編輯:關於Android編程
This archive is created by William Yi and it’s all the harvests which is properly shown to the freshmen of AS.
You can never copy this archive without permission!
Android is based on the IntelliJ Ideal which is a very good and powerful java platform and Android is the mobile operating system.
An Android app mainly contains four parts/module:
Activity BroadCastReciever ContentProvider ServiceThey mainly communicate with each by what we called ”intent” which is just like the message in OOP.
The process how an app is developed:
java
More detailed information can be found at the developer.android.com.
We always regard it as the UI of an app, and an well organized app always contains so many UIs/Activities. Each activity shows one unique function of a huge app.
For example: WeChat
it is a component that runs in the background to perform long-running operations or to perform work for remote processes.
A content provider manages a shared set of app data.
It is a component that responds to system-wide broadcast announcements.
Activities, services, and broadcast receivers are activated by an asynchronous message called an intent.
Intents bind individual components to each other at runtime(you can think of them as the messengers that request an action from other components)
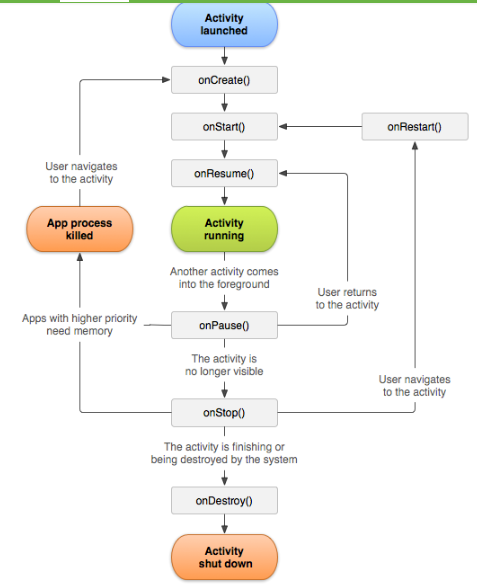
This following picture shows the details about how an activity starts and how it stops or destroys by calling several different method.
If you have a good understanding about the lifecycle about android then you will have a deeper understanding about android and the structure of android.
Linear Layout, just like it’s name, the layout is linearly independent with each other while Relative Layout is relevant to each other.
LinearLayout Example: ToggleButton and Switch(Function of Button)
activity_main.xml
MainActivity_java
package com.example.dell1.plumblossom;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.Switch;
import android.widget.ToggleButton;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ToggleButton toggleButton;
Switch aSwitch;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
toggleButton = (ToggleButton) findViewById(R.id.toggle);
aSwitch= (Switch) findViewById(R.id.aSwitch);
final LinearLayout changer = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.changer);
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener listener = new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton button, boolean isChecked) {
if(isChecked) {
changer.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
toggleButton.setChecked(true);
aSwitch.setChecked(true);
} else {
changer.setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);
toggleButton.setChecked(false);
aSwitch.setChecked(false);
}
}
};
toggleButton.setOnCheckedChangeListener(listener);
aSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener(listener);
}
}
RelativeLayout Example: Plum Blossom
activity_main.xml
TextView is the place that you can show a string in a layout while EditTest is derive from it and EditTest itself could be writeable.
TextView Example: HelloWorld
It is very easy. I suppose all of you can show t on your own.
EditText Example: FriendlyUI, CheckButton
ImageView Example: QuickContactBadge
activity_main.xml
MainActivity.java
Data and Time Example: DataPicker and TimePicker
activity_main.xml
Remain to be an extension: Content Example: AlertDialog
Extension: AdapterView, SimpleAdapterView
 Android經典面試題總結(未完待續)
Android經典面試題總結(未完待續)
1.生命周期場景演示 : 切換到該Fragment11-29 14:26:35.095: D/AppListFragment(7649): onAttach11-29 1
 Android:控件GridView的使用實例
Android:控件GridView的使用實例
如果是列表(單列多行形式)的使用ListView,如果是多行多列網狀形式的優先使用GridView。<?xml version=1.0 encoding=u
 Android NDK開發(一) 入門
Android NDK開發(一) 入門
開始之前 最近學習了一下NDK的開發, 就來分享一下. 對一個新鮮事物, 我們先解決的無非就是三件事情: 是什麼?為什麼?怎麼做?.NDK簡介 (英語:native de
 .Net程序員玩轉Android開發---(1)環境搭建
.Net程序員玩轉Android開發---(1)環境搭建
對於沒有接觸過Android開發的人員來說,可能感覺Android開發比較困難,接下來的一段時間,我們將了解Android開發的具體細節,主要是面對.NET程序員,來看看
 Android中通過ViewHelper.setTranslationY實現View移動控制(NineOldAndroids開源項目)
Android中通過ViewHelper.setTranslationY實現View移動控制(NineOldAndroids開源項目)
我們知道有不少開源工程,能實現很多不錯的效果。前幾天,我看了一個效果,剛