好了,Android系統系統控件的狀態整個保存以及恢復的過程到此分析完成。接下來我們來看看如果是我們自定義的控件,我們應該如何來保存我們的狀態數據。既然安卓系統控件的狀態保存我們都掌握了,那麼毫無懸念我們就按照安卓系統的方案走呗。這裡我舉例看看我的自定義控件的數據保存是怎麼干的,我這裡需要自定義一個輪播效果的引導頁,那肯定得把當前頁保存起來,不然不小心旋轉屏幕或者按下back鍵,再進入就不是離開時候的那個頁面了。來看看我是怎麼保存的。
@Override
public void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
SavedState savedState = (SavedState) state;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(savedState.getSuperState());
mCurrentPage = savedState.currentPage;
mSnapPage = savedState.currentPage;
requestLayout();
}
@Override
public Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Parcelable superState = super.onSaveInstanceState();
SavedState savedState = new SavedState(superState);
savedState.currentPage = mCurrentPage;
return savedState;
}
static class SavedState extends BaseSavedState {
int currentPage;
public SavedState(Parcelable superState) {
super(superState);
}
private SavedState(Parcel in) {
super(in);
currentPage = in.readInt();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
super.writeToParcel(dest, flags);
dest.writeInt(currentPage);
}
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedDeclaration")
public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
@Override
public SavedState createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new SavedState(in);
}
@Override
public SavedState[] newArray(int size) {
return new SavedState[size];
}
};
}
看到了吧,無非是按照Android系統控件保存的那幾個步驟,先把數據保存起來,需要的時候再把它取出來。
再來看看最常見的CheckBox是怎麼保存狀態。
static class SavedState extends BaseSavedState {
boolean checked;
/**
* Constructor called from {@link CompoundButton#onSaveInstanceState()}
*/
SavedState(Parcelable superState) {
super(superState);
}
/**
* Constructor called from {@link #CREATOR}
*/
private SavedState(Parcel in) {
super(in);
checked = (Boolean)in.readValue(null);
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
super.writeToParcel(out, flags);
out.writeValue(checked);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CompoundButton.SavedState{"
+ Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this))
+ " checked=" + checked + "}";
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR
= new Parcelable.Creator() {
public SavedState createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new SavedState(in);
}
public SavedState[] newArray(int size) {
return new SavedState[size];
}
};
}
@Override
public Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Parcelable superState = super.onSaveInstanceState();
SavedState ss = new SavedState(superState);
ss.checked = isChecked();
return ss;
}
@Override
public void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
SavedState ss = (SavedState) state;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(ss.getSuperState());
setChecked(ss.checked);
requestLayout();
}
總結:在安卓中有一個類(View.BaseSavedState)專門做數據保存這件事情。
(1)通過繼承它來實現保存上一級的狀態同時允許你保存自定義的屬性。在onRestoreInstanceState()期間我們則需要做相反的事情
(2)從指定的Parcelable中獲取上一級的狀態,同時讓你的父類通過調用super.onRestoreInstanceState(ss.getSuperState())來恢復它的狀態。之後我們才能恢復我們自己的狀態
 自定義View實現 “手機淘寶”物流進程模塊進度告知UI橫向版
自定義View實現 “手機淘寶”物流進程模塊進度告知UI橫向版
這些天都在浪幾乎沒撸代碼,然後今天下午找了個下午茶時間捯饬了個自定義View來實現 很多APP都有卻沒怎麼公開的一個“進度通知的View”實現po
 Android NDK——配置NDK及使用Android studio開發Hello JNI並簡單打包so庫
Android NDK——配置NDK及使用Android studio開發Hello JNI並簡單打包so庫
引言盡管Android Studio已經越來越流行了,但很多人還是習慣於Eclipse或源碼環境下開發JNI應用。筆者是從以前在學校參加谷歌大學學術合作項目的時候接觸JN
 Android之解析GML並顯示
Android之解析GML並顯示
本例主要實現在APP中解析GML數據並顯示GML,地理標記語言(外語全稱:Geography MarkupLanguage、外語縮寫:GML),它由開放式地理信息系統協會
 Android開發筆記(一百零一)滑出式菜單
Android開發筆記(一百零一)滑出式菜單
可移動頁面MoveActivity滑出式菜單從界面上看,像極了一個水平滾動視圖HorizontalScrollView,當然也可以使用HorizontalScrollVi