編輯:關於Android編程
每一個Activity組件都有一個關聯的Window對象,用來描述一個應用程序窗口。每一個應用程序窗口內部又包含有一個View對象,用來描述應用程序窗口的視圖。應用程序窗口視圖是真正用來實現UI內容和布局的,也就是說,每一個Activity組件的UI內容和布局都是通過與其所關聯的一個Window對象的內部的一個View對象來實現的。在本文中,我們就詳細分析應用程序窗口視圖的創建過程。
應用程序窗口內部所包含的視圖對象的實際類型為DecorView。DecorView類繼承了View類,是作為容器(ViewGroup)來使用的,它的實現如圖
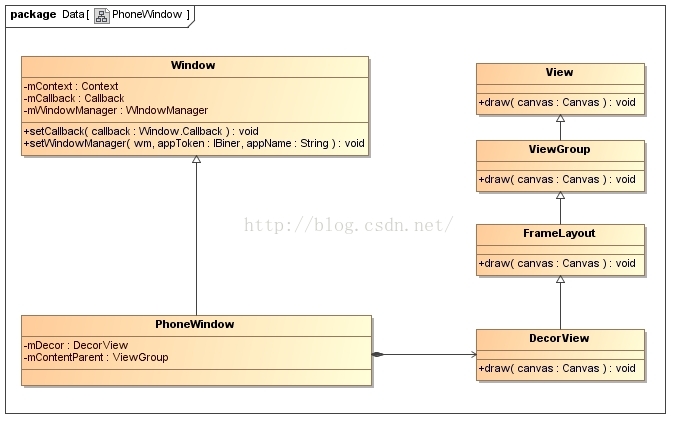
每一個Activity對象都有一個關聯的ViewRootImpl對象,相當於是MVC模型中的Controller,它有以下職責:
1. 負責為應用程序窗口視圖創建Surface。
2. 配合WindowManagerService來管理系統的應用程序窗口。
3. 負責管理、布局和渲染應用程序窗口視圖的UI。
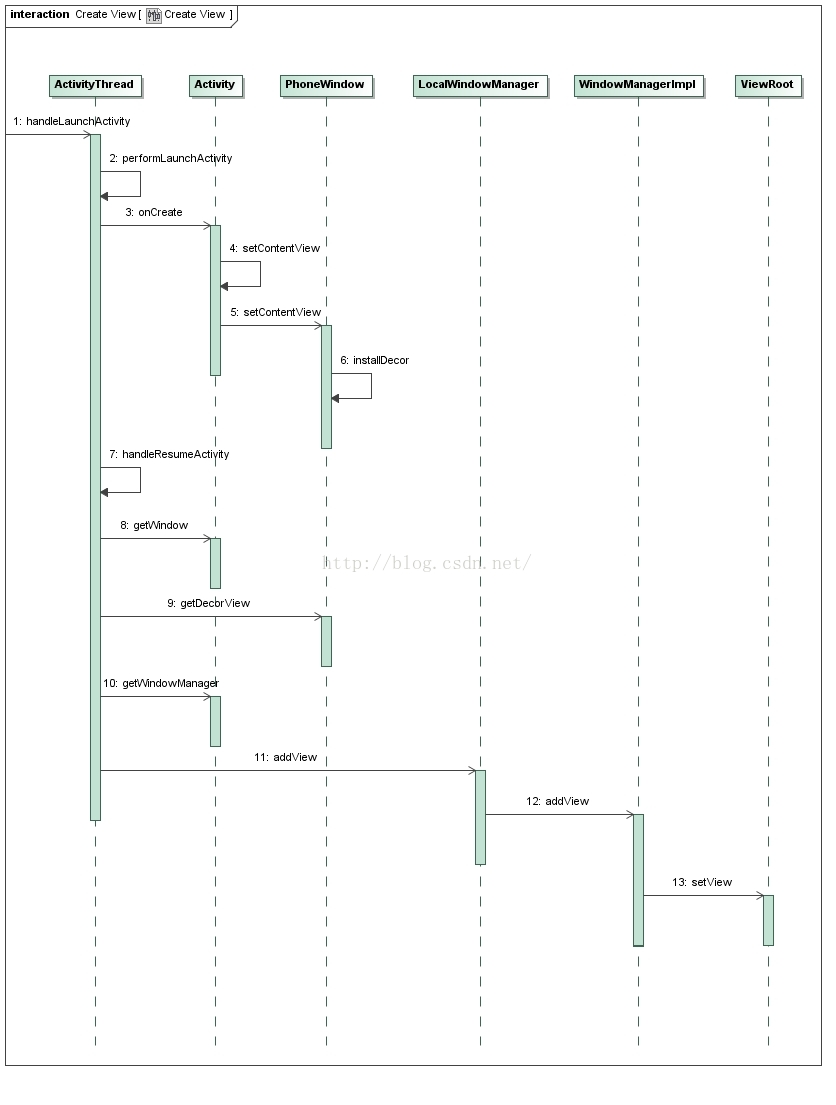
從前面Android應用程序啟動過程源代碼分析一文可以知道,Activity組件在啟動的過程中,會調用ActivityThread類的成員函數handleLaunchActivity,用來創建以及首次激活Activity組件,因此,接下來我們就從這個函數開始,具體分析應用程序窗口的視圖對象及其所關聯的ViewRootImpl對象的創建過程,如圖所示
一般在Activity的子類的onCreate方法中都會實現setContentView函數,我們來看Activity的這個函數:
public void setContentView(View view) {
getWindow().setContentView(view);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
調用了PhoneWindow的setContentView函數,而在這個函數中調用了installDecor函數來創建DecorView對象
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
final Scene newScene = new Scene(mContentParent, view);
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}
在installDecor函數中調用了generateDecor函數來創建DecorView
private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor();
......
protected DecorView generateDecor() {
return new DecorView(getContext(), -1);
}
下面我們再從ActivityThread的handleResumeActivity函數看,先調用了performResumeActivity函數來查找這個Activity,後面主要調用了WindowManager的addView函數。
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
// TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration
ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide);
if (r != null) {
final Activity a = r.activity;
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Resume " + r + " started activity: " +
a.mStartedActivity + ", hideForNow: " + r.hideForNow
+ ", finished: " + a.mFinished);
final int forwardBit = isForward ?
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
// If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager,
// and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity,
// then go ahead and add the window.
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
if (!willBeVisible) {
try {
willBeVisible = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().willActivityBeVisible(
a.getActivityToken());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);
}
我們先來看performResumeActivity函數,這個函數主要是根據token來尋找ActivityClientRecord,然後調用了Activity的performResume方法。
public final ActivityClientRecord performResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing resume of " + r
+ " finished=" + r.activity.mFinished);
if (r != null && !r.activity.mFinished) {
if (clearHide) {
r.hideForNow = false;
r.activity.mStartedActivity = false;
}
try {
r.activity.onStateNotSaved();
r.activity.mFragments.noteStateNotSaved();
if (r.pendingIntents != null) {
deliverNewIntents(r, r.pendingIntents);
r.pendingIntents = null;
}
if (r.pendingResults != null) {
deliverResults(r, r.pendingResults);
r.pendingResults = null;
}
r.activity.performResume();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_AM_ON_RESUME_CALLED,
UserHandle.myUserId(), r.activity.getComponentName().getClassName());
r.paused = false;
r.stopped = false;
r.state = null;
r.persistentState = null;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to resume activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
return r;
}
後面有調用了Activity的getWindowManager方法獲取WindowManager,之前的博客有分析過,這個WindowManager就是WindowManagerImpl對象。下面也就是調用了WindowManagerImpl的addView函數。
我們來看WindowManagerImpl的addView函數,其實就是調用了WindowManagerGlobal的addView函數
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
之前也分析過WindowManagerGlobal,它有3個重要的成員變量:
private final ArrayList mViews = new ArrayList();//所有的DecorView對象
private final ArrayList mRoots = new ArrayList();//所有的ViewRootImpl對象
private final ArrayList mParams =//所有頂層View的layout參數
new ArrayList();
我們再來看WindowManagerGlobal的addView函數,這個函數主要是創建了ViewRootImpl,並且把DecorView,RootViewRootImpl,layout參數都保存起來了。然後調用了ViewRootImpl的setView函數。
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
......
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
}
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
synchronized (mLock) {
final int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
}
throw e;
}
}
下面我們再來看看ViewRootImpl的setView函數:
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
mAttachInfo.mDisplayState = mDisplay.getState();
mDisplayManager.registerDisplayListener(mDisplayListener, mHandler);
mViewLayoutDirectionInitial = mView.getRawLayoutDirection();
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(view);
mWindowAttributes.copyFrom(attrs);
if (mWindowAttributes.packageName == null) {
mWindowAttributes.packageName = mBasePackageName;
}
attrs = mWindowAttributes;
// Keep track of the actual window flags supplied by the client.
mClientWindowLayoutFlags = attrs.flags;
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
if (view instanceof RootViewSurfaceTaker) {
mSurfaceHolderCallback =
((RootViewSurfaceTaker)view).willYouTakeTheSurface();
if (mSurfaceHolderCallback != null) {
mSurfaceHolder = new TakenSurfaceHolder();
mSurfaceHolder.setFormat(PixelFormat.UNKNOWN);
}
}
// Compute surface insets required to draw at specified Z value.
// TODO: Use real shadow insets for a constant max Z.
if (!attrs.hasManualSurfaceInsets) {
final int surfaceInset = (int) Math.ceil(view.getZ() * 2);
attrs.surfaceInsets.set(surfaceInset, surfaceInset, surfaceInset, surfaceInset);
}
CompatibilityInfo compatibilityInfo = mDisplayAdjustments.getCompatibilityInfo();
mTranslator = compatibilityInfo.getTranslator();
// If the application owns the surface, don't enable hardware acceleration
if (mSurfaceHolder == null) {
enableHardwareAcceleration(attrs);
}
boolean restore = false;
if (mTranslator != null) {
mSurface.setCompatibilityTranslator(mTranslator);
restore = true;
attrs.backup();
mTranslator.translateWindowLayout(attrs);
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.d(TAG, "WindowLayout in setView:" + attrs);
if (!compatibilityInfo.supportsScreen()) {
attrs.privateFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW;
mLastInCompatMode = true;
}
mSoftInputMode = attrs.softInputMode;
mWindowAttributesChanged = true;
mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = WindowManager.LayoutParams.EVERYTHING_CHANGED;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = view;
mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired = mTranslator != null;
mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale =
mTranslator == null ? 1.0f : mTranslator.applicationScale;
if (panelParentView != null) {
mAttachInfo.mPanelParentWindowToken
= panelParentView.getApplicationWindowToken();
}
mAdded = true;
int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();//繪制UI布局
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();//創建按鍵通道
}
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
if (mTranslator != null) {
mTranslator.translateRectInScreenToAppWindow(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
}
mPendingOverscanInsets.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
mPendingContentInsets.set(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
mPendingStableInsets.set(mAttachInfo.mStableInsets);
mPendingVisibleInsets.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Added window " + mWindow);
if (res < WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_OKAY) {
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mAdded = false;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
switch (res) {
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN:
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_SUBWINDOW_TOKEN:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- token " + attrs.token
+ " is not valid; is your activity running?");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_NOT_APP_TOKEN:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- token " + attrs.token
+ " is not for an application");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_APP_EXITING:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- app for token " + attrs.token
+ " is exiting");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_DUPLICATE_ADD:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window -- window " + mWindow
+ " has already been added");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_STARTING_NOT_NEEDED:
// Silently ignore -- we would have just removed it
// right away, anyway.
return;
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_MULTIPLE_SINGLETON:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window " + mWindow +
" -- another window of this type already exists");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED:
throw new WindowManager.BadTokenException(
"Unable to add window " + mWindow +
" -- permission denied for this window type");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_DISPLAY:
throw new WindowManager.InvalidDisplayException(
"Unable to add window " + mWindow +
" -- the specified display can not be found");
case WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_TYPE:
throw new WindowManager.InvalidDisplayException(
"Unable to add window " + mWindow
+ " -- the specified window type is not valid");
}
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to add window -- unknown error code " + res);
}
if (view instanceof RootViewSurfaceTaker) {
mInputQueueCallback =
((RootViewSurfaceTaker)view).willYouTakeTheInputQueue();
}
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,//創建按鍵應用層接受對象
Looper.myLooper());
}
view.assignParent(this);
mAddedTouchMode = (res & WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0;
mAppVisible = (res & WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_APP_VISIBLE) != 0;
if (mAccessibilityManager.isEnabled()) {
mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager.ensureConnection();
}
if (view.getImportantForAccessibility() == View.IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_AUTO) {
view.setImportantForAccessibility(View.IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_YES);
}
// Set up the input pipeline.
CharSequence counterSuffix = attrs.getTitle();
mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage();//按鍵的一些流程類
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage,
"aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage);
InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage,
"aq:ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage);
InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage,
"aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix);
mFirstInputStage = nativePreImeStage;
mFirstPostImeInputStage = earlyPostImeStage;
mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName = "aq:pending:" + counterSuffix;
}
}
}
這個函數主要是調用了requestLayout函數來對應用窗口的UI布局,然後創建了InputChannel。調用ViewRoot類的靜態成員變量sWindowSession所描述的一個類型為Session的Binder代理對象的成員函數add來請求WindowManagerService增加一個WindowState對象,以便可以用來描述當前正在處理的一個ViewRootImpl所關聯的一個應用程序窗口。
最後創建了WindowInputEventReceiver應用層的按鍵接受,以及一些按鍵在應用層的流程的相關類。
 Android應用APP自動更新功能的代碼實現
Android應用APP自動更新功能的代碼實現
由於Android項目開源所致,市面上出現了N多安卓軟件市場。為了讓我們開發的軟件有更多的用戶使用,我們需要向N多市場發布,軟件升級後,我們也必須到安卓市場上進行更新,給
 如何搭配最新的安卓開發環境
如何搭配最新的安卓開發環境
本章只是寫了如何配置JDK,以及adt-bundle的配置。對於以前的adt-bundle的版本,會自帶CPU/ABI系統鏡像,經過本文所描述的兩個步驟後可以直接創建AV
 Android 善用Okio簡化處理I/O操作
Android 善用Okio簡化處理I/O操作
Okio庫是一個由square公司開發的,它補充了java.io和java.nio的不足,以便能夠更加方便,快速的訪問、存儲和處理你的數據。而OkHttp的底層也使用該庫
 從源碼角度帶你分析 Android View 事件分發 dispatchTouchEvent,onTouch,onTouchEvent,onClick邏輯順序過程(一)
從源碼角度帶你分析 Android View 事件分發 dispatchTouchEvent,onTouch,onTouchEvent,onClick邏輯順序過程(一)
關於Android View 事件分發過程的文章網絡上可以搜到一把大,這裡貼一篇代碼性的文章,作者也是個牛人:Android事件分發機制完全解析,帶你從源碼的角度徹底理解