編輯:關於Android編程
DiffUtil是support-v7:24.2.0中的新工具類,它用來比較兩個數據集,尋找出舊數據集-》新數據集的最小變化量。
說到數據集,相信大家知道它是和誰相關的了,就是我的最愛,RecyclerView。
就我使用的這幾天來看,它最大的用處就是在RecyclerView刷新時,不再無腦mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged()。
以前無腦mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged()有兩個缺點:
不會觸發RecyclerView的動畫(刪除、新增、位移、change動畫) 性能較低,畢竟是無腦的刷新了一遍整個RecyclerView , 極端情況下:新老數據集一模一樣,效率是最低的。 使用DiffUtil後,改為如下代碼:
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffCallBack(mDatas, newDatas), true);
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(mAdapter);
它會自動計算新老數據集的差異,並根據差異情況,自動調用以下四個方法
adapter.notifyItemRangeInserted(position, count);
adapter.notifyItemRangeRemoved(position, count);
adapter.notifyItemMoved(fromPosition, toPosition);
adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(position, count, payload);
顯然,這個四個方法在執行時都是伴有RecyclerView的動畫的,且都是定向刷新方法,刷新效率蹭蹭的上升了。
老規矩,先上圖,
圖一是無腦mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged()的效果圖,可以看到刷新交互很生硬,Item突然的出現在某個位置:
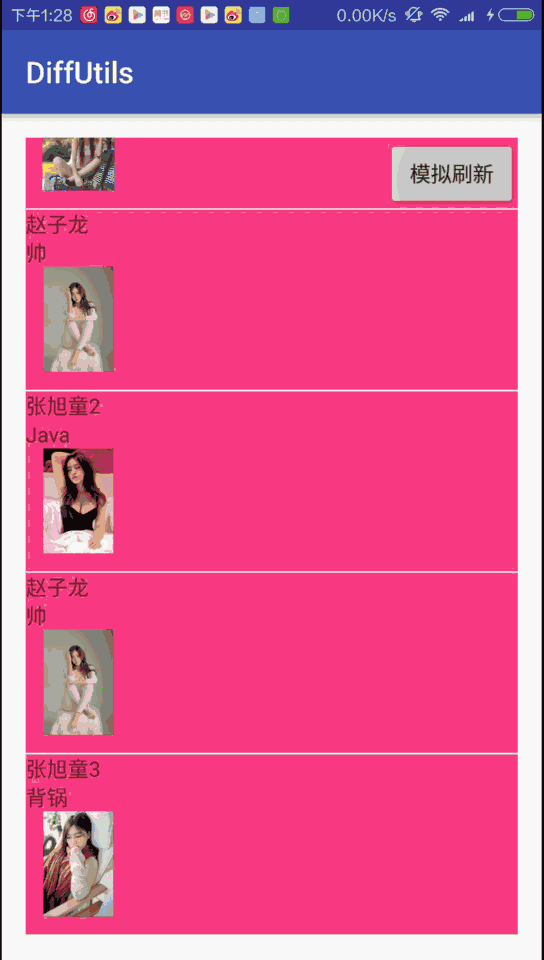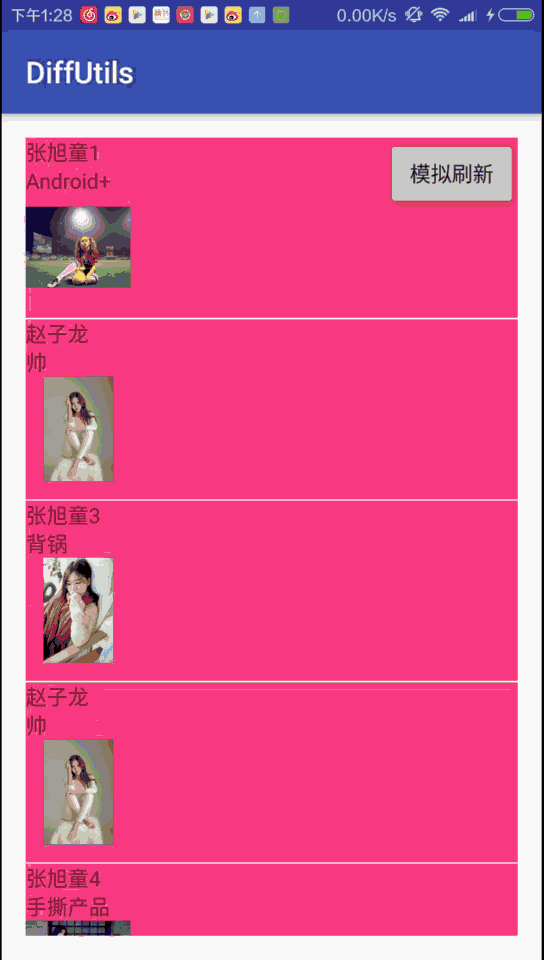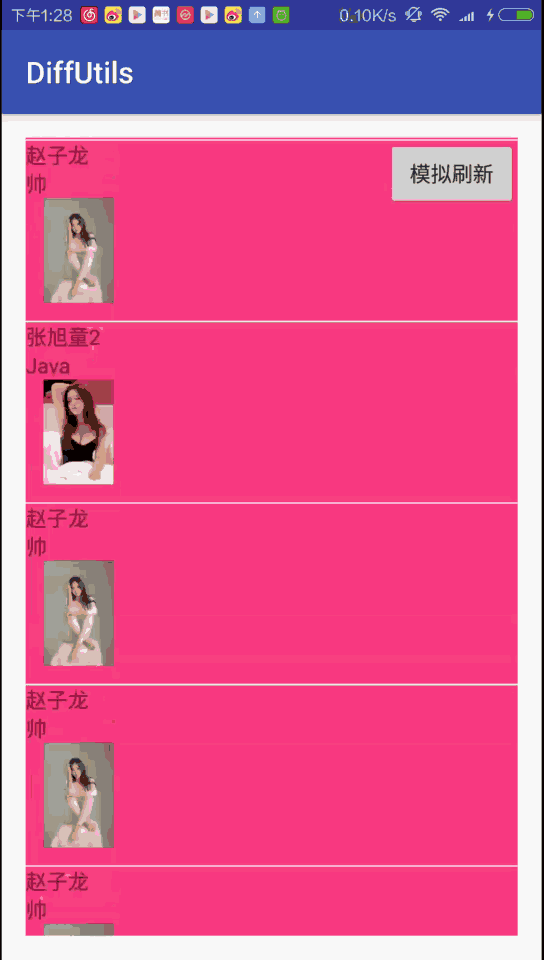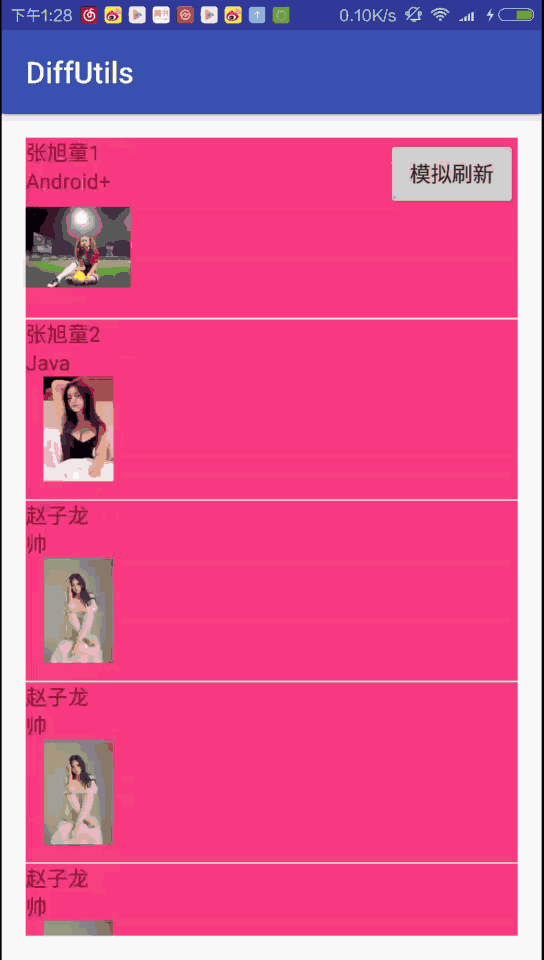
圖二是使用DiffUtils的效果圖,最明顯的是有插入、移動Item的動畫:

轉成GIF有些渣,下載文末Demo運行效果更佳哦。
本文將包含且不僅包含以下內容:1 先介紹DiffUtil的簡單用法,實現刷新時的“增量更新”效果。(“增量更新”是我自己的叫法)
2 DiffUtil的高級用法,在某項Item只有內容(data)變化,位置(position)未變化時,完成部分更新(官方稱之為Partial bind,部分綁定)。
3 了解到 RecyclerView.Adapter還有public void onBindViewHolder(VH holder, int position, List
二 DiffUtil的簡單用法前文也提到,DiffUtil是幫助我們在刷新RecyclerView時,計算新老數據集的差異,並自動調用RecyclerView.Adapter的刷新方法,以完成高效刷新並伴有Item動畫的效果。
那麼我們在學習它之前要先做一些准備工作,先寫一個普通青年版,無腦notifyDataSetChanged()刷新的Demo。
1 一個普通的JavaBean,但是實現了clone方法,僅用於寫Demo模擬刷新用,實際項目不需要,因為刷新時,數據都是從網絡拉取的。:
class TestBean implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private String desc;
....//get set方法省略
//僅寫DEMO 用 實現克隆方法
@Override
public TestBean clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
TestBean bean = null;
try {
bean = (TestBean) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
2 實現一個普普通通的RecyclerView.Adapter。
public class DiffAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter {
private final static String TAG = "zxt";
private List mDatas;
private Context mContext;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
public DiffAdapter(Context mContext, List mDatas) {
this.mContext = mContext;
this.mDatas = mDatas;
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(mContext);
}
public void setDatas(List mDatas) {
this.mDatas = mDatas;
}
@Override
public DiffVH onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new DiffVH(mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item_diff, parent, false));
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(final DiffVH holder, final int position) {
TestBean bean = mDatas.get(position);
holder.tv1.setText(bean.getName());
holder.tv2.setText(bean.getDesc());
holder.iv.setImageResource(bean.getPic());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mDatas != null ? mDatas.size() : 0;
}
class DiffVH extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView tv1, tv2;
ImageView iv;
public DiffVH(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
tv1 = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv1);
tv2 = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv2);
iv = (ImageView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.iv);
}
}
}
3 Activity代碼:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private List mDatas;
private RecyclerView mRv;
private DiffAdapter mAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initData();
mRv = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.rv);
mRv.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
mAdapter = new DiffAdapter(this, mDatas);
mRv.setAdapter(mAdapter);
}
private void initData() {
mDatas = new ArrayList<>();
mDatas.add(new TestBean("張旭童1", "Android", R.drawable.pic1));
mDatas.add(new TestBean("張旭童2", "Java", R.drawable.pic2));
mDatas.add(new TestBean("張旭童3", "背鍋", R.drawable.pic3));
mDatas.add(new TestBean("張旭童4", "手撕產品", R.drawable.pic4));
mDatas.add(new TestBean("張旭童5", "手撕測試", R.drawable.pic5));
}
/**
* 模擬刷新操作
*
* @param view
*/
public void onRefresh(View view) {
try {
List newDatas = new ArrayList<>();
for (TestBean bean : mDatas) {
newDatas.add(bean.clone());//clone一遍舊數據 ,模擬刷新操作
}
newDatas.add(new TestBean("趙子龍", "帥", R.drawable.pic6));//模擬新增數據
newDatas.get(0).setDesc("Android+");
newDatas.get(0).setPic(R.drawable.pic7);//模擬修改數據
TestBean testBean = newDatas.get(1);//模擬數據位移
newDatas.remove(testBean);
newDatas.add(testBean);
//別忘了將新數據給Adapter
mDatas = newDatas;
mAdapter.setDatas(mDatas);
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();//以前我們大多數情況下只能這樣
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
很簡單,只不過在構建新數據源newDatas時,是遍歷老數據源mDatas,調用每個data的clone()方法,確保新老數據源雖然數據一致,但是內存地址(指針不一致),這樣在後面修改newDatas裡的值時,不會牽連mDatas裡的值被一起改了。
4 activity_main.xml 刪掉了一些寬高代碼,就是一個RecyclerView和一個Button用於模擬刷新。:
以上是一個普通青年很容易寫出的,無腦notifyDataSetChanged()的demo,運行效果如第一節圖一。
但是我們都要爭做文藝青年,so
下面開始進入正題,簡單使用DiffUtil,我們需要且僅需要額外編寫一個類。想成為文藝青年,我們需要實現一個繼承自DiffUtil.Callback的類,實現它的四個abstract方法。
雖然這個類叫Callback,但是把它理解成:定義了一些用來比較新老Item是否相等的契約(Contract)、規則(Rule)的類, 更合適。
DiffUtil.Callback抽象類如下:
public abstract static class Callback {
public abstract int getOldListSize();//老數據集size
public abstract int getNewListSize();//新數據集size
public abstract boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition);//新老數據集在同一個postion的Item是否是一個對象?(可能內容不同,如果這裡返回true,會調用下面的方法)
public abstract boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition);//這個方法僅僅是上面方法返回ture才會調用,我的理解是只有notifyItemRangeChanged()才會調用,判斷item的內容是否有變化
//該方法在DiffUtil高級用法中用到 ,暫且不提
@Nullable
public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
return null;
}
}
本Demo如下實現DiffUtil.Callback,核心方法配有中英雙語注釋(說人話就是,翻譯了官方的英文注釋,方便大家更好理解)。
/**
* 介紹:核心類 用來判斷 新舊Item是否相等
* 作者:zhangxutong
* 郵箱:[email protected]
* 時間: 2016/9/12.
*/
public class DiffCallBack extends DiffUtil.Callback {
private List mOldDatas, mNewDatas;//看名字
public DiffCallBack(List mOldDatas, List mNewDatas) {
this.mOldDatas = mOldDatas;
this.mNewDatas = mNewDatas;
}
//老數據集size
@Override
public int getOldListSize() {
return mOldDatas != null ? mOldDatas.size() : 0;
}
//新數據集size
@Override
public int getNewListSize() {
return mNewDatas != null ? mNewDatas.size() : 0;
}
/**
* Called by the DiffUtil to decide whether two object represent the same Item.
* 被DiffUtil調用,用來判斷 兩個對象是否是相同的Item。
* For example, if your items have unique ids, this method should check their id equality.
* 例如,如果你的Item有唯一的id字段,這個方法就 判斷id是否相等。
* 本例判斷name字段是否一致
*
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list
* @return True if the two items represent the same object or false if they are different.
*/
@Override
public boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
return mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition).getName().equals(mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition).getName());
}
/**
* Called by the DiffUtil when it wants to check whether two items have the same data.
* 被DiffUtil調用,用來檢查 兩個item是否含有相同的數據
* DiffUtil uses this information to detect if the contents of an item has changed.
* DiffUtil用返回的信息(true false)來檢測當前item的內容是否發生了變化
* DiffUtil uses this method to check equality instead of {@link Object#equals(Object)}
* DiffUtil 用這個方法替代equals方法去檢查是否相等。
* so that you can change its behavior depending on your UI.
* 所以你可以根據你的UI去改變它的返回值
* For example, if you are using DiffUtil with a
* {@link android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView.Adapter RecyclerView.Adapter}, you should
* return whether the items' visual representations are the same.
* 例如,如果你用RecyclerView.Adapter 配合DiffUtil使用,你需要返回Item的視覺表現是否相同。
* This method is called only if {@link #areItemsTheSame(int, int)} returns
* {@code true} for these items.
* 這個方法僅僅在areItemsTheSame()返回true時,才調用。
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list which replaces the
* oldItem
* @return True if the contents of the items are the same or false if they are different.
*/
@Override
public boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
TestBean beanOld = mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition);
TestBean beanNew = mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition);
if (!beanOld.getDesc().equals(beanNew.getDesc())) {
return false;//如果有內容不同,就返回false
}
if (beanOld.getPic() != beanNew.getPic()) {
return false;//如果有內容不同,就返回false
}
return true; //默認兩個data內容是相同的
}
注釋張寫了這麼詳細的注釋+簡單的代碼,相信一眼可懂。
然後在使用時,注釋掉你以前寫的notifyDatasetChanged()方法吧,替換成以下代碼:
//文藝青年新寵
//利用DiffUtil.calculateDiff()方法,傳入一個規則DiffUtil.Callback對象,和是否檢測移動item的 boolean變量,得到DiffUtil.DiffResult 的對象
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffCallBack(mDatas, newDatas), true);
//利用DiffUtil.DiffResult對象的dispatchUpdatesTo()方法,傳入RecyclerView的Adapter,輕松成為文藝青年
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(mAdapter);
//別忘了將新數據給Adapter
mDatas = newDatas;
mAdapter.setDatas(mDatas);
講解:步驟一在將newDatas 設置給Adapter之前,先調用DiffUtil.calculateDiff()方法,計算出新老數據集轉化的最小更新集,就是DiffUtil.DiffResult對象。
DiffUtil.calculateDiff()方法定義如下:
第一個參數是DiffUtil.Callback對象,
第二個參數代表是否檢測Item的移動,改為false算法效率更高,按需設置,我們這裡是true。
public static DiffResult calculateDiff(Callback cb, boolean detectMoves)
步驟二然後利用DiffUtil.DiffResult對象的dispatchUpdatesTo()方法,傳入RecyclerView的Adapter,替代普通青年才用的mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged()方法。
查看源碼可知,該方法內部,就是根據情況調用了adapter的四大定向刷新方法。
public void dispatchUpdatesTo(final RecyclerView.Adapter adapter) {
dispatchUpdatesTo(new ListUpdateCallback() {
@Override
public void onInserted(int position, int count) {
adapter.notifyItemRangeInserted(position, count);
}
@Override
public void onRemoved(int position, int count) {
adapter.notifyItemRangeRemoved(position, count);
}
@Override
public void onMoved(int fromPosition, int toPosition) {
adapter.notifyItemMoved(fromPosition, toPosition);
}
@Override
public void onChanged(int position, int count, Object payload) {
adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(position, count, payload);
}
});
}
小結:所以說,DiffUtil不僅僅只能和RecyclerView配合,我們也可以自己實現ListUpdateCallback接口的四個方法去做一些事情。(我暫時不負責任隨便一項想,想到可以配合自己項目裡的九宮格控件?或者優化我上篇文章寫的NestFullListView?小安利,見 ListView、RecyclerView、ScrollView裡嵌套ListView 相對優雅的解決方案:http://blog.csdn.net/zxt0601/article/details/52494665)
至此,我們已進化成文藝青年,運行效果和第一節圖二基本一致,
唯一不同的是此時adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged()會有Item白光一閃的更新動畫 (本文Demo的postion為0的item)。 這個Item一閃的動畫有人喜歡有人恨,不過都不重要了,
因為當我們學會了第三節的DiffUtil搞基用法,你愛不愛這個ItemChange動畫,它都將隨風而去。(不知道是不是官方bug)
效果就是第一節的圖二,我們的item0其實圖片和文字都變化了,但是這個改變並沒有伴隨任何動畫。
讓我們邁向 文藝青年中的文藝青年 之路。
三 DiffUtil的高級用法理論:高級用法只涉及到兩個方法,
我們需要分別實現DiffUtil.Callback的
public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition)方法,
返回的Object就是表示Item改變了哪些內容。
再配合RecyclerView.Adapter的
public void onBindViewHolder(VH holder, int position, List
好吧,那我們就先看看這個方法是何方神聖:
在v7-24.2.0的源碼裡,它長這個樣子:
/**
* Called by RecyclerView to display the data at the specified position. This method
* should update the contents of the {@link ViewHolder#itemView} to reflect the item at
* the given position.
*
* Note that unlike {@link android.widget.ListView}, RecyclerView will not call this method * again if the position of the item changes in the data set unless the item itself is * invalidated or the new position cannot be determined. For this reason, you should only * use the position parameter while acquiring the related data item inside * this method and should not keep a copy of it. If you need the position of an item later * on (e.g. in a click listener), use {@link ViewHolder#getAdapterPosition()} which will * have the updated adapter position. *
* Partial bind vs full bind: *
* The payloads parameter is a merge list from {@link #notifyItemChanged(int, Object)} or * {@link #notifyItemRangeChanged(int, int, Object)}. If the payloads list is not empty, * the ViewHolder is currently bound to old data and Adapter may run an efficient partial * update using the payload info. If the payload is empty, Adapter must run a full bind. * Adapter should not assume that the payload passed in notify methods will be received by * onBindViewHolder(). For example when the view is not attached to the screen, the * payload in notifyItemChange() will be simply dropped. * * @param holder The ViewHolder which should be updated to represent the contents of the * item at the given position in the data set. * @param position The position of the item within the adapter's data set. * @param payloads A non-null list of merged payloads. Can be empty list if requires full * update. */ public void onBindViewHolder(VH holder, int position, List
原來它內部就僅僅調用了兩個參數的onBindViewHolder(holder, position) ,(題外話,哎喲喂,我的NestFullListView 的Adapter也有幾分神似這種寫法,看來我離Google大神又近了一步)
看到這我才明白,其實onBind的入口,就是這個方法,它才是和onCreateViewHolder對應的方法,
源碼往下翻幾行可以看到有個public final void bindViewHolder(VH holder, int position),它內部調用了三參的onBindViewHolder。
關於RecyclerView.Adapter 也不是三言兩句說的清楚的。(其實我只掌握到這裡)
好了不再跑題,回到我們的三參數的onBindViewHolder(VH holder, int position, List
翻譯:由RecyclerView調用 用來在在指定的位置顯示數據。
這個方法應該更新ViewHolder裡的ItemView的內容,以反映在給定的位置 Item(的變化)。
請注意,不像ListView,如果給定位置的item的數據集變化了,RecyclerView不會再次調用這個方法,除非item本身失效了(invalidated ) 或者新的位置不能確定。
出於這個原因,在這個方法裡,你應該只使用 postion參數 去獲取相關的數據item,而且不應該去保持 這個數據item的副本。
如果你稍後需要這個item的position,例如設置clickListener。應該使用 ViewHolder.getAdapterPosition(),它能提供 更新後的位置。
(二筆的我看到這裡發現 這是在講解兩參的onbindViewHolder方法
下面是這個三參方法的獨特部分:)
**部分(partial)綁定**vs完整(full)綁定
payloads 參數 是一個從(notifyItemChanged(int, Object)或notifyItemRangeChanged(int, int, Object))裡得到的合並list。
如果payloads list 不為空,那麼當前綁定了舊數據的ViewHolder 和Adapter, 可以使用 payload的數據進行一次 高效的部分更新。
如果payload 是空的,Adapter必須進行一次完整綁定(調用兩參方法)。
Adapter不應該假定(想當然的認為) 在那些notifyxxxx通知方法傳遞過來的payload, 一定會在 onBindViewHolder()方法裡收到。(這一句翻譯不好 QAQ 看舉例就好)
舉例來說,當View沒有attached 在屏幕上時,這個來自notifyItemChange()的payload 就簡單的丟掉好了。
payloads對象不會為null,但是它可能是空(empty),這時候需要完整綁定(所以我們在方法裡只要判斷isEmpty就好,不用重復判空)。
作者語:這方法是一個高效的方法。 我是個低效的翻譯者,我看了40+分鐘。才終於明白,重要的部分已經加粗顯示。
實戰:說了這麼多話,其實用起來超級簡單:
先看如何使用getChangePayload()方法,又附帶了中英雙語注釋
/**
* When {@link #areItemsTheSame(int, int)} returns {@code true} for two items and
* {@link #areContentsTheSame(int, int)} returns false for them, DiffUtil
* calls this method to get a payload about the change.
*
* 當{@link #areItemsTheSame(int, int)} 返回true,且{@link #areContentsTheSame(int, int)} 返回false時,DiffUtils會回調此方法,
* 去得到這個Item(有哪些)改變的payload。
*
* For example, if you are using DiffUtil with {@link RecyclerView}, you can return the
* particular field that changed in the item and your
* {@link android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView.ItemAnimator ItemAnimator} can use that
* information to run the correct animation.
*
* 例如,如果你用RecyclerView配合DiffUtils,你可以返回 這個Item改變的那些字段,
* {@link android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView.ItemAnimator ItemAnimator} 可以用那些信息去執行正確的動畫
*
* Default implementation returns {@code null}.\
* 默認的實現是返回null
*
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list
* @return A payload object that represents the change between the two items.
* 返回 一個 代表著新老item的改變內容的 payload對象,
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
//實現這個方法 就能成為文藝青年中的文藝青年
// 定向刷新中的部分更新
// 效率最高
//只是沒有了ItemChange的白光一閃動畫,(反正我也覺得不太重要)
TestBean oldBean = mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition);
TestBean newBean = mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition);
//這裡就不用比較核心字段了,一定相等
Bundle payload = new Bundle();
if (!oldBean.getDesc().equals(newBean.getDesc())) {
payload.putString("KEY_DESC", newBean.getDesc());
}
if (oldBean.getPic() != newBean.getPic()) {
payload.putInt("KEY_PIC", newBean.getPic());
}
if (payload.size() == 0)//如果沒有變化 就傳空
return null;
return payload;//
}
簡單的說,這個方法返回一個Object類型的payload,它包含了某個item的變化了的那些內容。
我們這裡使用Bundle保存這些變化。
在Adapter裡如下重寫三參的onBindViewHolder:
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(DiffVH holder, int position, List
這裡傳遞過來的payloads是一個List,由注釋可知,一定不為null,所以我們判斷是否是empty,
如果是empty,就調用兩參的函數,進行一次Full Bind。
如果不是empty,就進行partial bind,
通過下標0取出我們在getChangePayload方法裡返回的payload,然後遍歷payload的key,根據key檢索,如果payload裡攜帶有相應的改變,就取出來 然後更新在ItemView上。
(這裡,通過mDatas獲得的也是最新數據源的數據,所以用payload的數據或者新數據的數據 進行更新都可以)
至此,我們已經掌握了刷新RecyclerView,文藝青年中最文藝的那種寫法。
四 在子線程中使用DiffUtil在DiffUtil的源碼頭部注釋中介紹了DiffUtil的相關信息,
DiffUtil內部采用的Eugene W. Myers’s difference 算法,但該算法不能檢測移動的item,所以Google在其基礎上改進支持檢測移動項目,但是檢測移動項目,會更耗性能。
在有1000項數據,200處改動時,這個算法的耗時:
打開了移動檢測時:平均值:27.07ms,中位數:26.92ms。
關閉了移動檢測時:平均值:13.54ms,中位數:13.36ms。
有興趣可以自行去源碼頭部閱讀注釋,對我們比較有用的是其中一段提到,
如果我們的list過大,這個計算出DiffResult的時間還是蠻久的,所以我們應該將獲取DiffResult的過程放到子線程中,並在主線程中更新RecyclerView。
這裡我采用Handler配合DiffUtil使用:
代碼如下:
private static final int H_CODE_UPDATE = 1;
private List mNewDatas;//增加一個變量暫存newList
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case H_CODE_UPDATE:
//取出Result
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = (DiffUtil.DiffResult) msg.obj;
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(mAdapter);
//別忘了將新數據給Adapter
mDatas = mNewDatas;
mAdapter.setDatas(mDatas);
break;
}
}
};
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//放在子線程中計算DiffResult
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffCallBack(mDatas, mNewDatas), true);
Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage(H_CODE_UPDATE);
message.obj = diffResult;//obj存放DiffResult
message.sendToTarget();
}
}).start();
就是簡單的Handler使用,不再贅述。
五總結和其他1 其實本文代碼量很少,可下載Demo查看,一共就四個類。
但是不知不覺又被我寫的這麼長,主要涉及到了一些源碼的注釋的翻譯,方便大家更好的理解。
2 DiffUtil很適合下拉刷新這種場景,
更新的效率提高了,而且帶動畫,而且~還不用你動腦子算了。
不過若是就做個刪除 點贊這種,完全不用DiffUtils。自己記好postion,判斷一下postion在不在屏幕裡,調用那幾個定向刷新的方法即可。
3 其實DiffUtil不是只能和RecyclerView.Adapter配合使用,
我們可以自己實現 ListUpdateCallback接口,利用DIffUtil幫我們找到新舊數據集的最小差異集 來做更多的事情。
4 注意 寫DEMO的時候,用於比較的新老數據集,不僅ArrayList不同,裡面每個data也要不同。 否則changed 無法觸發。
實際項目中遇不到,因為新數據往往是網絡來的。
5 今天是中秋節的最後一天,我們公司居然就開始上班了!!!氣憤之余,我怒碼一篇DiffUtil,我都不需要用DiffUtil,也能輕易比較出我們公司和其他公司的差異。QAQ,而且今天狀態不佳,居然寫了8個小時才完工。本以為這篇文章是可以入選微作文集的,沒想到也是蠻長的。沒有耐心的其實可以下載DEMO看看,代碼量沒多少,使用起來還是很輕松的。
github傳送門:
https://github.com/mcxtzhang/DiffUtils
 Android自定義等待對話框
Android自定義等待對話框
最近,看了好多的APP的等待對話框,發現自己的太lower,於是就研究了一番,最後經過苦心努力,實現一個。 自定義一個LoadingIndicatorView(exte
 Android UI開發神兵利器之Angrytools
Android UI開發神兵利器之Angrytools
最近很多人在問我,個人App開發者如何去設計UI。 其實這是個人開發者最頭痛的問題,搞技術的人,確實沒法做到面面俱到,不可能花大量的時間去切圖,去做原型設計,去做美工。
 [Android 插件化(一)] DynamicLoadApk的用法
[Android 插件化(一)] DynamicLoadApk的用法
1 簡介Android大型項目中為了減小apk的體積,可以采用插件化的方法,即一些不常用的功能獨立成插件,當用戶需要的使用的時候再從服務器上下載回來,動態加載。這樣就避免
 Android中的Telephony學習筆記(2)
Android中的Telephony學習筆記(2)
上一篇文章中學習了android.provider中Telephony類。這一篇文章學習android.telephony包中的類,這些類是android提供給上層調用的