編輯:關於Android編程
上一篇主要講解了BootAnimation是從何而來,如何啟動,從開機,到SurfaceFlinger服務起來,然後到執行開機動畫,如果要深入的看裡面的代碼,是需要花一定的時間的,我們旨在了解大致的流程,具體流程中的函數,變量意義,具體實現,讀者請自研。
由來已知,執行待述~
###BootAnimation執行
1. 代碼位置
frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation
目錄中包含如下文件
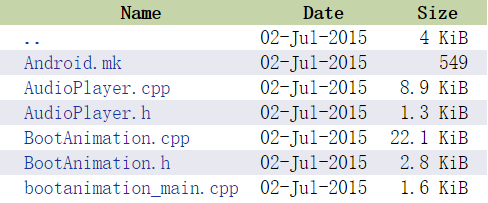
文件名作用Android.mk
mk文件,編譯模塊使用
AudioPlayer.cpp、AudioPlayer.h
音頻播放
BootAnimation.cpp、BootAnimation.h
開機動畫的源文件和頭文件
bootanimation_main.cpp
開機動畫的入口
2. 源碼分析
bootanimation_main.cpp
文件中定義main函數,也就是C語言中的執行文件的入口函數
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
//宏定義判斷是否設置進程的優先級
#if defined(HAVE_PTHREADS)
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, ANDROID_PRIORITY_DISPLAY);
#endif
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
//這個配置項決定是否存在開機動畫
property_get("debug.sf.nobootanimation", value, "0");
int noBootAnimation = atoi(value);
ALOGI_IF(noBootAnimation, "boot animation disabled");
if (!noBootAnimation) {
//創建ProcessSate對象
// 這個過程會打開/dev/binder設備,形成和內核binder機制的交互的通道; 映射fd到內存
sp proc(ProcessState::self());
//創建線程並加入到線程池
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
// 創建開機動畫對象
sp boot = new BootAnimation();
//把主線程加入到線程池
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
return 0;
}
創建開機動畫對象會執行到BootAnimation的構造方法,先看下BootAnimation的頭文件
BootAnimation.h
......
namespace android {
class AudioPlayer;
class Surface;
class SurfaceComposerClient;
class SurfaceControl;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class BootAnimation : public Thread, public IBinder::DeathRecipient
{
public:
BootAnimation();
virtual ~BootAnimation();
sp session() const;
private:
virtual bool threadLoop();
virtual status_t readyToRun();
virtual void onFirstRef();
virtual void binderDied(const wp& who);
//Texture類定義
struct Texture {
GLint w; //寬度
GLint h; //高度
GLuint name; //名稱
};
//動畫內容結構體
struct Animation {
//動畫幀
struct Frame {
String8 name;
FileMap* map;
mutable GLuint tid;
bool operator < (const Frame& rhs) const {
return name < rhs.name;
}
};
//動畫部分,因為動畫可能是由幾個部分組成
struct Part {
int count;
int pause;
String8 path;
SortedVector frames;
bool playUntilComplete;
float backgroundColor[3];
FileMap* audioFile;
};
int fps;
int width;
int height;
Vector parts;
};
status_t initTexture(Texture* texture, AssetManager& asset, const char* name);
status_t initTexture(const Animation::Frame& frame);
bool android();
bool readFile(const char* name, String8& outString);
bool movie();
void checkExit();
sp mSession;
sp mAudioPlayer;
AssetManager mAssets;
Texture mAndroid[2];
int mWidth;
int mHeight;
EGLDisplay mDisplay;
EGLDisplay mContext;
EGLDisplay mSurface;
sp mFlingerSurfaceControl;
sp mFlingerSurface;
ZipFileRO *mZip;
};
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
}; // namespace android
#endif // ANDROID_BOOTANIMATION_H
大致的定義和聲明就是這麼多,看下具體實現
BootAnimation.cpp
首先執行構造方法
BootAnimation::BootAnimation() : Thread(false), mZip(NULL)
{
//用於界面顯示的mSession,與SurfaceFlinger交互的客戶端
mSession = new SurfaceComposerClient();
}
然後執行
void BootAnimation::onFirstRef() {
status_t err = mSession->linkToComposerDeath(this);
ALOGE_IF(err, "linkToComposerDeath failed (%s) ", strerror(-err));
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
run("BootAnimation", PRIORITY_DISPLAY);
}
}
由於BootAnimation繼承Thread類,首先會調用readyToRun函數
status_t BootAnimation::readyToRun() {
mAssets.addDefaultAssets();
sp dtoken(SurfaceComposerClient::getBuiltInDisplay(
ISurfaceComposer::eDisplayIdMain));
DisplayInfo dinfo;
status_t status = SurfaceComposerClient::getDisplayInfo(dtoken, &dinfo);
if (status)
return -1;
// create the native surface
sp control = session()->createSurface(String8("BootAnimation"),
dinfo.w, dinfo.h, PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565);
SurfaceComposerClient::openGlobalTransaction();
control->setLayer(0x40000000);
SurfaceComposerClient::closeGlobalTransaction();
sp s = control->getSurface();
// initialize opengl and egl
const EGLint attribs[] = {
EGL_RED_SIZE, 8,
EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 8,
EGL_BLUE_SIZE, 8,
EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, 0,
EGL_NONE
};
EGLint w, h, dummy;
EGLint numConfigs;
EGLConfig config;
EGLSurface surface;
EGLContext context;
EGLDisplay display = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
eglInitialize(display, 0, 0);
eglChooseConfig(display, attribs, &config, 1, &numConfigs);
surface = eglCreateWindowSurface(display, config, s.get(), NULL);
context = eglCreateContext(display, config, NULL, NULL);
eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_WIDTH, &w);
eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_HEIGHT, &h);
if (eglMakeCurrent(display, surface, surface, context) == EGL_FALSE)
return NO_INIT;
mDisplay = display;
mContext = context;
mSurface = surface;
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
mFlingerSurfaceControl = control;
mFlingerSurface = s;
// If the device has encryption turned on or is in process
// of being encrypted we show the encrypted boot animation.
char decrypt[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("vold.decrypt", decrypt, "");
bool encryptedAnimation = atoi(decrypt) != 0 || !strcmp("trigger_restart_min_framework", decrypt);
ZipFileRO* zipFile = NULL;
if ((encryptedAnimation &&
(access(SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) &&
((zipFile = ZipFileRO::open(SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE)) != NULL)) ||
((access(OEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) &&
((zipFile = ZipFileRO::open(OEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE)) != NULL)) ||
((access(SYSTEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) &&
((zipFile = ZipFileRO::open(SYSTEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE)) != NULL))) {
mZip = zipFile;
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
上面主要做兩個操作:
1. 初始化顯示界面用於播放開機動畫,egl的一些內容;
2. 根據手機是否加密選擇不同的開機動畫文件,然後拿到入口zipFile
其中用到了一個文件路徑在BootAnimation.cpp的開頭有定義
#define OEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE "/oem/media/bootanimation.zip" //這個應該是OEM廠商自己定制
#define SYSTEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE "/system/media/bootanimation.zip" //正常情況下的Android原始開機動畫
#define SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE "/system/media/bootanimation-encrypted.zip" //加密手機的開機動畫
readyToRun方法執行完之後,接著看threaLoop函數
bool BootAnimation::threadLoop()
{
bool r;
// We have no bootanimation file, so we use the stock android logo
// animation.
if (mZip == NULL) {
r = android(); //沒有開機動畫文件,執行android logo
} else {
r = movie(); //存在開機動畫文件,則執行對應的開機動畫文件解析出來的內容
}
eglMakeCurrent(mDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
eglDestroyContext(mDisplay, mContext);
eglDestroySurface(mDisplay, mSurface);
mFlingerSurface.clear();
mFlingerSurfaceControl.clear();
eglTerminate(mDisplay);
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
return r;
}
——————————————>android()
bool BootAnimation::android()
{
//初始化兩個紋理用於顯示logo
initTexture(&mAndroid[0], mAssets, "images/android-logo-mask.png");
initTexture(&mAndroid[1], mAssets, "images/android-logo-shine.png");
// clear screen 清屏
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
glDisable(GL_DITHER);
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glClearColor(0,0,0,1);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexEnvx(GL_TEXTURE_ENV, GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, GL_REPLACE);
const GLint xc = (mWidth - mAndroid[0].w) / 2;
const GLint yc = (mHeight - mAndroid[0].h) / 2;
const Rect updateRect(xc, yc, xc + mAndroid[0].w, yc + mAndroid[0].h);
glScissor(updateRect.left, mHeight - updateRect.bottom, updateRect.width(),
updateRect.height());
// Blend state
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
glTexEnvx(GL_TEXTURE_ENV, GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, GL_REPLACE);
const nsecs_t startTime = systemTime();
//不停的顯示知道exitPending()返回true
do {
......
EGLBoolean res = eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
......
checkExit();
} while (!exitPending());
glDeleteTextures(1, &mAndroid[0].name);
glDeleteTextures(1, &mAndroid[1].name);
return false;
}
主要工作,初始化顯示的logo紋理,不斷刷新界面直到exitPending()返回true,exitPenging()是Thread類中定義的函數,在checkExit()函數中通過requestExit()來執行退出
void BootAnimation::checkExit() {
// Allow surface flinger to gracefully request shutdown
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
//EXIT_PROP_NAME "service.bootanim.exit" 這個配置項在SurfaceFlinger的bootFinished函數中設置為1,然後這裡才能退出開機動畫,這個過程設計到開機啟動到launcher的整個過程,這裡不贅述
property_get(EXIT_PROP_NAME, value, "0");
int exitnow = atoi(value);
if (exitnow) {
requestExit();
if (mAudioPlayer != NULL) {
mAudioPlayer->requestExit();
}
}
}
——————————————>movie()
movie()這個函數有點長,我們截斷一點一點的看
1. 讀取bootanimation.zip中的配置文件
if (!readFile("desc.txt", desString)) {
return false;
}
char const* s = desString.string();
//讀取desc.txt文件
// Create and initialize an AudioPlayer if we have an audio_conf.txt file
String8 audioConf;
//判斷是否需要創建AudioPlayer,這部分我們暫時不關注
if (readFile("audio_conf.txt", audioConf)) {
mAudioPlayer = new AudioPlayer;
if (!mAudioPlayer->init(audioConf.string())) {
ALOGE("mAudioPlayer.init failed");
mAudioPlayer = NULL;
}
}
解析desc.txt文件,就是上面拿到的那個char const *s
for (;;) {
//一行一行的截取
const char* endl = strstr(s, "\n");
if (!endl) break;
String8 line(s, endl - s);
const char* l = line.string();
//幾個需要捕獲的參數,幀率 寬高,次數
int fps, width, height, count, pause;
char path[ANIM_ENTRY_NAME_MAX];
char color[7] = "000000"; // default to black if unspecified
char pathType;
//讀取幀率和寬高
if (sscanf(l, "%d %d %d", &width, &height, &fps) == 3) {
// ALOGD("> w=%d, h=%d, fps=%d", width, height, fps);
animation.width = width;
animation.height = height;
animation.fps = fps;
}
//或者讀取part內容
else if (sscanf(l, " %c %d %d %s #%6s", &pathType, &count, &pause, path, color) >= 4) {
// ALOGD("> type=%c, count=%d, pause=%d, path=%s, color=%s", pathType, count, pause, path, color);
Animation::Part part;
part.playUntilComplete = pathType == 'c';
part.count = count;
part.pause = pause;
part.path = path;
part.audioFile = NULL;
if (!parseColor(color, part.backgroundColor)) {
ALOGE("> invalid color '#%s'", color);
part.backgroundColor[0] = 0.0f;
part.backgroundColor[1] = 0.0f;
part.backgroundColor[2] = 0.0f;
}
animation.parts.add(part);
}
s = ++endl;
}
讀取所有的數據
// read all the data structures
const size_t pcount = animation.parts.size();
void *cookie = NULL;
if (!mZip->startIteration(&cookie)) {
return false;
}
ZipEntryRO entry;
char name[ANIM_ENTRY_NAME_MAX];
while ((entry = mZip->nextEntry(cookie)) != NULL) {
const int foundEntryName = mZip->getEntryFileName(entry, name, ANIM_ENTRY_NAME_MAX);
if (foundEntryName > ANIM_ENTRY_NAME_MAX || foundEntryName == -1) {
ALOGE("Error fetching entry file name");
continue;
}
const String8 entryName(name);
const String8 path(entryName.getPathDir());
const String8 leaf(entryName.getPathLeaf());
if (leaf.size() > 0) {
for (size_t j=0 ; jgetEntryInfo(entry, &method, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL)) {
if (method == ZipFileRO::kCompressStored) {
FileMap* map = mZip->createEntryFileMap(entry);
if (map) {
Animation::Part& part(animation.parts.editItemAt(j));
if (leaf == "audio.wav") {
// a part may have at most one audio file
part.audioFile = map;
} else {
Animation::Frame frame;
frame.name = leaf;
frame.map = map;
part.frames.add(frame);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
mZip->endIteration(cookie);
顯示動畫
<code> // clear screen
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
glDisable(GL_DITHER);
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glDisable(GL_BLEND);
glClearColor(0,0,0,1);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0);
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexEnvx(GL_TEXTURE_ENV, GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, GL_REPLACE);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
const int xc = (mWidth - animation.width) / 2;
const int yc = ((mHeight - animation.height) / 2);
nsecs_t lastFrame = systemTime();
nsecs_t frameDuration = s2ns(1) / animation.fps;
Region clearReg(Rect(mWidth, mHeight));
clearReg.subtractSelf(Rect(xc, yc, xc+animation.width, yc+animation.height));
for (size_t i=0 ; i<pcount 0="" const="" size_t="" fcount="part.frames.size();" for="" int="" r="=" part.count="" exit="" any="" non="" playuntil="" complete="" parts="" immediately="" play="" audio="" file="" the="" first="" time="" we="" animate="" part="" if="" maudioplayer="" maudioplayer-="" data-cke-pa-only="">playFile(part.audioFile);
}
glClearColor(
part.backgroundColor[0],
part.backgroundColor[1],
part.backgroundColor[2],
1.0f);
for (size_t j=0 ; j<fcount const="" nsecs_t="" lastframe="systemTime();" if="" r=""> 0) {
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid);
} else {
if (part.count != 1) {
glGenTextures(1, &frame.tid);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
}
initTexture(frame);
}
if (!clearReg.isEmpty()) {
Region::const_iterator head(clearReg.begin());
Region::const_iterator tail(clearReg.end());
glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
while (head != tail) {
const Rect& r(*head++);
glScissor(r.left, mHeight - r.bottom,
r.width(), r.height());
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
}
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
}
glDrawTexiOES(xc, yc, 0, animation.width, animation.height);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
nsecs_t now = systemTime();
nsecs_t delay = frameDuration - (now - lastFrame);
//ALOGD("%lld, %lld", ns2ms(now - lastFrame), ns2ms(delay));
lastFrame = now;
if (delay > 0) {
struct timespec spec;
spec.tv_sec = (now + delay) / 1000000000;
spec.tv_nsec = (now + delay) % 1000000000;
int err;
do {
err = clock_nanosleep(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, TIMER_ABSTIME, &spec, NULL);
} while (err<0 && errno == EINTR);
}
checkExit();
}
usleep(part.pause * ns2us(frameDuration));
// For infinite parts, we've now played them at least once, so perhaps exit
if(exitPending() && !part.count)
break;
}
// free the textures for this part
if (part.count != 1) {
for (size_t j=0 ; j<fcount const="" pre="">
主要工作,貼代碼,加自己的理解,有問題留言。
 Android對稱加密與非對稱加密
Android對稱加密與非對稱加密
凱撒密碼1. 介紹凱撒密碼作為一種最為古老的對稱加密體制,在古羅馬的時候都已經很流行,他的基本思想是:通過把字母移動一定的位數來實現加密和解密。明文中的所有字母都在字母表
 ListView擴展上拉加載更多,下拉刷新
ListView擴展上拉加載更多,下拉刷新
一、加載過程動態展示動畫在APP的研發中,加載過程用動畫更改時間的消耗,增強用戶體驗。而有個更精細的加載過程動畫,會不斷從細節優化APP的體驗。且隨著APP與服務器交互的
 淺談android中的自定義封裝易用的Dialog
淺談android中的自定義封裝易用的Dialog
好久沒寫android的博客,最近在做一個android的項目,裡面用到我們經常用的一個控件就是對話框,大家都知道android自帶的對話框是很丑的,android5.x
 Android實現偵聽電池狀態顯示、電量及充電動態顯示的方法
Android實現偵聽電池狀態顯示、電量及充電動態顯示的方法
本文實例講述了Android實現偵聽電池狀態顯示、電量及充電動態顯示的方法,是Android應用程序開發中非常常用的重要功能。分享給大家供大家參考之用。具體方法如下:使用