編輯:關於Android編程
在多線程的世界中,是那麼的神奇 與 高效以及合理;
官方推薦使用Executors類工廠方法來創建線程池管理,Executors類是官方提供的一個工廠類,裡面封裝了好多功能不一樣的線程池,從而使得我們創建線程池非常的簡單:
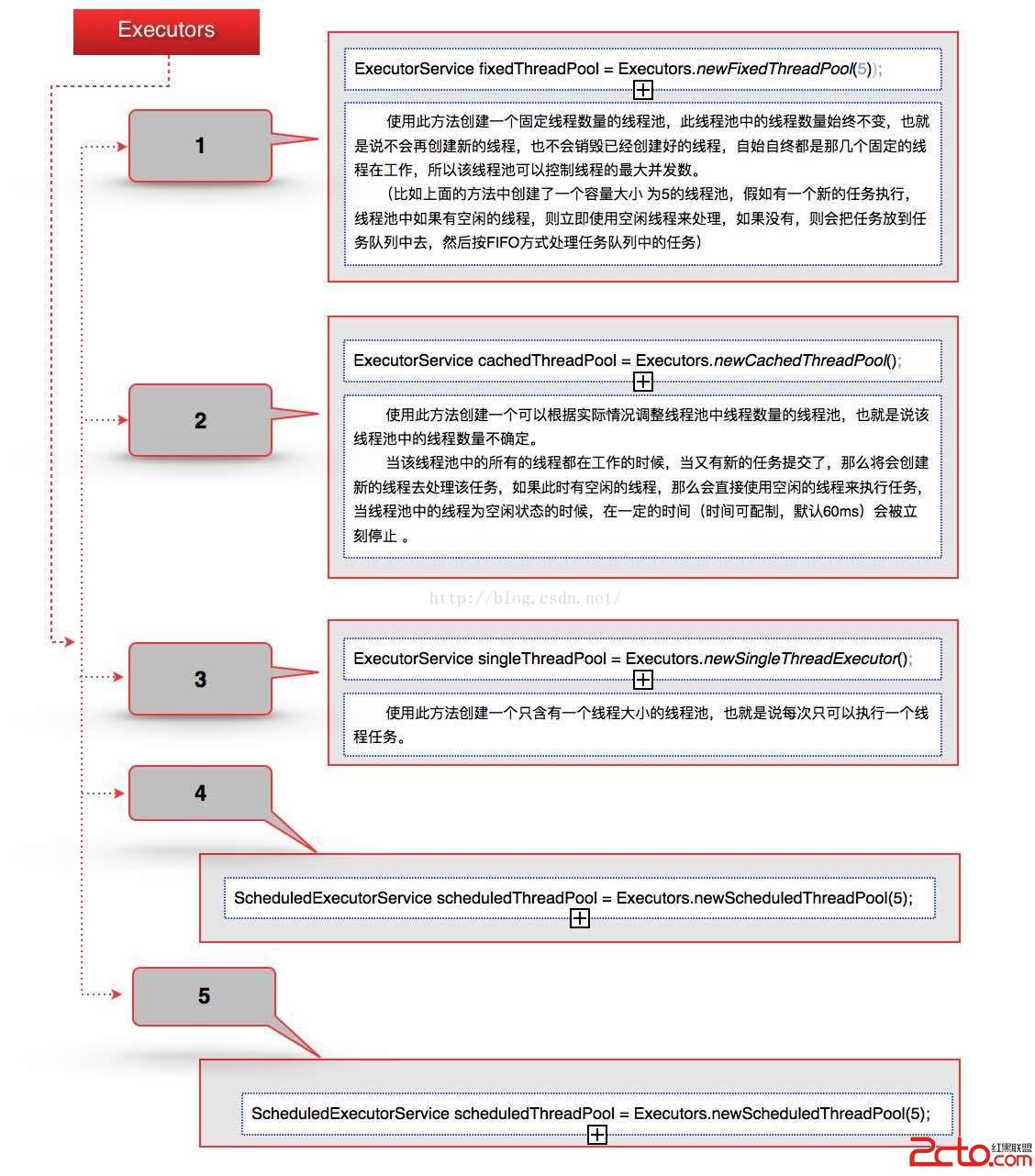
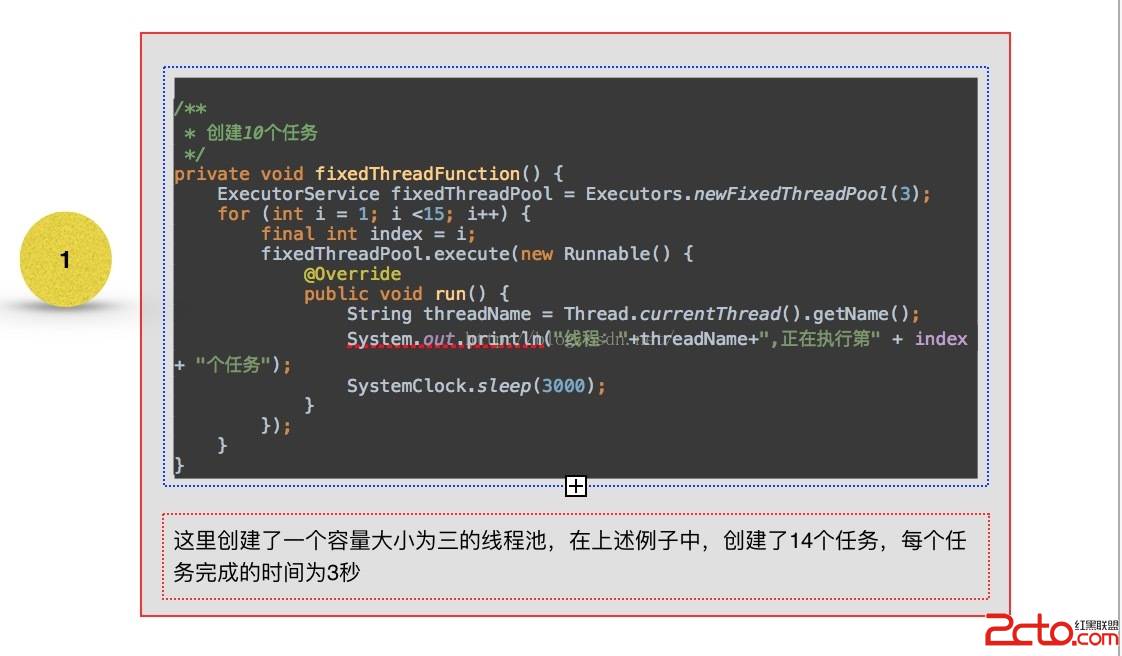
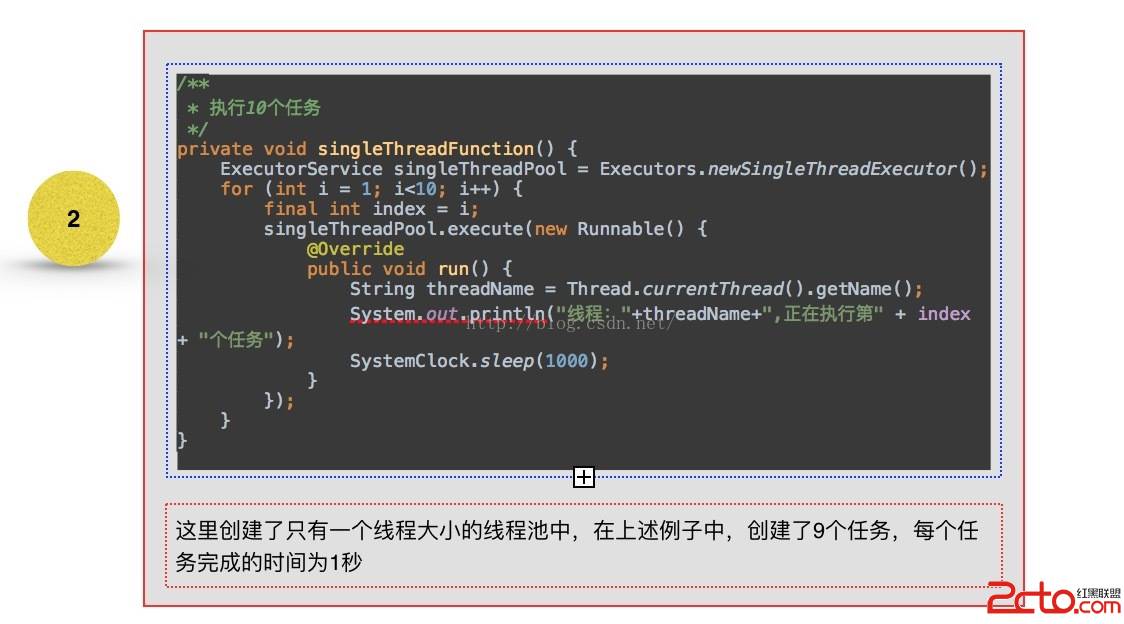
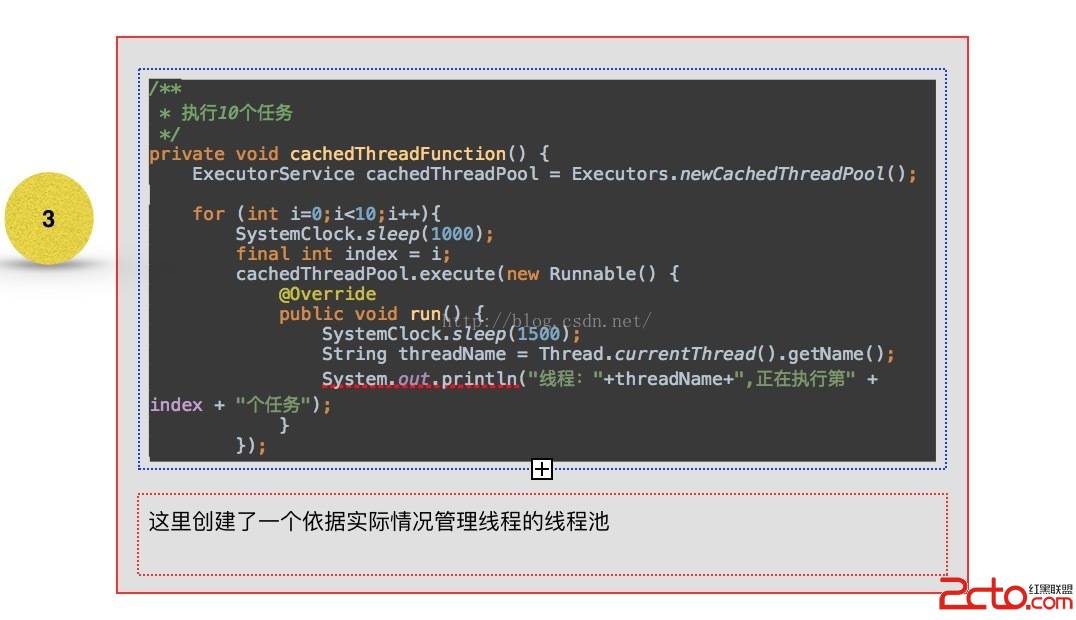
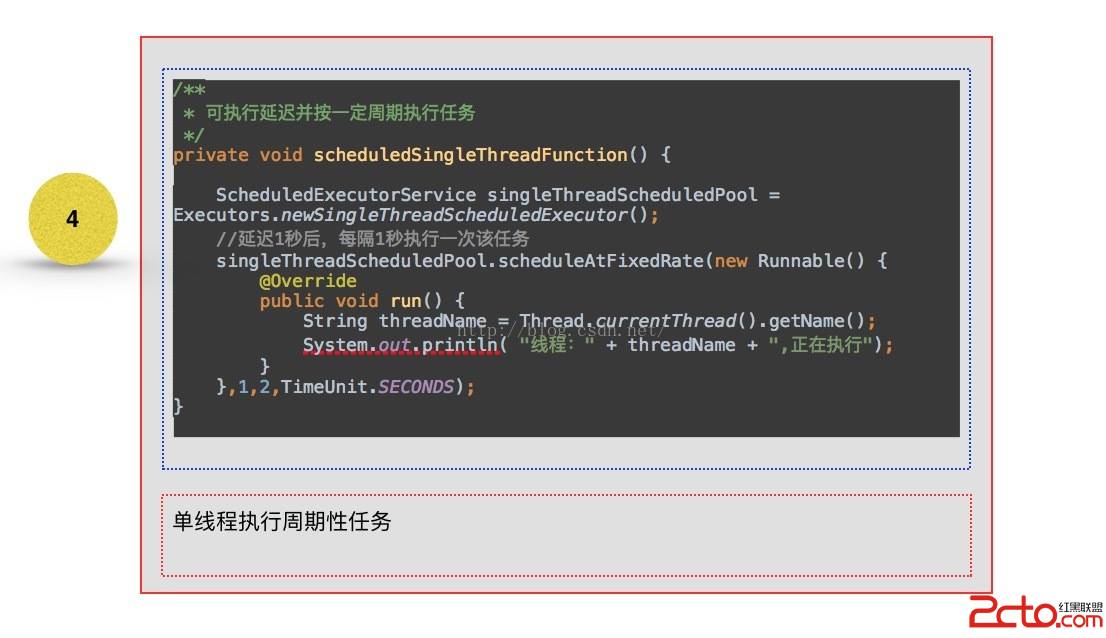
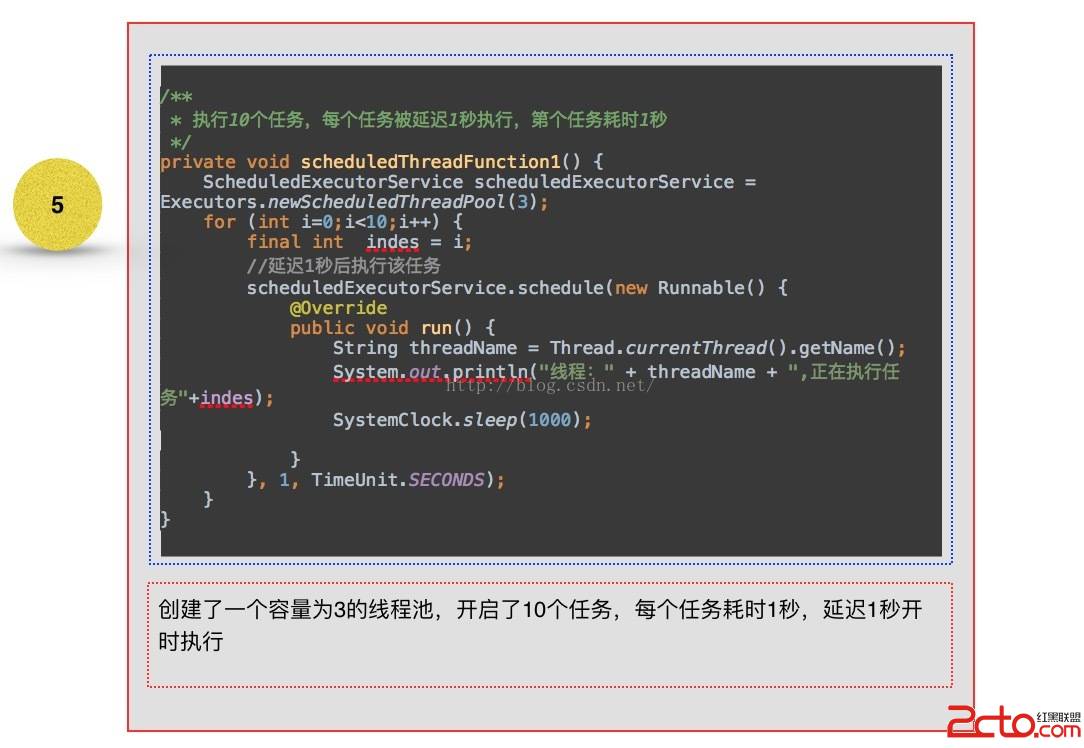
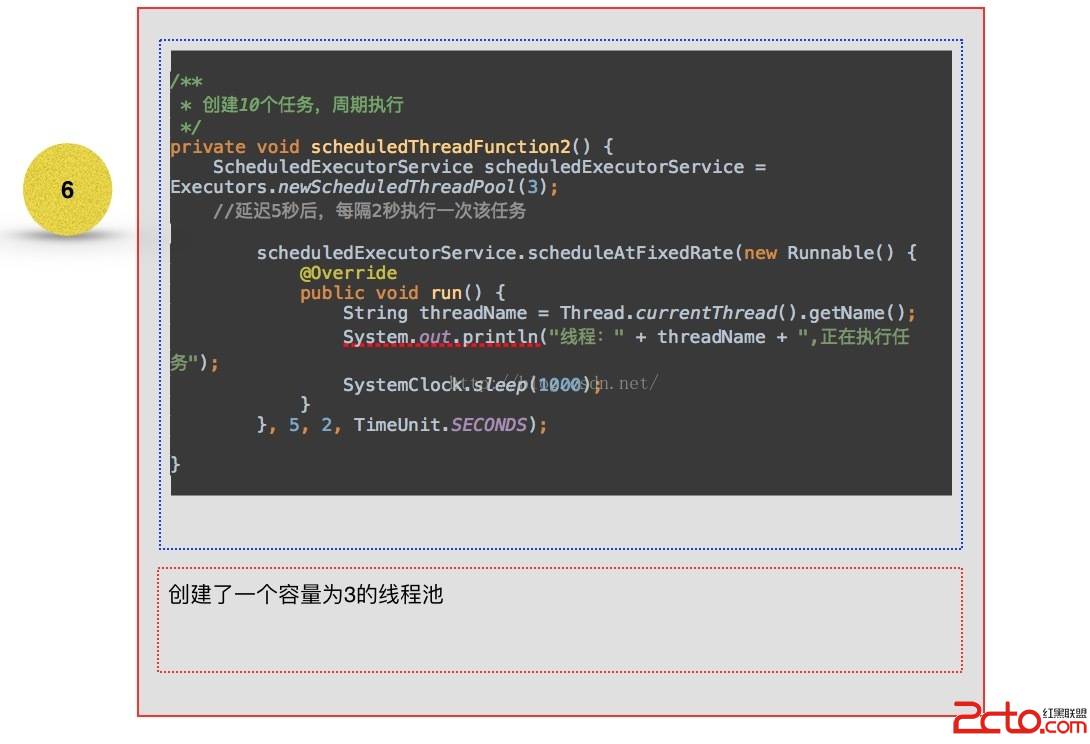
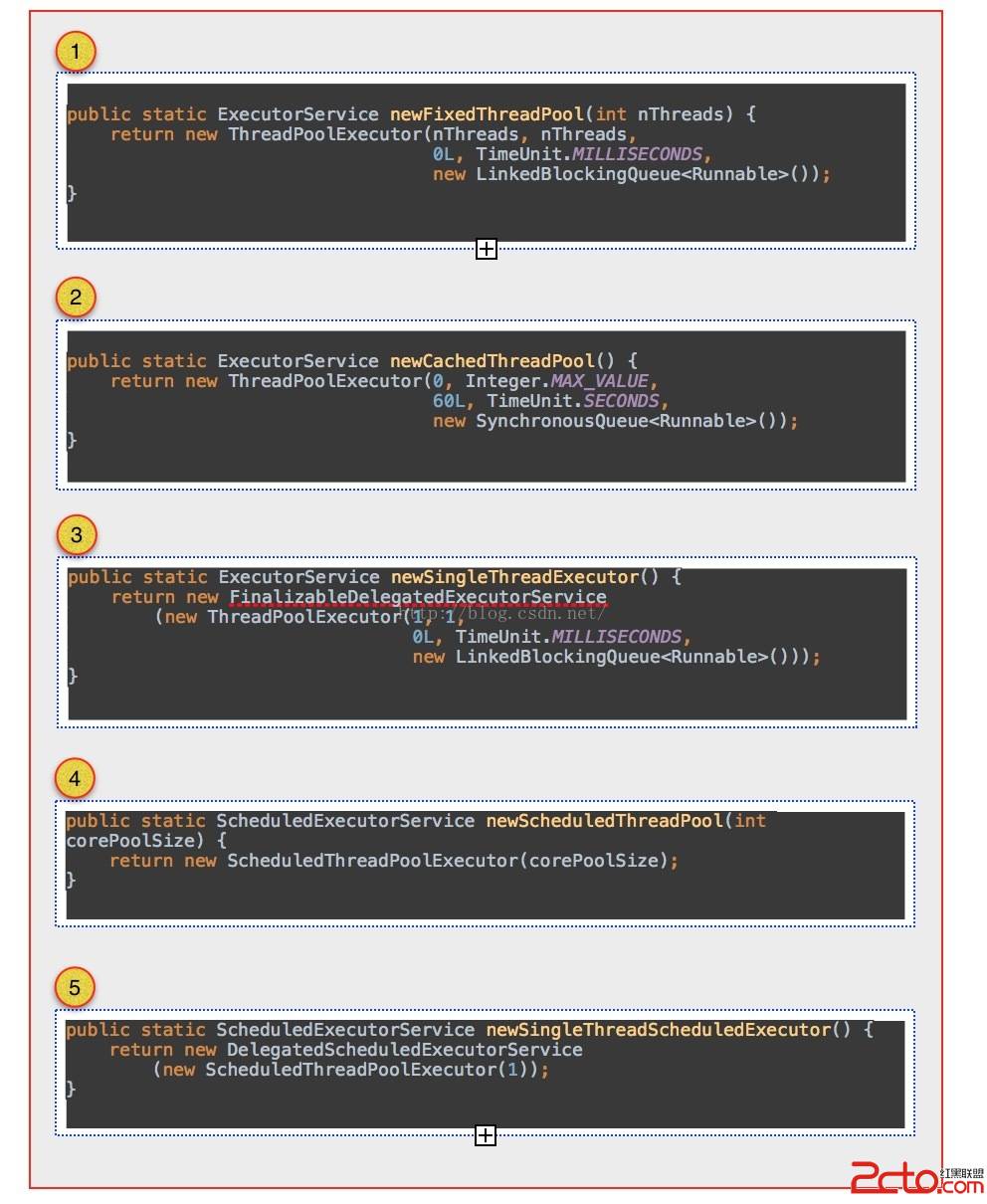
可以看到1 - 3 創建線程池的方法中,全部是創建了ThreadPoolExecutor這個對象實例,不同的只是構造中的參數不一至,而在4 與5 ,從其繼承的角度來看
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
extends ThreadPoolExecutor
implements ScheduledExecutorService {
可以看到其實質也是繼承於ThreadPoolExecutor這個對象實例。
也就是說上述一種類型的線程池其都是 ThreadPoolExecutor子類,其實直接創建ThreadPoolExecutor實例對象,只需要傳入相對應的配制參數,就可以創建出來與上述五種效果相一至的線程池管理,只不過是在書寫的時候太過於繁鎖。
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters and default thread factory and rejected execution handler.
* It may be more convenient to use one of the {@link Executors} factory
* methods instead of this general purpose constructor.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue} is null
*/
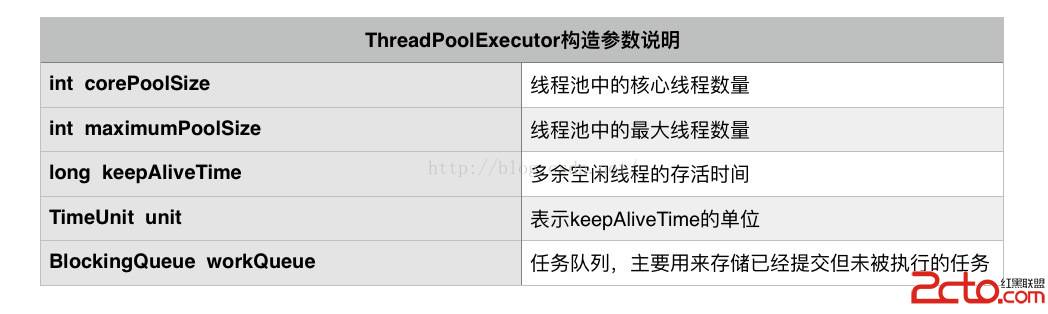
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
從上述創建ThreadPoolEecutor實例的構造來說,
/**
* 創建線程池也是需要資源的,所以線程池內線程數量的大小也會影響系統的性能,
* 大了反而浪費資源,小了反而影響系統的吞吐量,
* 所以我們創建線程池需要把握一個度才能合理的發揮它的優點,
* 通常來說我們要考慮的因素有CPU的數量、內存的大小、並發請求的數量等因素,按需調整。
*通常核心線程數可以設為CPU數量+1,而最大線程數可以設為CPU的數量*2+1。
*/
private void customThreadFunction() {
/**
* 獲取CPU數量
*/
int processors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* 核心線程數量
*/
int corePoolSize =processors + 1;
/**
* 最大線程數量
*/
int maximumPoolSize = processors * 2 + 1;
/**
* 空閒有效時間
*/
long keepAliveTime = 60;
/**
* 創建自定義線程池
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new PriorityBlockingQueue());
/**
* 添加執行任務
*/
for (int i=1;i<=20;i++){
final int prites = i;
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new CustomRunnable(prites){
@Override
public void doRun() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("curentThread name is "+name +"and prites is "+prites);
SystemClock.sleep(1000);
}
});
}
}
public abstract class CustomRunnable implements Runnable,Comparable{ private int priority; public CustomRunnable(int priority) { if (priority<0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.priority = priority; } @Override public int compareTo(CustomRunnable another) { int my = this.getPriority(); int other = another.getPriority(); if (my>other){ return -1; }else{ return 0; } } @Override public void run() { doRun(); } public abstract void doRun(); public int getPriority() { return priority; } }
public class CustomExpanThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
private CustomExpanThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}
public static CustomExpanThreadPool getInstance() {
/**
* 獲取CPU數量
*/
int processors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* 核心線程數量
*/
int corePoolSize = processors + 1;
/**
* 最大線程數量
*/
int maximumPoolSize = processors * 2 + 1;
/**
* 空閒有效時間
*/
long keepAliveTime = 60;
/**
* 創建自定義線程池
*/
return new CustomExpanThreadPool(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new PriorityBlockingQueue());
}
/**
* 用於控制線程開始與停止執行的方法
*/
private boolean isPaused;
private ReentrantLock pauseLock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition unpaused = pauseLock.newCondition();
/**
* 任務執行前要執行的方法
*
* @param t
* @param r
*/
@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 任務執行開始 ");
pauseLock.lock();
try {
while (isPaused) unpaused.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
t.interrupt();
} finally {
}
}
/**
* 任務執行後要執行的方法
*
* @param r
* @param t
*/
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
super.afterExecute(r, t);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 任務執行over ");
}
/**
* 線程池關閉後要執行的方法
*/
@Override
protected void terminated() {
super.terminated();
}
/**
* 暫停執行任務的方法
*/
public void pause() {
pauseLock.lock();
try {
isPaused = true;
} finally {
pauseLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 恢復執行任務的方法
*/
public void resume() {
pauseLock.lock();
try {
isPaused = false;
unpaused.signalAll();
} finally {
pauseLock.unlock();
}
}
}
private void customThreadFunction2() {
CustomExpanThreadPool threadPoolExecutor = CustomExpanThreadPool.getInstance();
/**
* 添加執行任務
*/
for (int i=1;i<=20;i++){
final int prites = i;
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new CustomRunnable(prites){
@Override
public void doRun() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("curentThread name is "+name +"and prites is "+prites);
SystemClock.sleep(1000);
}
});
}
}
 Android UI設計系列之HTML標簽實現TextView設置中文字體加粗效果(6)
Android UI設計系列之HTML標簽實現TextView設置中文字體加粗效果(6)
搞軟件開發的都知道項目中各種需求都有,而有時候各種奇葩的需求真是讓人大跌眼鏡,為了實現這些奇葩的需求我們往往苦逼的廢寢忘食,我現在的項目中就有一個應該算得上奇葩的需求吧,
 Android:Pull解析XML
Android:Pull解析XML
在上一篇文章寫了SAX解析XML,感覺Pull方式和SAX方式非常相似,只是SAX需要一個輔助的類,解析時觸發事件後在回調方法裡面寫代碼,而Pull則通過調
 Android中自定義View實現圓環等待及相關的音量調節效果
Android中自定義View實現圓環等待及相關的音量調節效果
圓環交替、等待效果效果就這樣,分析了一下,大概有這幾個屬性,兩個顏色,一個速度,一個圓環的寬度。自定View的幾個步驟:1、自定義View的屬性2、在View的構造方法中
 Android插件開發初探——基礎篇
Android插件開發初探——基礎篇
Android插件開發初探對於Android的插件化其實已經討論已久了,但是市面上還沒有非常靠譜成熟的插件框架供我們使用。這裡我們就嘗試性的對比一下Java中,我們使用插