編輯:關於Android編程
在Activity中含有EditText時,我們常常在AndroidManifest.xml中為該Activity設置android:windowSoftInputMode屬性,其中最常用的值就是adjustResize和adjustPan。在此請思考幾個問題:
adjustResize和adjustPan有什麼區別? adjustResize和adjustPan的應用場景有何差異? 當設置android:windowSoftInputMode後如何監聽軟鍵盤的彈起與隱藏?在看到第三個問題的時候,有人會想:
干嘛要去監聽軟鍵盤的彈起呢?有什麼用呢?
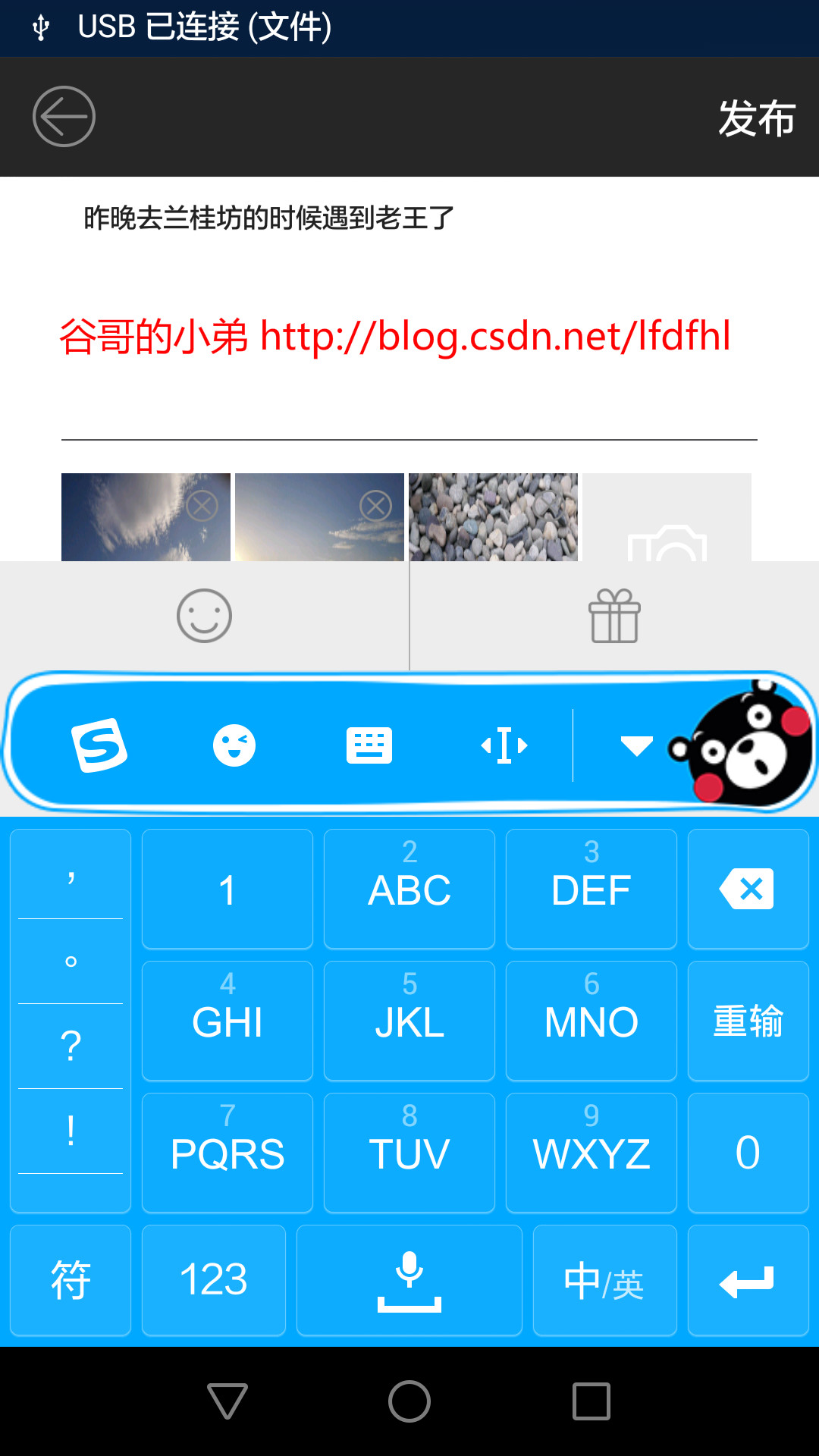
嗯哼,看到了吧:當鍵盤彈起來的時候在緊靠鍵盤上方的地方出現了一個自定義布局,點擊笑臉就可以發送專屬emoji表情,點擊禮盒就可以發送福利。
當然,在鍵盤收起的時候這個布局也就不可見了。
除此以外,在其他不少場景也會有類似的UI設計。在這些情況下,我們都要監聽鍵盤軟鍵盤的彈起與隱藏。善良的童鞋會想:這個沒難度呀,調用一下官方的API就行。很久以前,我也是這麼想的。可是,事與願違,官方文檔中根本就沒有提供檢測軟鍵盤狀態的接口。
既然官方沒有把這個API洗干淨整整齊齊的擺在眼前,那我們就自己實現它。
adjustResize
在AndroidManifest.xml中為該Activity設置
android:windowSoftInputMode=”adjustResize”
該模式下系統會調整屏幕的大小以保證軟鍵盤的顯示空間。
舉個例子:
屏幕的高為1920px,那麼整個Activity的布局高度也為1920px。當設置該屬性後點擊界面中的EditText,此時彈出軟鍵盤其高度為800px。為了完整地顯示此軟鍵盤,系統會調整Activity布局的高度為1920px-800px=1120px。
所以,此時的布局與原本的布局就發生了一些變化,比如:整體布局顯示不完整,控件外觀的變形,控件顯示位置的錯亂等等。這些現象都是因為原布局的高度變小所導致。
以下,再結合代碼詳細分析該情況。
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
/**
* 原創作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class RelativeLayoutSubClass extends RelativeLayout{
private OnSoftKeyboardListener mSoftKeyboardListener;
public RelativeLayoutSubClass(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
System.out.println("----> onMeasure");
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mSoftKeyboardListener.onSoftKeyboardChange();
System.out.println("----> onLayout");
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
System.out.println("----> onSizeChanged");
}
public void setSoftKeyboardListener(OnSoftKeyboardListener listener){
mSoftKeyboardListener=listener;
}
public interface OnSoftKeyboardListener{
public void onSoftKeyboardChange();
}
}
我們將該自定義RelativeLayout作為Activity布局的根
效果如下:

點擊EditText,彈出軟鍵盤:
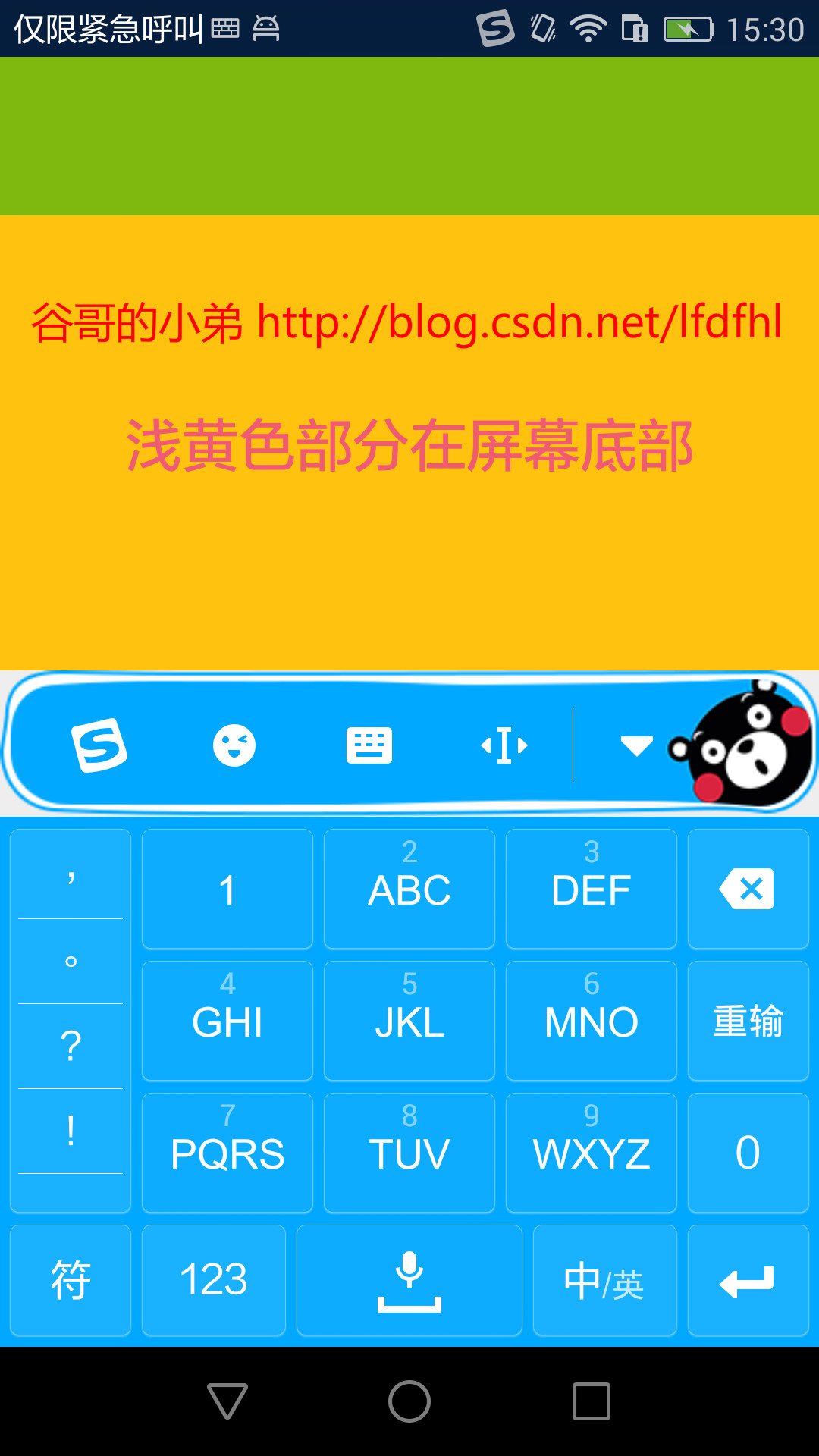
現象呢,我們已經看到了。我們再來瞅瞅當軟鍵盤狀態變化的時候RelativeLayoutSubClass中有哪些行為發生:
軟鍵盤狀態變化時會調用其onMeasure(),onLayout(),onSizeChanged() 在onSizeChanged()中可以確知軟鍵盤狀態變化前後布局寬高的數值至此,發現一個關鍵點:onSizeChanged()
我們可以以此為切入點檢測軟鍵盤的狀態變化,所以定義一個接口OnSoftKeyboardListener提供給Activity使用,具體代碼如下:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
/**
* 原創作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private RelativeLayoutSubClass mRootLayout;
private int screenHeight;
private int screenWidth;
private int threshold;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init(){
screenHeight=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
screenWidth=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
threshold=screenHeight/3;
mRootLayout= (RelativeLayoutSubClass) findViewById(R.id.rootLayout);
mRootLayout.setSoftKeyboardListener(new RelativeLayoutSubClass.OnSoftKeyboardListener() {
@Override
public void onSoftKeyboardChange(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
if (oldh-h>threshold){
System.out.println("----> 軟鍵盤彈起");
}else if(h-oldh>threshold){
System.out.println("----> 軟鍵盤收起");
}
}
});
}
}
請注意onSoftKeyboardChange()的回調:
假若oldh-h大於屏幕高度的三分之一,則軟鍵盤彈起 假若h-oldh大於屏幕高度的三分之一,則軟鍵盤收起小結:
當軟鍵盤狀態發生改變時,通過對Activity布局文件根Layout的onSizeChanged()判斷軟鍵盤的彈起或隱藏
adjustPan
在AndroidManifest.xml中為該Activity設置
android:windowSoftInputMode=”adjustPan”
該模式下系統會將界面中的內容自動移動從而使得焦點不被鍵盤覆蓋,即用戶能總是看到輸入內容的部分
比如,還是剛才的那個布局,現在將其windowSoftInputMode設置為adjustPan再點擊EditText,效果如下:
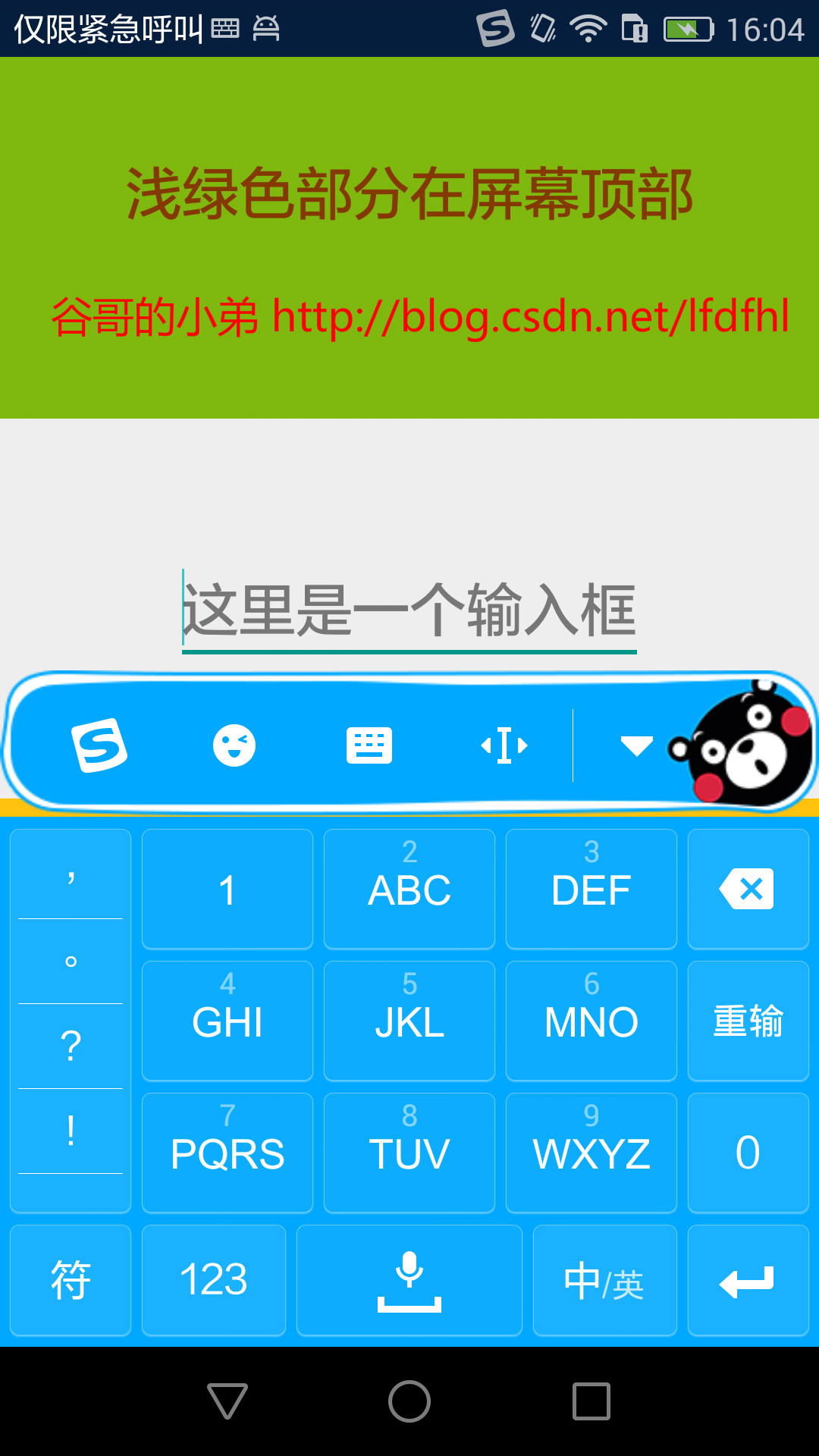
嗯哼,看到了吧:
為了避免軟鍵盤彈起後遮擋EditText,系統將整個布局上移了,也就是我們常說的將布局頂上去了。
此時再來看看當軟鍵盤狀態變化的時候RelativeLayoutSubClass中有哪些行為發生:
軟鍵盤狀態變化時會調用其onMeasure(),onLayout() onSizeChanged()並沒有被調用 整個布局的高度也沒有變化哦噢,這時並沒有執行onSizeChanged()方法,這也就說原本檢測軟鍵盤狀態的方法在這就行不通了,得另辟蹊徑了。
當軟鍵盤彈起時,原布局中是不是有一部分被鍵盤完全遮擋了呢?
對吧,也就是說原布局的可視范圍(更精確地說是可視高度)發生了變化:變得比以前小了。所以,我們可以以此為突破口,具體代碼如下:
public boolean isSoftKeyboardShow(View rootView) {
screenHeight=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
screenWidth=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
threshold=screenHeight/3;
int rootViewBottom=rootView.getBottom();
Rect rect = new Rect();
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int visibleBottom=rect.bottom;
int heightDiff = rootViewBottom - visibleBottom;
System.out.println("----> rootViewBottom="+rootViewBottom+",visibleBottom="+visibleBottom);
System.out.println("----> heightDiff="+heightDiff+",threshold="+threshold);
return heightDiff > threshold;
}
獲取根布局(RelativeLayoutSubClass)原本的高度int rootViewBottom=rootView.getBottom();
獲取當前根布局的可視高度
計算兩者的差值Rect rect = new Rect();
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int visibleBottom=rect.bottom;
int heightDiff = rootViewBottom - visibleBottom;
判斷軟鍵盤是否彈起
return heightDiff > threshold;
具體的方法是有了,那麼該在哪裡調用該方法呢?
其實,和之前的類似,只需在RelativeLayoutSubClass的onLayout()中執行即可。具體代碼如下:
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
/**
* 原創作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class RelativeLayoutSubClass extends RelativeLayout{
private OnSoftKeyboardListener mSoftKeyboardListener;
public RelativeLayoutSubClass(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
System.out.println("----> onMeasure");
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mSoftKeyboardListener.onSoftKeyboardChange();
System.out.println("----> onLayout");
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
System.out.println("----> onSizeChanged");
}
public void setSoftKeyboardListener(OnSoftKeyboardListener listener){
mSoftKeyboardListener=listener;
}
public interface OnSoftKeyboardListener{
public void onSoftKeyboardChange();
}
}
在對應的Activity中實現該Listener,具體代碼如下:
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
/**
* 原創作者:
* 谷哥的小弟
*
* 博客地址:
* http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
private RelativeLayoutSubClass mRootLayout;
private int screenHeight;
private int screenWidth;
private int threshold;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init(){
mRootLayout= (RelativeLayoutSubClass) findViewById(R.id.rootLayout);
mRootLayout.setSoftKeyboardListener(new RelativeLayoutSubClass.OnSoftKeyboardListener() {
@Override
public void onSoftKeyboardChange() {
boolean isShow=isSoftKeyboardShow(mRootLayout);
System.out.println("----> isShow="+isShow);
}
});
}
public boolean isSoftKeyboardShow(View rootView) {
screenHeight=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
screenWidth=getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
threshold=screenHeight/3;
int rootViewBottom=rootView.getBottom();
Rect rect = new Rect();
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
int visibleBottom=rect.bottom;
int heightDiff = rootViewBottom - visibleBottom;
System.out.println("----> rootViewBottom="+rootViewBottom+",visibleBottom="+visibleBottom);
System.out.println("----> heightDiff="+heightDiff+",threshold="+threshold);
return heightDiff > threshold;
}
}
嗯哼,至此當windowSoftInputMode設置為adjustPan時軟鍵盤的狀態監聽也得到了實現
 Android官方MVP架構示例項目解析[轉載]
Android官方MVP架構示例項目解析[轉載]
項目MVP實現方式這節我們就具體來看官方示例到底是如何實現mvp的。這裡我們先看下總體的輪廓,關於項目中業務代碼我們僅列出了任務詳情頁(taskDetail)的相關類,其
 Android對話框(四)PopupWindow
Android對話框(四)PopupWindow
主布局 Popup對話框布局 package com.example.popupwindow; import
 飛信忘記密碼怎麼辦?
飛信忘記密碼怎麼辦?
飛信現在在生活之中運用越來越廣泛,他是中國移動推出的一款可以免費點對點短信的軟件,那麼如果我們把密碼忘記了怎麼辦呢?怎樣修改呢?下面小編來給大家介紹怎樣去找
 如何寫一個正經的Android音樂播放器 一
如何寫一個正經的Android音樂播放器 一
以前寫過很多次音樂播放器,但是總有一些問題出現,例如: 1,音樂長時間播放問題(即便是放在service中去播放,依然會被殺死); 2,音樂的播放進度如何掌握?(如何利用