編輯:關於Android編程
對於android_media_MediaScanner.cpp來說,主要分析三個函數native_init,native_setup和processDirectory。
static void
android_media_MediaScanner_native_init(JNIEnv *env)
{
ALOGV("native_init");
jclass clazz = env->FindClass(kClassMediaScanner);
if (clazz == NULL) {
return;
}
//將之後創建的native對象的指針保存到MediaScanner.java的mNativeContext字段中
fields.context = env->GetFieldID(clazz, "mNativeContext", "J");
if (fields.context == NULL) {
return;
}
}
android_media_MediaScanner_native_init的功能主要是動態注冊。
static void
android_media_MediaScanner_native_setup(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz)
{
//獲取Stagefright的MediaScanner對象
MediaScanner *mp = new StagefrightMediaScanner;
if (mp == NULL) {
jniThrowException(env, kRunTimeException, "Out of memory");
return;
}
//將對象保存到mNativeContext中
env->SetLongField(thiz, fields.context, (jlong)mp);
}
android_media_MediaScanner_native_setup方法的作用是創建native的MediaScanner對象,並且用的是StagefrightMediaScanner,等會分析。
static void
android_media_MediaScanner_processDirectory(
JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring path, jobject client)
{
//傳入的參數path是需要掃描的路徑,client是MediaScannerClient.java對象
//獲取之前保存到mNativeContext的StagefrightMediaScanner對象
MediaScanner *mp = getNativeScanner_l(env, thiz);
if (mp == NULL) {
jniThrowException(env, kRunTimeException, "No scanner available");
return;
}
if (path == NULL) {
jniThrowException(env, kIllegalArgumentException, NULL);
return;
}
const char *pathStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, NULL);
if (pathStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
return;
}
//構造native層的MyMediaScannerClient對象,參數是java層的MyMediaScannerClient
//對象
MyMediaScannerClient myClient(env, client);
//調用native層processDirectory方法,參數是掃描路徑和native的MyMediaScannerClient
//對象
MediaScanResult result = mp->processDirectory(pathStr, myClient);
if (result == MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR) {
ALOGE("An error occurred while scanning directory '%s'.", pathStr);
}
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
}
android_media_MediaScanner_processDirectory方法的作用是啟動native層processDirectory掃描方法,在配置過程稍顯復雜,其一是java的MediaScanner的上下文環境傳遞給native額MediaScanner對象中,其二是native的MyMediaScannerClient對象與java的MyMediaScannerClient對象建立聯系,方便將結果回調到java層。
下面分析的是native層的相關處理,StagefrightMediaScanner.cpp繼承自MediaScanner.cpp,在JNI調用的方法processDirectory也是由父類實現的。
先分析MediaScanner.cpp父類的方法。
MediaScanResult MediaScanner::processDirectory(
const char *path, MediaScannerClient &client) {
//前期的一些准備工作
int pathLength = strlen(path);
if (pathLength >= PATH_MAX) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_SKIPPED;
}
char* pathBuffer = (char *)malloc(PATH_MAX + 1);
if (!pathBuffer) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
int pathRemaining = PATH_MAX - pathLength;
strcpy(pathBuffer, path);
if (pathLength > 0 && pathBuffer[pathLength - 1] != '/') {
pathBuffer[pathLength] = '/';
pathBuffer[pathLength + 1] = 0;
--pathRemaining;
}
//設置native的MyMediaScannerClient對象的local信息
client.setLocale(locale());
//執行doProcessDirectory方法
MediaScanResult result = doProcessDirectory(pathBuffer, pathRemaining, client, false);
//釋放資源
free(pathBuffer);
return result;
}
MediaScanResult MediaScanner::doProcessDirectory(
char *path, int pathRemaining, MediaScannerClient &client, bool noMedia) {
// place to copy file or directory name
char* fileSpot = path + strlen(path);
struct dirent* entry;
if (shouldSkipDirectory(path)) {
ALOGD("Skipping: %s", path);
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_OK;
}
// Treat all files as non-media in directories that contain a ".nomedia" file
if (pathRemaining >= 8 /* strlen(".nomedia") */ ) {
strcpy(fileSpot, ".nomedia");
if (access(path, F_OK) == 0) {
ALOGV("found .nomedia, setting noMedia flag");
noMedia = true;
}
// restore path
fileSpot[0] = 0;
}
//打開對應的文件夾路徑
DIR* dir = opendir(path);
if (!dir) {
ALOGW("Error opening directory '%s', skipping: %s.", path, strerror(errno));
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_SKIPPED;
}
MediaScanResult result = MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_OK;
//循環遍歷所有文件
while ((entry = readdir(dir))) {
//調用doProcessDirectoryEntry方法
if (doProcessDirectoryEntry(path, pathRemaining, client, noMedia, entry, fileSpot)
== MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR) {
result = MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
break;
}
}
//關閉文件夾
closedir(dir);
return result;
}
MediaScanResult MediaScanner::doProcessDirectoryEntry(
char *path, int pathRemaining, MediaScannerClient &client, bool noMedia,
struct dirent* entry, char* fileSpot) {
struct stat statbuf;
//枚舉目錄中的文件和子文件夾信息
const char* name = entry->d_name;
// ignore "." and ".."
if (name[0] == '.' && (name[1] == 0 || (name[1] == '.' && name[2] == 0))) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_SKIPPED;
}
int nameLength = strlen(name);
if (nameLength + 1 > pathRemaining) {
// path too long!
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_SKIPPED;
}
strcpy(fileSpot, name);
int type = entry->d_type;
if (type == DT_UNKNOWN) {
// If the type is unknown, stat() the file instead.
// This is sometimes necessary when accessing NFS mounted filesystems, but
// could be needed in other cases well.
//執行stat方法,獲取文件的所有屬性,成功返回0失敗返回-1
if (stat(path, &statbuf) == 0) {
if (S_ISREG(statbuf.st_mode)) {
type = DT_REG;
} else if (S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode)) {
type = DT_DIR;
}
} else {
ALOGD("stat() failed for %s: %s", path, strerror(errno) );
}
}
if (type == DT_DIR) {
bool childNoMedia = noMedia;
// set noMedia flag on directories with a name that starts with '.'
// for example, the Mac ".Trashes" directory
if (name[0] == '.')
childNoMedia = true;
// report the directory to the client
if (stat(path, &statbuf) == 0) {
//調用MyMediaScannerClient的scanFile函數
status_t status = client.scanFile(path, statbuf.st_mtime, 0,
true /*isDirectory*/, childNoMedia);
if (status) {
//返回值是checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback,如果是true就出錯
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
}
// and now process its contents
strcat(fileSpot, "/");
MediaScanResult result = doProcessDirectory(path, pathRemaining - nameLength - 1,
client, childNoMedia);
if (result == MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
} else if (type == DT_REG) {
stat(path, &statbuf);
status_t status = client.scanFile(path, statbuf.st_mtime, statbuf.st_size,
false /*isDirectory*/, noMedia);
if (status) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
}
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_OK;
}
從上面的分析中看到調用到了MyMediaScannerClient的scanFile函數,下面分析這個函數
virtual status_t scanFile(const char* path, long long lastModified,
long long fileSize, bool isDirectory, bool noMedia)
{
jstring pathStr;
if ((pathStr = mEnv->NewStringUTF(path)) == NULL) {
mEnv->ExceptionClear();
return NO_MEMORY;
}
//此處的mClient是java層的MyMediaScannerClient,調用的也是java層的scanFile方法
mEnv->CallVoidMethod(mClient, mScanFileMethodID, pathStr, lastModified,
fileSize, isDirectory, noMedia);
mEnv->DeleteLocalRef(pathStr);
return checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(mEnv, "scanFile");
}
可以看出在native層的MyMediaScannerClient調用的是java層MyMediaScannerClient的scanFile函數,下面分析java層的邏輯。
public void scanFile(String path, long lastModified, long fileSize,
boolean isDirectory, boolean noMedia) {
// This is the callback funtion from native codes.
//調用了doScanFile方法
doScanFile(path, null, lastModified, fileSize, isDirectory, false, noMedia);
}
public Uri doScanFile(String path, String mimeType, long lastModified,
long fileSize, boolean isDirectory, boolean scanAlways, boolean noMedia) {
//參數scanAlways控制是否強制掃描
Uri result = null;
try {
// beginFile方法的作用主要是1. 生成FileEntry,2.判斷是否有修改文件
FileEntry entry = beginFile(path, mimeType, lastModified,
fileSize, isDirectory, noMedia);
// if this file was just inserted via mtp, set the rowid to zero
// (even though it already exists in the database), to trigger
// the correct code path for updating its entry
if (mMtpObjectHandle != 0) {
entry.mRowId = 0;
}
// rescan for metadata if file was modified since last scan
if (entry != null && (entry.mLastModifiedChanged || scanAlways)) {
if (noMedia) {
//不是media的情況
result = endFile(entry, false, false, false, false, false);
} else {
//重新掃描獲取的信息
String lowpath = path.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT);
boolean ringtones = (lowpath.indexOf(RINGTONES_DIR) > 0);
boolean notifications = (lowpath.indexOf(NOTIFICATIONS_DIR) > 0);
boolean alarms = (lowpath.indexOf(ALARMS_DIR) > 0);
boolean podcasts = (lowpath.indexOf(PODCAST_DIR) > 0);
boolean music = (lowpath.indexOf(MUSIC_DIR) > 0) ||
(!ringtones && !notifications && !alarms && !podcasts);
boolean isaudio = MediaFile.isAudioFileType(mFileType);
boolean isvideo = MediaFile.isVideoFileType(mFileType);
boolean isimage = MediaFile.isImageFileType(mFileType);
if (isaudio || isvideo || isimage) {
//如過類型是音頻、視頻和圖片的話,對路徑進行處理
//If the given path exists on emulated external storage,
//return the translated backing path hosted on internal storage.
path = Environment.maybeTranslateEmulatedPathToInternal
(new File(path)).getAbsolutePath();
}
// we only extract metadata for audio and video files
if (isaudio || isvideo) {
//調用processFile方法,把MyMediaScannerClient作為參數傳入
// processFile方法是native方法,稍後分析
processFile(path, mimeType, this);
}
if (isimage) {
//如果是圖片,單獨處理,調用processImageFile方法
//Decode a file path into a bitmap.
processImageFile(path);
}
// endFile方法是更新數據庫
result = endFile(entry, ringtones, notifications, alarms, music, podcasts);
}
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "RemoteException in MediaScanner.scanFile()", e);
}
return result;
}
從上面的分析可以看到,其實又調用到了processFile方法中,他也是一個native方法,需要再回到jni層繼續分析此方法。
static void
android_media_MediaScanner_processFile(
JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring path,
jstring mimeType, jobject client)
{
// Lock already hold by processDirectory
//獲取的還是native層的MediaScanner對象,實際類型是StagefrightMediaScanner對象
MediaScanner *mp = getNativeScanner_l(env, thiz);
const char *pathStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, NULL);
if (pathStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
return;
}
//構造了新的native層的MyMediaScannerClient對象,傳入的還是java層的MyMediaScannerClient對象
MyMediaScannerClient myClient(env, client);
//調用的是StagefrightMediaScanner對象的processFile方法,等會分析
MediaScanResult result = mp->processFile(pathStr, mimeTypeStr, myClient);
if (result == MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR) {
ALOGE("An error occurred while scanning file '%s'.", pathStr);
}
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
if (mimeType) {
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(mimeType, mimeTypeStr);
}
}
從上面的分析可以看出,調用了StagefrightMediaScanner對象的processFile方法,下面分析此方法。
MediaScanResult StagefrightMediaScanner::processFile(
const char *path, const char *mimeType,
MediaScannerClient &client) {
//調用native層的MyMediaScannerClient對象進行local信息,語言設置
client.setLocale(locale());
//beginFile方法是由MyMediaScannerClient的父類實現的,其實谷歌並沒有實現此方法
client.beginFile();
//具體的方法是調用processFileInternal實現的
MediaScanResult result = processFileInternal(path, mimeType, client);
//根據設置的區域信息來對字符串進行轉換
client.endFile();
return result;
}
MediaScanResult StagefrightMediaScanner::processFileInternal(
const char *path, const char * /* mimeType */,
MediaScannerClient &client) {
//獲取擴展名信息
const char *extension = strrchr(path, '.');
if (!extension) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_SKIPPED;
}
//對擴展名不符合的跳過掃描
if (!FileHasAcceptableExtension(extension)
&& !AVUtils::get()->isEnhancedExtension(extension)) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_SKIPPED;
}
// MediaMetadataRetriever將一個輸入媒體文件中設置幀和元數據
sp mRetriever(new MediaMetadataRetriever);
//打開資源
int fd = open(path, O_RDONLY | O_LARGEFILE);
status_t status;
if (fd < 0) {
// couldn't open it locally, maybe the media server can?
//打開資源失敗
status = mRetriever->setDataSource(NULL /* httpService */, path);
} else {
//設置資源
status = mRetriever->setDataSource(fd, 0, 0x7ffffffffffffffL);
close(fd);
}
if (status) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
const char *value;
if ((value = mRetriever->extractMetadata(
METADATA_KEY_MIMETYPE)) != NULL) {
//設置類型
status = client.setMimeType(value);
if (status) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
}
//構造元數據的tag
struct KeyMap {
const char *tag;
int key;
};
static const KeyMap kKeyMap[] = {
{ "tracknumber", METADATA_KEY_CD_TRACK_NUMBER },
{ "discnumber", METADATA_KEY_DISC_NUMBER },
{ "album", METADATA_KEY_ALBUM },
{ "artist", METADATA_KEY_ARTIST },
{ "albumartist", METADATA_KEY_ALBUMARTIST },
{ "composer", METADATA_KEY_COMPOSER },
{ "genre", METADATA_KEY_GENRE },
{ "title", METADATA_KEY_TITLE },
{ "year", METADATA_KEY_YEAR },
{ "duration", METADATA_KEY_DURATION },
{ "writer", METADATA_KEY_WRITER },
{ "compilation", METADATA_KEY_COMPILATION },
{ "isdrm", METADATA_KEY_IS_DRM },
{ "width", METADATA_KEY_VIDEO_WIDTH },
{ "height", METADATA_KEY_VIDEO_HEIGHT },
};
static const size_t kNumEntries = sizeof(kKeyMap) / sizeof(kKeyMap[0]);
//循環遍歷
for (size_t i = 0; i < kNumEntries; ++i) {
const char *value;
if ((value = mRetriever->extractMetadata(kKeyMap[i].key)) != NULL) {
//設置tag和value到MyMediaScannerClient中,稍後分析
status = client.addStringTag(kKeyMap[i].tag, value);
if (status != OK) {
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_ERROR;
}
}
}
return MEDIA_SCAN_RESULT_OK;
}
從上面的分析中,設置tag和value是通過MyMediaScannerClient調用的,在MyMediaScannerClient的父類MediaScannerClient有addStringTag方法,在方法中又調用了子類MyMediaScannerClient的handleStringTag方法。
status_t MediaScannerClient::addStringTag(const char* name, const char* value)
{
//調用子類的handleStringTag方法
handleStringTag(name, value);
return OK;
}
virtual status_t handleStringTag(const char* name, const char* value)
{
jstring nameStr, valueStr;
//獲取字符串的值
if ((nameStr = mEnv->NewStringUTF(name)) == NULL) {
mEnv->ExceptionClear();
return NO_MEMORY;
}
char *cleaned = NULL;
//如果value的值不是utf-8編碼,則需要特殊處理
if (!isValidUtf8(value)) {
cleaned = strdup(value);
char *chp = cleaned;
char ch;
while ((ch = *chp)) {
if (ch & 0x80) {
*chp = '?';
}
chp++;
}
value = cleaned;
}
//將處理完成的值賦值到新的字符串valueStr中
valueStr = mEnv->NewStringUTF(value);
//釋放資源
free(cleaned);
if (valueStr == NULL) {
mEnv->DeleteLocalRef(nameStr);
mEnv->ExceptionClear();
return NO_MEMORY;
}
//調用java層MyMediaScanner的handleStringTag方法
mEnv->CallVoidMethod(
mClient, mHandleStringTagMethodID, nameStr, valueStr);
mEnv->DeleteLocalRef(nameStr);
mEnv->DeleteLocalRef(valueStr);
return checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(mEnv, "handleStringTag");
}
此時在native層中又去調用java層的方法了,此處調用的是handleStringTag方法。
public void handleStringTag(String name, String value) {
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("title") || name.startsWith("title;")) {
// Don't trim() here, to preserve the special \001 character
// used to force sorting. The media provider will trim() before
// inserting the title in to the database.
//將tag信息中的value值都賦值到了成員變量中
mTitle = value;
} else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("artist") || name.startsWith("artist;")) {
mArtist = value.trim();
} else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("albumartist") || name.startsWith("albumartist;")
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("band") || name.startsWith("band;")) {
mAlbumArtist = value.trim();
... ...
}
到此文件的讀取過程分析完成了,這些成員變量裝填完成之後就會調用到endFile方法中,進行更新數據庫了。
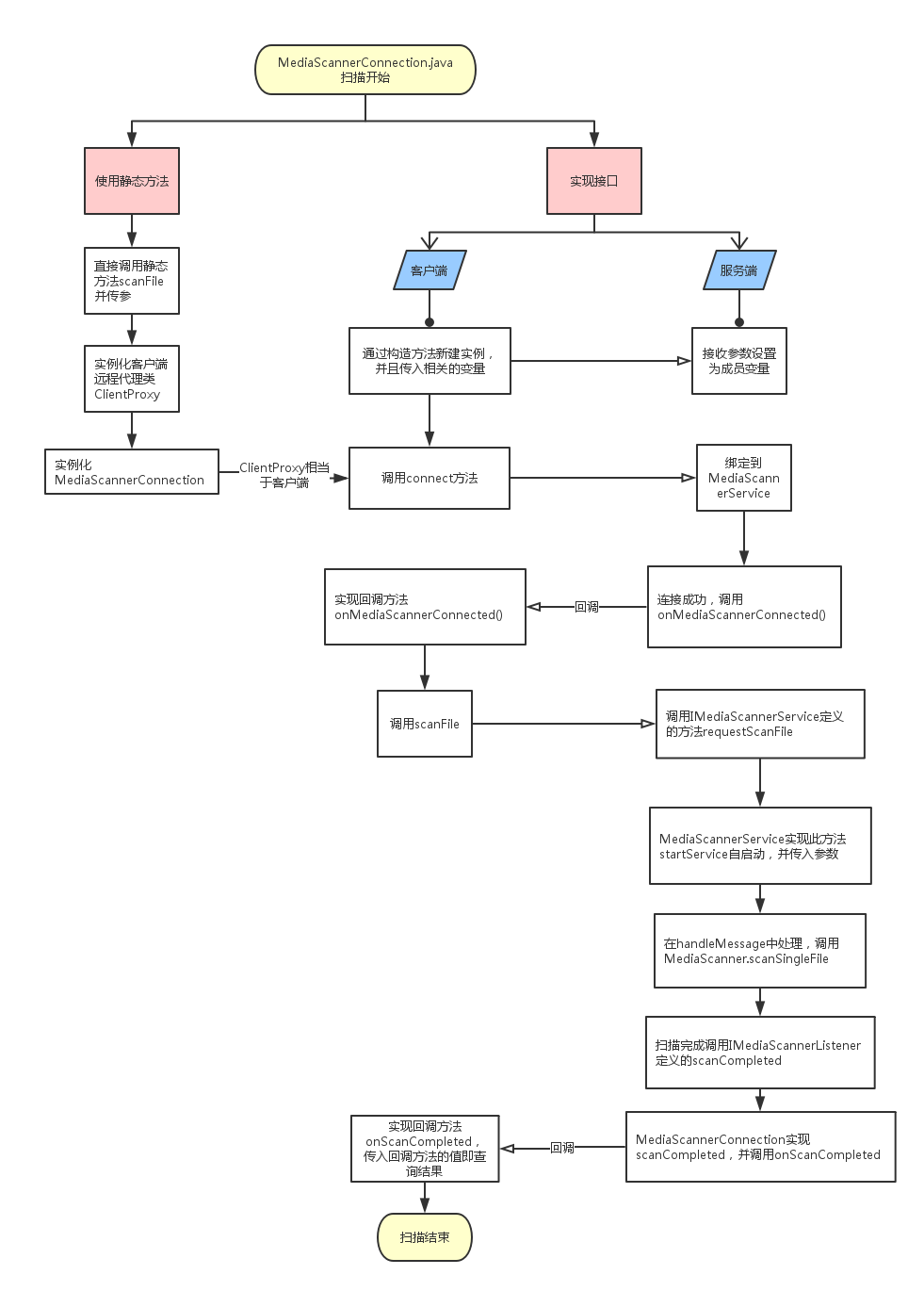
由於發廣播的方式無法實時地獲取連接的狀態,所以Android又提供了一種查詢方法,就是通過IPC,也就是進程間通信的方式去啟動掃描,然後獲取掃描的狀態。
/** * MediaScannerConnection provides a way for applications to pass a * newly created or downloaded media file to the media scanner service. * The media scanner service will read metadata from the file and add * the file to the media content provider. * The MediaScannerConnectionClient provides an interface for the * media scanner service to return the Uri for a newly scanned file * to the client of the MediaScannerConnection class. */
通過注釋可以看出,MediaScannerConnection可以提供另一種非發廣播的方式去主動掃描文件,他的調用過程是跨進程的,掃描的結果會通過回調函數獲得。
在MediaScannerConnection內部提供了兩種方式去供客戶端使用,一種是實現接口和回調方法,另一種是使用代理模式所提供的靜態方法。
(1)實現接口
首先通過構造方法新建實例,並且設置相關的成員變量。然後在客戶端處調用connect方法,去綁定service,並且調用requestScanFile方法去跨進程調用MediaScannerService中的方法。當連接到MediaScannerService後回調客戶端onMediaScannerConnected方法,當MediaScannerService掃描完成後,回調客戶端onScanCompleted方法,整個過程完成。
//監聽掃描完成的接口
public interface OnScanCompletedListener {
public void onScanCompleted(String path, Uri uri);
}
//客戶端需要實現的接口,同時也是在服務端所獲取的客戶端的實例
public interface MediaScannerConnectionClient extends OnScanCompletedListener {
public void onMediaScannerConnected();
public void onScanCompleted(String path, Uri uri);
}
//構造方法,傳入的參數是客戶端的上下文環境和客戶端的實例
public MediaScannerConnection(Context context, MediaScannerConnectionClient client) {
mContext = context;
mClient = client;
}
// ServiceConnection的回調方法,當service連接時回調
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
synchronized (this) {
//獲取IMediaScannerService的實例mService
mService = IMediaScannerService.Stub.asInterface(service);
if (mService != null && mClient != null) {
//當service連接上時,回調到客戶端的onMediaScannerConnected方法
mClient.onMediaScannerConnected();
}
}
}
// IMediaScannerListener是AIDL文件,只有一個方法scanCompleted
//這裡獲取了服務端IMediaScannerListener的實例
private final IMediaScannerListener.Stub mListener = new IMediaScannerListener.Stub() {
public void scanCompleted(String path, Uri uri) {
MediaScannerConnectionClient client = mClient;
if (client != null) {
//當回調到scanCompleted時,調用客戶端的onScanCompleted方法
client.onScanCompleted(path, uri);
}
}
};
//此方法是在客戶端處調用,傳入需要掃描的路徑和文件類型
public void scanFile(String path, String mimeType) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mService == null || !mConnected) {
throw new IllegalStateException("not connected to MediaScannerService");
}
try {
//調用IMediaScannerService的方法
mService.requestScanFile(path, mimeType, mListener);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
//在客戶端調用方法,bindService到MediaScannerService
public void connect() {
synchronized (this) {
if (!mConnected) {
Intent intent = new Intent(IMediaScannerService.class.getName());
intent.setComponent(
new ComponentName("com.android.providers.media",
"com.android.providers.media.MediaScannerService"));
mContext.bindService(intent, this, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
mConnected = true;
}
}
}
MediaScannerConnection部分分析完成,可以看出在connect方法中去綁定了遠程的MediaScannerService,接下來分析在MediaScannerService完成的操作。
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent){
return mBinder;
}
//在綁定之後獲取到了服務端的實例,實現requestScanFile的具體方法
private final IMediaScannerService.Stub mBinder =
new IMediaScannerService.Stub() {
//此處是requestScanFile實現的具體方法
public void requestScanFile(String path, String mimeType, IMediaScannerListener listener){
Bundle args = new Bundle();
//將相關的參數都放入到了bundle中
args.putString("filepath", path);
args.putString("mimetype", mimeType);
if (listener != null) {
args.putIBinder("listener", listener.asBinder());
}
// 用startService的啟動方式去啟動,傳入bundle
startService(new Intent(MediaScannerService.this,
MediaScannerService.class).putExtras(args));
}
//此處是scanFile實現的具體方法
public void scanFile(String path, String mimeType) {
requestScanFile(path, mimeType, null);
}
};
//在onStartCommand方法中將intent的值發送到了ServiceHandler處理
private final class ServiceHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
{
Bundle arguments = (Bundle) msg.obj;
String filePath = arguments.getString("filepath");
try {
if (filePath != null) {
//從intent中獲取IBinder對象
IBinder binder = arguments.getIBinder("listener");
//獲取IMediaScannerListener的實例
IMediaScannerListener listener = (binder == null ? null :
IMediaScannerListener.Stub.asInterface(binder));
Uri uri = null;
try {
uri = scanFile(filePath, arguments.getString("mimetype"));
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Exception scanning file", e);
}
if (listener != null) {
//查詢完成後,回調到IMediaScannerListener,客戶端處也隨之回調
listener.scanCompleted(filePath, uri);
}
... ...
在MediaScannerService的主要作用就是接受intent,調用scanFile方法掃描,掃描完成之後調用回調方法,給客戶端回調。
(2) 靜態方法實現
在MediaScannerConnection也可以通過提供的靜態方法去實現掃描。其原理就是實現代理模式,遠程代理客戶端的實例進行相關操作,客戶端只需要傳入相應的參數即可,不需要手動連接service等操作,比較方便實用。
public static void scanFile(Context context, String[] paths, String[] mimeTypes,
OnScanCompletedListener callback) {
//實例化ClientProxy,並給構造函數傳參
ClientProxy client = new ClientProxy(paths, mimeTypes, callback);
//實例化MediaScannerConnection,並給構造函數傳參
MediaScannerConnection connection = new MediaScannerConnection(context, client);
client.mConnection = connection;
//調用connect函數
connection.connect();
}
//客戶端的遠程代理類
static class ClientProxy implements MediaScannerConnectionClient {
final String[] mPaths;
final String[] mMimeTypes;
final OnScanCompletedListener mClient;
MediaScannerConnection mConnection;
int mNextPath;
//構造函數,配置參數
ClientProxy(String[] paths, String[] mimeTypes, OnScanCompletedListener client) {
mPaths = paths;
mMimeTypes = mimeTypes;
mClient = client;
}
//實現回調方法
public void onMediaScannerConnected() {
scanNextPath();
}
public void onScanCompleted(String path, Uri uri) {
if (mClient != null) {
mClient.onScanCompleted(path, uri);
}
scanNextPath();
}
//因為傳入的路徑是數組,進行循環掃描
void scanNextPath() {
if (mNextPath >= mPaths.length) {
mConnection.disconnect();
return;
}
String mimeType = mMimeTypes != null ? mMimeTypes[mNextPath] : null;
mConnection.scanFile(mPaths[mNextPath], mimeType);
mNextPath++;
}
}
所以對於客戶端來說,實現此靜態方法去掃描,只需要傳入上下文,查詢的路徑(可以是多個路徑,用數組表示),文件類型和監聽器即可,不需要考慮其他,比較方便使用。
 Android開發之Drag&Drop框架實現拖放手勢
Android開發之Drag&Drop框架實現拖放手勢
Android3.0提供了drag/drop框架,利用此框架可以實現使用拖放手勢將一個view拖放到當前布局中的另外一個view中。本文將介紹如何使用拖放框架。 一、實
 android listview長按,單擊各種事件捕捉
android listview長按,單擊各種事件捕捉
之前一直想總結一下這樣知識,後面各種忙,就不想寫。還是自已總結一下比較好。listview需要注意事項有很多吧,也是最常用的控件之一。我們可以自動計算listview的高
 【Android】Scrollview返回頂部,快速返回頂部的功能實現,詳解代碼。
【Android】Scrollview返回頂部,快速返回頂部的功能實現,詳解代碼。
首先給大家看一下我們今天這個最終實現的效果圖:我這裡只是單純的實現了scrollview返回頂部的功能。具體效果大家可以適當地美化在實際項目中可以換圖標,去掉右側滾動條等
 Android CircleImageView圓形ImageView
Android CircleImageView圓形ImageView
CircleImageView是github上一個第三方開源的實現圓形ImageView的項目。其在github上的項目主頁是:https://github.com/hd