編輯:關於Android編程
觸控事件
MotionEvent類:
//單擊觸摸按下動作
public static final int ACTION_DOWN = 0;
/**
* Constant for {@link #getActionMasked}: A pressed gesture has finished, the
* motion contains the final release location as well as any intermediate
* points since the last down or move event.
* 單擊觸摸離開動作
*/
public static final int ACTION_UP = 1;
/**
* Constant for {@link #getActionMasked}: A change has happened during a
* press gesture (between {@link #ACTION_DOWN} and {@link #ACTION_UP}).
* The motion contains the most recent point, as well as any intermediate
* points since the last down or move event.
* 觸摸點移動動作
*/
public static final int ACTION_MOVE = 2;
/**
* Constant for {@link #getActionMasked}: The current gesture has been aborted.
* You will not receive any more points in it. You should treat this as
* an up event, but not perform any action that you normally would.
* 觸摸動作取消
*/
public static final int ACTION_CANCEL = 3;
/**
* Constant for {@link #getActionMasked}: A movement has happened outside of the
* normal bounds of the UI element. This does not provide a full gesture,
* but only the initial location of the movement/touch.
* 觸摸動作超出邊界
*/
public static final int ACTION_OUTSIDE = 4;
/**
* Constant for {@link #getActionMasked}: A non-primary pointer has gone down.
* <p>
* Use {@link #getActionIndex} to retrieve the index of the pointer that changed.
* </p><p>
* The index is encoded in the {@link #ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_MASK} bits of the
* unmasked action returned by {@link #getAction}.
* </p>
* 多點觸摸按下動作
*/
public static final int ACTION_POINTER_DOWN = 5;
/**
* Constant for {@link #getActionMasked}: A non-primary pointer has gone up.
* <p>
* Use {@link #getActionIndex} to retrieve the index of the pointer that changed.
* </p><p>
* The index is encoded in the {@link #ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_MASK} bits of the
* unmasked action returned by {@link #getAction}.
* </p>
* 多點離開動作
*/
public static final int ACTION_POINTER_UP = 6;
MotionEvent提供的方法:
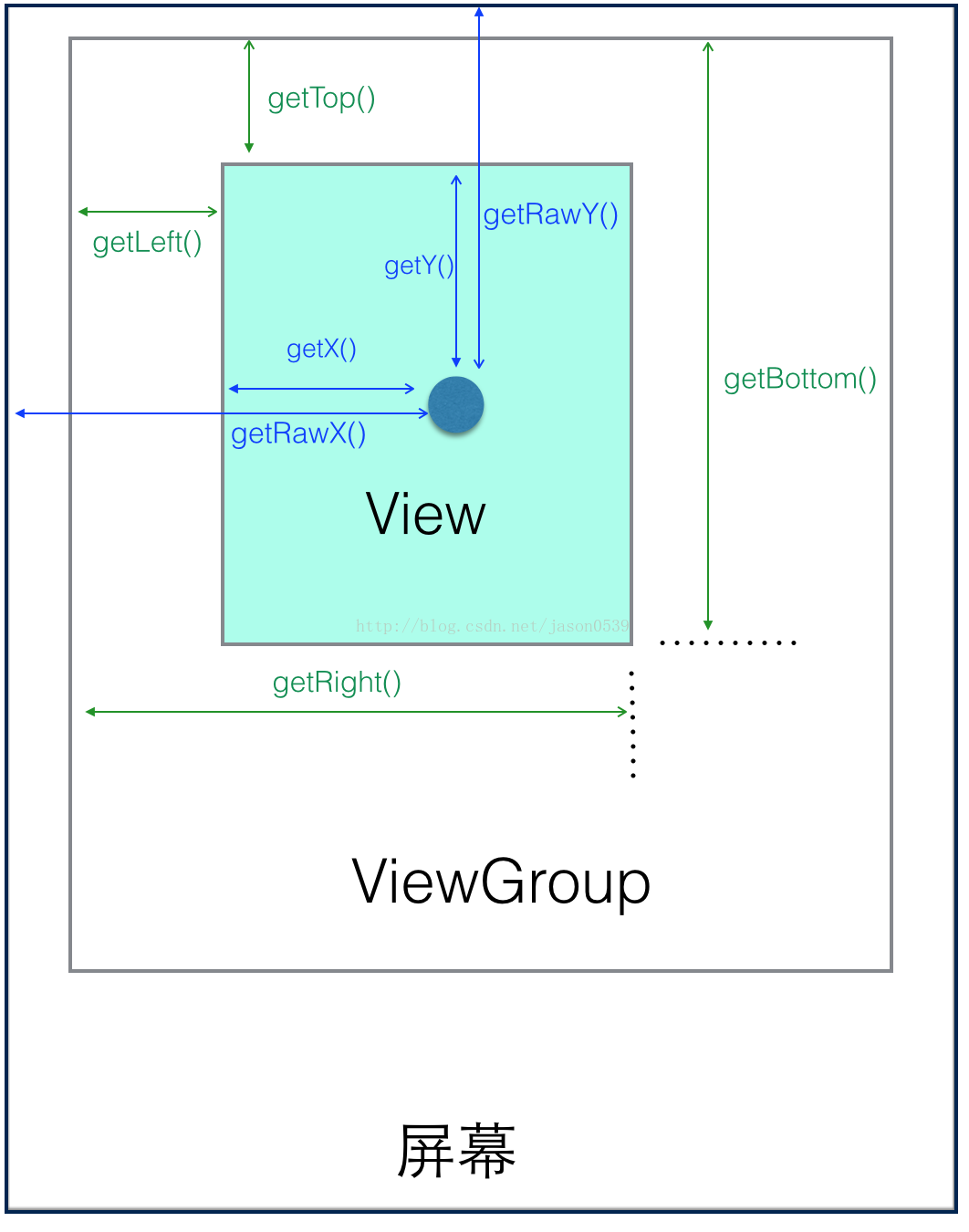
getTop():獲取到的是View自身的頂邊到其父布局頂邊的距離。
getLeft():獲取到的是View自身的左邊到其父布局左邊的距離。
getRight():獲取到的是View自身的右邊到其父布局右邊的距離。
getBottom():獲取到的是View自身的底邊到其父布局底邊的距離。
getX():獲取點擊事件距離控件左邊的距離
getY():獲取點擊事件距離控件頂邊的距離
getRawX():獲取點擊事距離整個屏幕左邊的距離,即絕對坐標。
getRawY():獲取點擊事距離整個屏幕頂邊的距離,即絕對坐標。
**實現滑動的基本原理(核心思想):
當觸摸View時候,系統記錄當前觸摸點的坐標,當手指移動時候,系統記錄下移動的觸摸點坐標,從而獲取到相對於前一次坐標點的偏移量,並且通過偏移量修改view的坐標,這樣不斷重復,從而實現滑動效果。**
實現滑動的常用方法:
layout方法:
package com.example.drawdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView5 extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
public MyView5(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
initView();
}
public MyView5(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView();
}
public MyView5(Context context) {
super(context);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE);
}
// 視圖坐標方式
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 計算偏移量
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
layout(getLeft() + offsetX, getTop() + offsetY, getRight() + offsetX, getBottom() + offsetY);
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
}
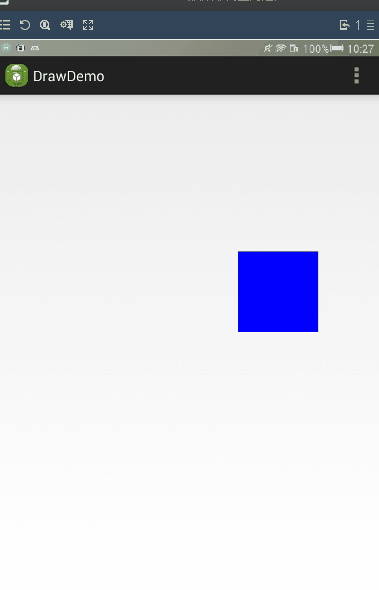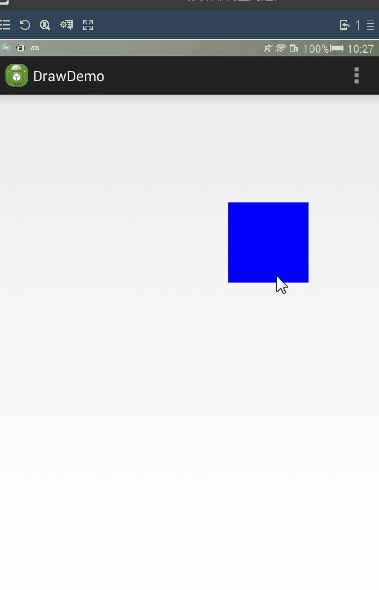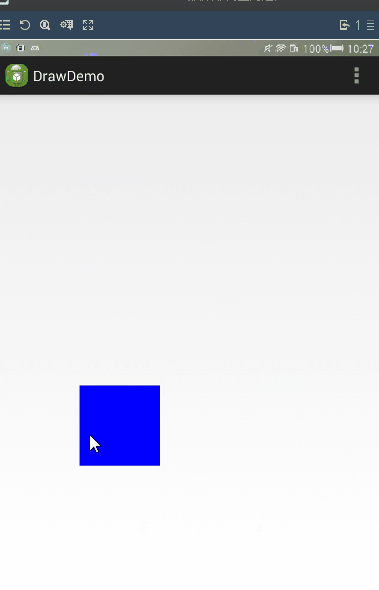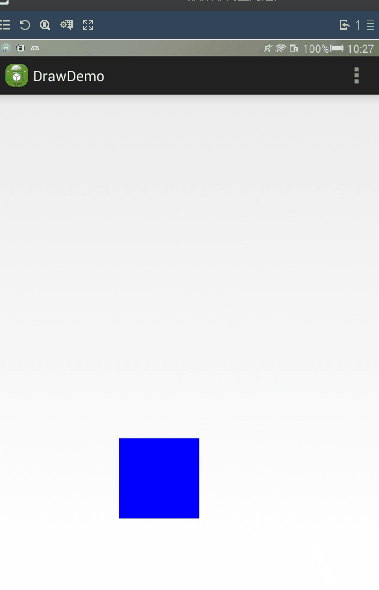
通過LayoutParams進行滑動。
LayoutParams 保存了一個View的布局參數,因此在程序中,通過改變LayoutParams修改一個布局的位置參數,從而達到改變View位置的效果。
而且我們可以使用getLayoutparams()來獲取一個View的LayoutParams.計算偏移量的方法與在Layout方法中計算offset也是一樣的,當獲取偏移量後,就可以通過setLayoutParams來改變Layoutparams.
當然獲取父容易布局,會有不同的布局(如果父容易是LinearLatyou,那麼就要使用LinearLayout.LayoutParams.如果是RelativeLayout,那麼就要使用RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.),所以我們直接使用ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams來實現這個功能。
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
// LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams =(LinearLayout.LayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.leftMargin = getLeft() + offsetX;
layoutParams.topMargin = getTop() + offsetY;
這個使用更加方便,不用考錄父容器布局。
package com.example.drawdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class MyView6 extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
public MyView6(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
ininView();
}
public MyView6(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
ininView();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public MyView6(Context context) {
super(context);
ininView();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
private void ininView() {
setBackgroundColor(Color.GREEN);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// 記錄觸摸點坐標
lastX = (int) event.getX();
lastY = (int) event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 計算偏移量
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
// LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.leftMargin = getLeft() + offsetX;
layoutParams.topMargin = getTop() + offsetY;
setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
break;
}
return true;
}
}
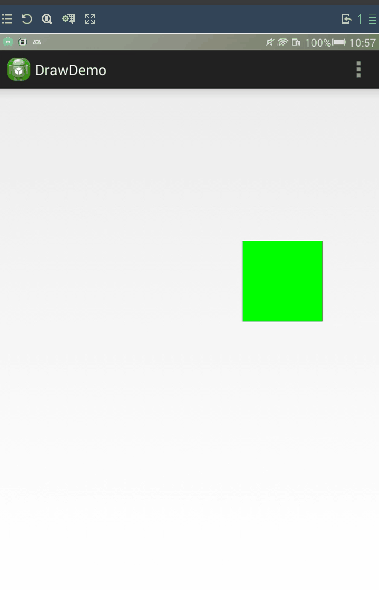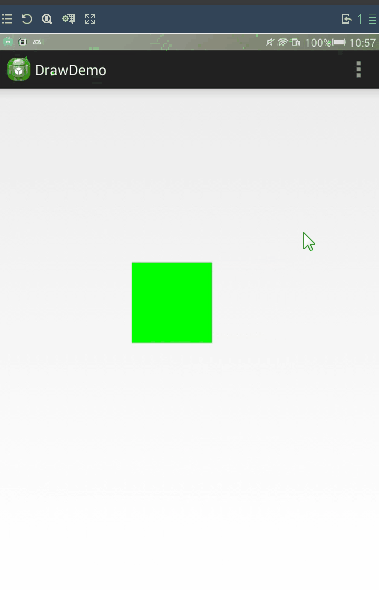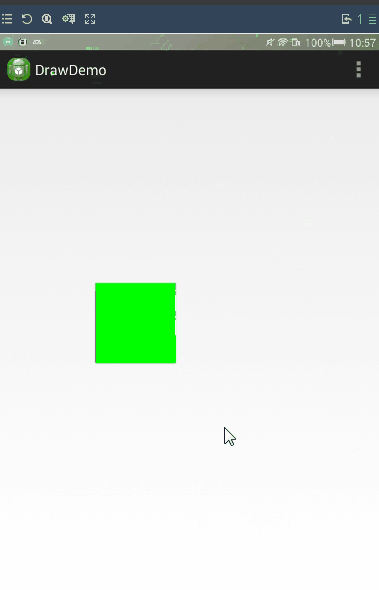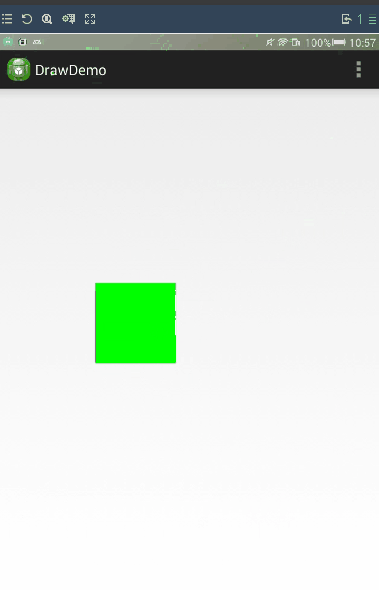
通過scrollTo與scorllBy進行滑動。
android 系統提供這個兩個方式進行改變一個View的位置
與前面的方法相同,也是計算偏移量。
package com.example.drawdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView7 extends View{
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
public MyView7(Context context) {
super(context);
ininView();
}
public MyView7(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
ininView();
}
public MyView7(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
ininView();
}
private void ininView() {
setBackgroundColor(Color.YELLOW);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = (int) event.getX();
lastY = (int) event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
((View) getParent()).scrollBy(-offsetX, -offsetY);
break;
}
return true;
}
}
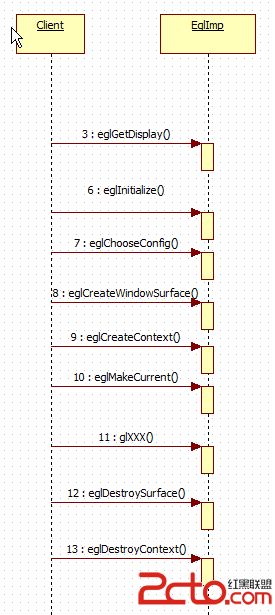 理解 Android 2D/3D 圖形架構
理解 Android 2D/3D 圖形架構
首先理解Android 的 egl 的函數調用,先要得到display (對應顯示器),而後選擇一個支持的config(這是顯卡支持的),而後創建WindowSurfac
 Android Mediaplayer本地音樂播放器(綁定服務)
Android Mediaplayer本地音樂播放器(綁定服務)
本文章介紹MediaPlayer本地音樂播放器,而當應用程序不再位於前台且沒有正在使用它的活動時,為了確保音頻繼續播放,我們需要建立一個服務Service。 Activi
 [Android] 環境配置之Android Studio開發NDK
[Android] 環境配置之Android Studio開發NDK
說到 NDK 開發,其實是為了有些時候為了項目需求需要調用底層的一些 C/C++ 的一些東西;另外就是為了效率更加高些。 但是很多時候能不用就不用;這個是啥
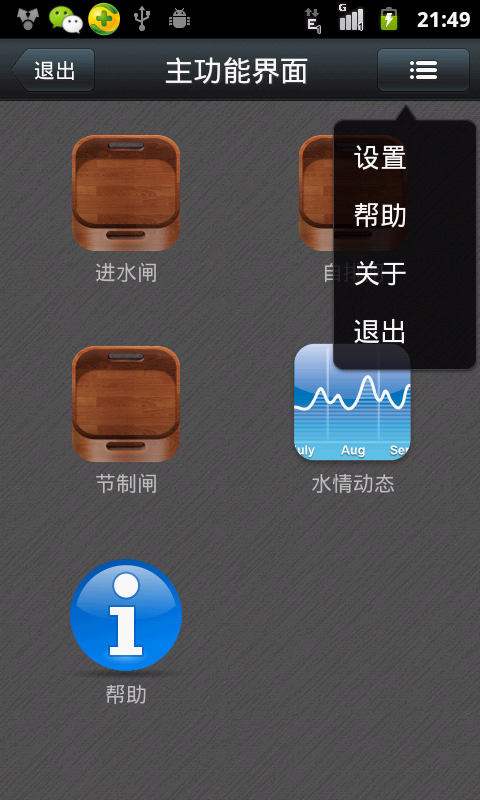 Android編程之ICS式下拉菜單PopupWindow實現方法詳解(附源碼下載)
Android編程之ICS式下拉菜單PopupWindow實現方法詳解(附源碼下載)
本文實例講述了Android編程之ICS式下拉菜單PopupWindow實現方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:運行效果截圖如下:右邊這個就是下拉菜單啦,看見有的地方叫