編輯:關於Android編程
由於本人所作的項目需要用到這種列表式的收縮與展開,因此,就好好研究了有關這方面的一些知識,當然,也借鑒了網上一些成功的案列。下面就是我模擬測試的一個展示界面。
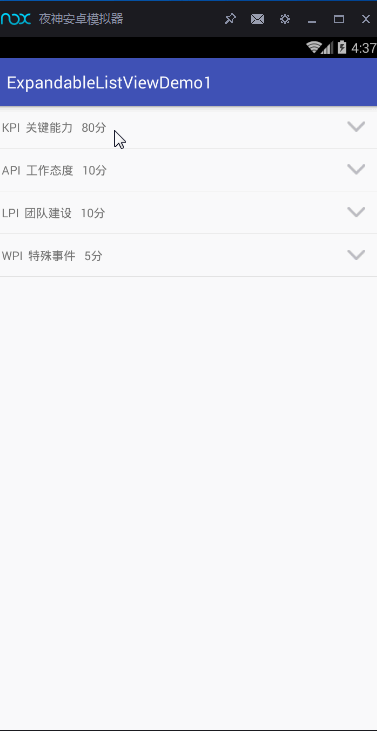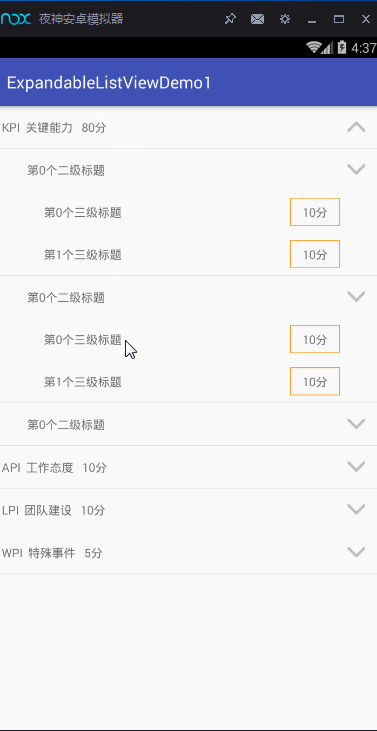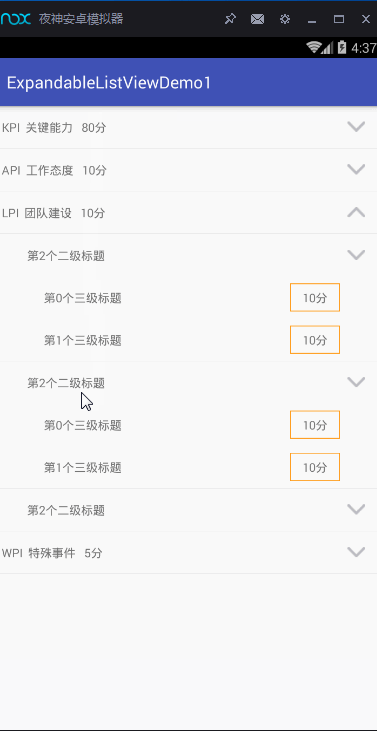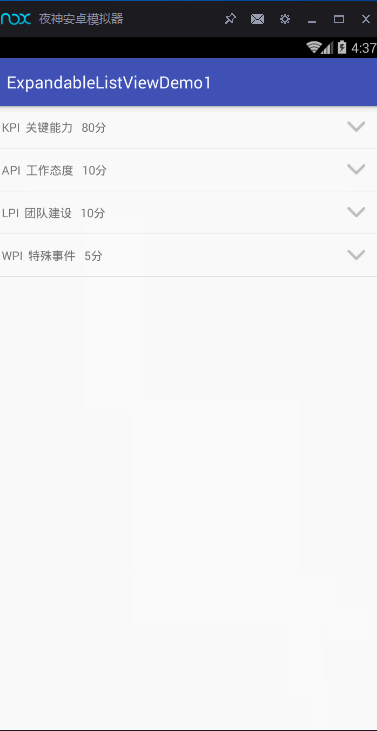
實現上面的這些功能,我主要是通過ExpandableListView這一控件,以及BaseExpandableListAdapter適配器。這兩者關聯實現的。好的,那接下來,就對這些進行詳細的展示。
所有的xml布局展示
## parent_group_item.xml##
## child_adapter.xml##
## child_child.xml##
## activity_content.xml##
接下來就是獲取數據、適配數據,以及對控件的操作事件。首先是獲取數據,由於項目接口不宜公開,固這裡采用的是測試數據其主要代碼如下。
/**
* 初始化數據
*/
private void initData() {
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
FirstBean firstBean = new FirstBean();
ArrayList mArrlistSecondBean = new ArrayList();
if(i==0){
firstBean.setScore("80分");
firstBean.setTitle("KPI 關鍵能力");
}else if(i==1){
firstBean.setScore("10分");
firstBean.setTitle("API 工作態度");
}else if(i==2){
firstBean.setScore("10分");
firstBean.setTitle("LPI 團隊建設");
}else if(i==3){
firstBean.setScore("5分");
firstBean.setTitle("WPI 特殊事件");
}
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
SecondBean secondBean = new SecondBean();
secondBean.setTitle("第"+i+"個二級標題");
ArrayList mArrlistBean = new ArrayList();
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
ThirdBean thirdBean = new ThirdBean();
thirdBean.setTitle("第"+k+"個三級標題");
mArrlistBean.add(thirdBean);
}
secondBean.setSecondBean(mArrlistBean);
mArrlistSecondBean.add(secondBean);
}
firstBean.setFirstData(mArrlistSecondBean);
mDatas.add(firstBean);
Log.e("xxx",mDatas.get(i).getTitle());
}
}
由於是三級菜單,所以這裡的實體用了3個,理論上,n級菜單的話,那就得n個實體,但是一般的app用到的至多就是3級,4級以上的都比較少見。其適配器那就得用兩個。接下來講解第一個適配器,它不是繼承BaseAdapter,繼承的是BaseExpandableListAdapter,通過重寫它的方法能很好的把數據與控件結合在一起。其主要的方法有:getGroupView()、getChildView()….主要代碼如下。
/**
* 第一級菜單適配器布局
* @param parentPosition
* @param isExpanded
*
* @param convertView
* @param viewGroup
* @return
*/
@Override
public View getGroupView(int parentPosition, boolean isExpanded, View convertView, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(
R.layout.parent_group_item, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.upImg = (ImageView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.kpi_back_img);
holder.score = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.kpi_score);
holder.title = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.title);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
//區分箭頭往上還是
if(isExpanded){
holder.upImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.dowm);
}else{
holder.upImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.up);
}
holder.title.setText(mData.get(parentPosition).getTitle());
holder.score.setText(mData.get(parentPosition).getScore());
return convertView;
}
class ViewHolder{
private TextView title;
private TextView score;
private ImageView upImg;
}
public ExpandableListView getExpandableListView() {
ExpandableListView mExpandableListView = new ExpandableListView(
mContext);
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = new AbsListView.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, (int) mContext
.getResources().getDimension(
R.dimen.parent_list_height));
mExpandableListView.setLayoutParams(lp);
mExpandableListView.setDividerHeight(0);// 取消group項的分割線
mExpandableListView.setChildDivider(null);// 取消child項的分割線
mExpandableListView.setGroupIndicator(null);// 取消展開折疊的指示圖標
return mExpandableListView;
}
/**
* 第二級菜單式配
* @param parentPosition
* @param childPosition
* @param isExpanded
* @param view
* @param viewGroup
* @return
*/
@Override
public View getChildView(final int parentPosition, final int childPosition, boolean isExpanded, View view, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
final ExpandableListView childListView = getExpandableListView();
//獲取子菜單的數據
final ArrayList childData = new ArrayList();
final SecondBean bean = getChild(parentPosition,childPosition);
childData.add(bean);
ChildAdapter adapter = new ChildAdapter(mContext,childData,parentPosition);
childListView.setAdapter(adapter);
/**
* 點擊最小級菜單,調用該方法
* */
childListView.setOnChildClickListener(new ExpandableListView.OnChildClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onChildClick(ExpandableListView arg0, View arg1,
int groupIndex, int childIndex, long arg4) {
if(mListener != null){
mListener.onclick(parentPosition,childPosition, childIndex);
//點擊三級菜單,跳轉到編輯菜單界面
Intent intent = new Intent(mContext, ContentActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("content","你點的位置是: "+"parentPosition>>"+parentPosition+
"childPosition>>"+childPosition+"childIndex>>"+childIndex);
mContext.startActivity(intent);
}
return false;
}
});
/**
*子ExpandableListView展開時,因為group只有一項,所以子ExpandableListView的總高度=
* (子ExpandableListView的child數量 + 1 )* 每一項的高度
* */
childListView.setOnGroupExpandListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupExpandListener() {
@Override
public void onGroupExpand(int groupPosition) {
Log.e("xxx",groupPosition+"onGroupExpand>>");
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = new AbsListView.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
(bean.getSecondBean().size() + 1)* (int) mContext
.getResources().getDimension(R.dimen.parent_list_height));
childListView.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
});
/**
*子ExpandableListView關閉時,此時只剩下group這一項,
* 所以子ExpandableListView的總高度即為一項的高度
* */
childListView.setOnGroupCollapseListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupCollapseListener() {
@Override
public void onGroupCollapse(int groupPosition) {
Log.e("xxx",groupPosition+">>onGroupCollapse");
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = new AbsListView.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, (int) mContext
.getResources().getDimension(R.dimen.parent_list_height));
childListView.setLayoutParams(lp);
holder.upImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.up);
}
});
/**
* 在這裡對二級菜單的點擊事件進行操作
*/
childListView.setOnGroupClickListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onGroupClick(ExpandableListView parent, View v, int Position, long id) {
// if(isClick){
// holder.mUpImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.dowm);
// isClick = false;
// }else{
// holder.mUpImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.up);
// isClick = true;
// }
Log.e("Xxx","恭喜你,點擊了"+parentPosition+"childpos>>>"+childPosition);
return false;
}
});
return childListView;
}
第二個適配器與上述差不多,也是主要通過以上的方法來實現的。
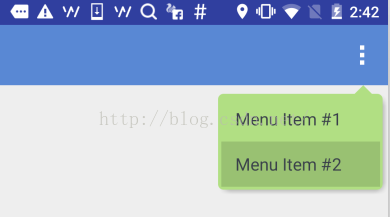 Android自定義ViewGroup(一)——帶箭頭的圓角矩形菜單
Android自定義ViewGroup(一)——帶箭頭的圓角矩形菜單
今天要做一個帶箭頭的圓角矩形菜單,大概長下面這個樣子: 要求頂上的箭頭要對准菜單錨點,菜單項按壓反色,菜單背景色和按壓色可配置。最簡單的做法就是讓UX給個三角形
 直接拿來用的Android刮獎控件
直接拿來用的Android刮獎控件
直接上效果圖 功能特色: 1、可以設置刮開後顯示文字或圖片 2、可以統計已刮開區域所占百分比 Demo下載地址:RubberDem
 Android實習札記(5)---Fragment之底部導航欄的實現
Android實習札記(5)---Fragment之底部導航欄的實現
在Part 4我們回顧了一下Fragment的基本概念,在本節中我們就來學習Fragment應用的簡單例子吧! 就是使用Fragment來實現
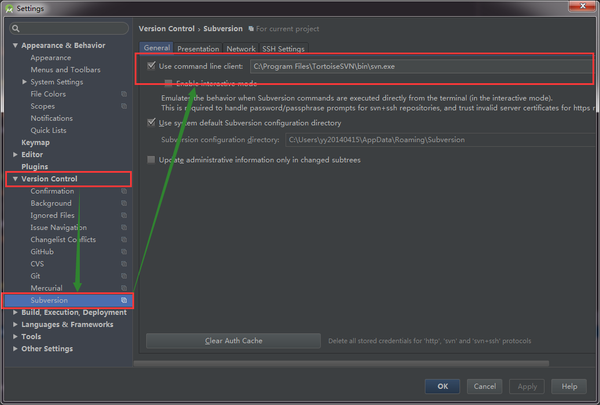 Android Studio配置SVN
Android Studio配置SVN
一、 Android Studio配置SVN Android Studio關聯配置SVN很簡單,在Settings裡面,找到Version Control->Sub