編輯:關於Android編程
定位(Location) 和 傳感器(Sensors)API充分發揮了移動設備的優勢,您可以調用這些API,制作出交互性較高的應用程序,比如使用設備自帶的GPS模塊定位、或使用網絡定位;使用加速器模塊(accelerometer)監聽設備的加速度、陀螺儀模塊(gyroscope)監聽設備偏轉/傾斜時的轉動角速度、溫度計模塊(temperature)測量當前設備所處環境的溫度、氣壓計模塊(barometer)測量當前設備所處環境的氣壓 等。
本文將介紹Android中地理定位的技術要點。在下一篇文章中,我將介紹有關傳感器的相關知識,如需本文的訪問官方原文,您可以點擊這個鏈接:《Location and Sensors APIs》;
有關定位的API都在android.location包中。可以定位的應用程序已經屢見不鮮。您可以使用GPS 定位、或者Network Location Provider定位。GPS定位更加精准,但更加費電、且更適用於戶外,而且不能立即返回設備所在的地理位置(Although GPS is most accurate, it only works outdoors, it quickly consumes battery power, and doesn’t return the location as quickly as users want);而Network Location Provider則是使用蜂窩網絡或Wi-Fi網絡定位,這種定位方式並不局限於戶外,而且它的反應更加靈敏、費電較少。您可以根據實際情況選擇選擇哪一種定位方式(當然也可以同時使用兩種定位方式)。
獲取設備的所在位置是一件復雜的事情(complicated),下面解釋了為何在移動設備上定位會經常產生偏差:
定位方式的抉擇(Multitude of location sources):GPS、Cell-ID、 Wi-Fi 等 都是定位的技術,為了決定應該使用哪一種方式(或哪幾種方式)定位,您需要同時權衡精確性、定位速度、以及省電性 等多方面因素(a matter of trade-offs in accuracy, speed, and battery-efficiency)。
用戶可能是不斷移動的(User movement):由於用戶的位置經常改變,您必須定時更新用戶所在位置(you must account for movement by re-estimating user location every so often)。
定位的精確性也在變化(Varying accuracy):由於定位的結果可能來自不同的定位方式,而不同的方式精確性不同。某一種定位方式在10秒之前的定位結果可能比另一種方式在當前時刻的定位結果還要准確(A location obtained 10 seconds ago from one source might be more accurate than the newest location from another)。
上述幾點導致了定位偶爾不准確的問題,下面將介紹如何克服這些問題。
在解決上述問題之前,我們先了解下如何在Android設備上獲取當前的位置。
獲取位置信息的方式是通過回調(callback)。您可以調用 requestLocationUpdates()方法,並傳入規定的參數(將在下面介紹),如LocationManager類中的常量值表示選取哪一種方式進行定位,以及LocationListener回調接口等參數。其中您需要實現LocationListener接口中的方法,當設備的位置發生變化或定位方式發生改變時,相應的方法將被回調。示例如下所示:
// 獲取LocationManager對象的引用
LocationManager locationManager = (LocationManager) this.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
// 實現LocationListener接口,並實現其中的方法
LocationListener locationListener = new LocationListener() {
//當設備的位置發生變化時,該方法將被回調
public void onLocationChanged(Location location) {
//利用回傳的位置參數location定制邏輯
makeUseOfNewLocation(location);
}
public void onStatusChanged(String provider, int status, Bundle extras) {}
public void onProviderEnabled(String provider) {}
public void onProviderDisabled(String provider) {}
};
// 調用requestLocationUpdates()方法注冊位置監聽
locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER, 0, 0, locationListener);
在requestLocationUpdates()方法中,參數1表示您使用的定位方式,(上例使用的是蜂窩網和Wi-Fi定位);參數2和參數3可以控制位置信息的更新頻率:參數2表示獲取位置信息的最小時間間隔(minimum time interval between notifications)、參數3表示獲取位置信息的最小移動距離( the third is the minimum change in distance between notifications),若這兩個參數都為0,表示盡可能頻繁地獲取位置信息(setting both to zero requests location notifications as frequently as possible);參數4是LocationListener回調接口,用於接收更新的位置等回調信息。
如果您需要使用GPS進行定位,那麼可以把上例中的LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER常量替換為LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER 。如果您需要同時使用GPS和蜂窩網絡/Wi-Fi定位,那麼您可以調用requestLocationUpdates()方法兩次,一次傳入LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER,一次傳入LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER。
請求用戶權限(Requesting User Permissions)如使用NETWORK_PROVIDER(蜂窩網/Wi-Fi)定位,那麼需要申請ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION權限;如使用GPS_PROVIDER(GPS)定位,那麼需要申請ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION權限。如:
...
定義一個最佳的定位模型(Defining a Model for the Best Performance)為了解決上面所述的若干問題,您需要設計一個在良好電量續航的前提下實現相對精確定位的模型。這個模型的設計要點是:在何時需要使用監聽的形式獲得位置信息、在何時需要使用緩存的位置信息。(when you start and stop listening for updates and when to use cached location data.)
獲取位置信息的步驟(Flow for obtaining user location)打開應用(Start application);
開啟定位監聽,有時候可以稍晚些時候開啟(Sometime later, start listening for updates from desired location providers.)
保證獲取的位置信息是最新的、但不必十分精確(Maintain a “current best estimate” of location by filtering out new, but less accurate fixes.)
停止監聽位置信息更新(Stop listening for location updates)
使用最新的位置信息估計值定制邏輯(Take advantage of the last best location estimate)
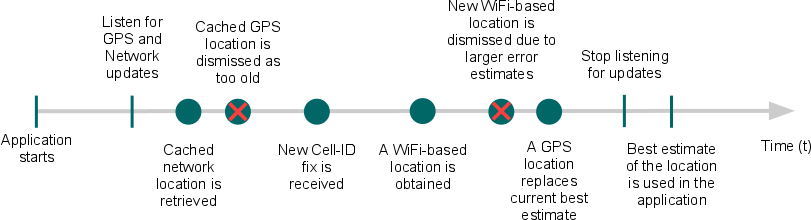
上圖是一個時間軸,它表示上述步驟按時間的執行順序,即應用程序監聽及更新位置信息的過程,這也是一般包含定位功能的應用程序的定位模型。
確定何時開始監聽位置信息的更新(Deciding when to start listening for updates)您可能希望在程序一啟動就開始監聽位置的實時變化,或者僅僅是某個功能需要得到位置信息時才啟動定位功能。需要注意的是,長時間的開啟定位功能是非常耗電的,而在短時間內開啟定位功能又不能保證定位的精確性。
一般情況下,調用requestLocationUpdates()方法就意味著定位功能已開啟:
String locationProvider = LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER;
// Or, use GPS location data:
// String locationProvider = LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER;
locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(locationProvider, 0, 0, locationListener);
使用最新的位置信息快速定位(Getting a fast fix with the last known location)使用監聽器首次獲取實時位置信息經常比較耗時(The time it takes for your location listener to receive the first location fix is often too long for users wait),在監聽器返回精確的定位信息之前,您需要調用getLastKnownLocation(String)方法獲取緩存的位置信息(Until a more accurate location is provided to your location listener, you should utilize a cached location by calling getLastKnownLocation(String)):
String locationProvider = LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER;
// Or use LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER
Location lastKnownLocation = locationManager.getLastKnownLocation(locationProvider);
確定何時停止監聽位置信息的更新(Deciding when to stop listening for updates)在監聽位置信息時,您應當時刻考慮到好點的情況,當獲取到位置信息後,應當調用removeUpdates(PendingIntent)方法停止監聽位置信息:
// Remove the listener you previously added
locationManager.removeUpdates(locationListener);
保證持有當前實時位置的最佳估計值(Maintaining a current best estimate)您可能會認為監聽到最新的位置信息都是最精確的。但事實並非如此——因為定位的方式和所處環境不盡相同。您需要根據不同的場景和情況切換定位的模式。
您可以通過下面的步驟來檢測得到的當前位置信息是否准確:
檢查當前獲取的位置信息是否跟之前的位置有顯著的變化;
檢查當前的定位方式是否比之前的定位方式精確性更高;
檢查在當前環境下,哪一種定位方式可以進行更加精確的定位;
示例如下:
private static final int TWO_MINUTES = 1000 * 60 * 2;
/** Determines whether one Location reading is better than the current Location fix
* @param location The new Location that you want to evaluate
* @param currentBestLocation The current Location fix, to which you want to compare the new one
*/
protected boolean isBetterLocation(Location location, Location currentBestLocation) {
if (currentBestLocation == null) {
// A new location is always better than no location
return true;
}
// Check whether the new location fix is newer or older
long timeDelta = location.getTime() - currentBestLocation.getTime();
boolean isSignificantlyNewer = timeDelta > TWO_MINUTES;
boolean isSignificantlyOlder = timeDelta < -TWO_MINUTES;
boolean isNewer = timeDelta > 0;
// If it's been more than two minutes since the current location, use the new location
// because the user has likely moved
if (isSignificantlyNewer) {
return true;
// If the new location is more than two minutes older, it must be worse
} else if (isSignificantlyOlder) {
return false;
}
// Check whether the new location fix is more or less accurate
int accuracyDelta = (int) (location.getAccuracy() - currentBestLocation.getAccuracy());
boolean isLessAccurate = accuracyDelta > 0;
boolean isMoreAccurate = accuracyDelta < 0;
boolean isSignificantlyLessAccurate = accuracyDelta > 200;
// Check if the old and new location are from the same provider
boolean isFromSameProvider = isSameProvider(location.getProvider(),
currentBestLocation.getProvider());
// Determine location quality using a combination of timeliness and accuracy
if (isMoreAccurate) {
return true;
} else if (isNewer && !isLessAccurate) {
return true;
} else if (isNewer && !isSignificantlyLessAccurate && isFromSameProvider) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/** Checks whether two providers are the same */
private boolean isSameProvider(String provider1, String provider2) {
if (provider1 == null) {
return provider2 == null;
}
return provider1.equals(provider2);
}
在省電和精確定位之間作出權衡(Adjusting the model to save battery and data exchange)縮減監聽位置的生命周期(Reduce the size of the window):這樣可以減少GPS等模塊的調用,即延長電池續航,但這樣可能不會得到精確的位置信息;
減少監聽方法的回調頻率(Set the location providers to return updates less frequently):這樣同樣可以省電,但是以定位精確性作為代價的,您可以在requestLocationUpdates()方法的第二個和第三個參數進行設置(增大它們的值);
限制同時使用多種定位方式(Restrict a set of providers):您可以根據實際情況,僅使用某一種定位方式即可,這樣同樣可以增加續航時間。
 向上滾動公告欄
向上滾動公告欄
項目中需要用到類似公告欄的控件,能用的基本不支持多行顯示,於是只好自己動手,苦於沒有自定義過一個像樣的控件,實現了多行向上滾動的控件。在原控件基礎之上添加如下功能:傳入數
 Android基礎入門教程——8.3.14 Paint幾個枚舉-常量值以及ShadowLayer陰影效果
Android基礎入門教程——8.3.14 Paint幾個枚舉-常量值以及ShadowLayer陰影效果
Android基礎入門教程——8.3.14 Paint幾個枚舉/常量值以及ShadowLayer陰影效果標簽(空格分隔): Android基礎入門
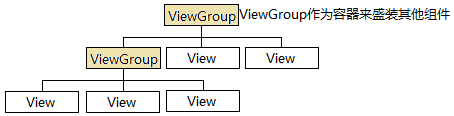 Android 界面編程 探險(一)
Android 界面編程 探險(一)
Android應用大部分UI組件都放在android.widget包及其子包、android.view包及其子包中,所有UI組件都繼承了View類,Android采用&l
 Android實戰技巧之四十六:用patch更新Android Studio
Android實戰技巧之四十六:用patch更新Android Studio
公司機器上的Android Studio很時髦,每次都會准時接收到官方穩定版的推送。目前最新的穩定版本是1.4.1,增加了很多心動的功能。可是我的筆記本上的AS還在1.3