編輯:關於Android編程
在Activity的attach方法中通過調用PolicyManager.makeNewWindo創建Window,將一個View add到WindowManager時,WindowManagerImpl創建一個ViewRoot來管理該窗口的根View。並通過ViewRoot.setView方法把該View傳給ViewRoot。
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachActivity(this, mContainer, null);
mWindow = PolicyManager.makeNewWindow(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
DecorView為整個Window界面的最頂層View。
Activity中的Window對象幫我們創建了一個PhoneWindow內部類DecorView(父類為FrameLayout)窗口頂層視圖,然後通過LayoutInflater將xml內容布局解析成View樹形結構添加到DecorView頂層視圖中id為content的FrameLayout父容器上面。Activity的content內容布局最終會添加到DecorView窗口頂層視圖上面。
protected boolean initializePanelDecor(PanelFeatureState st) {
st.decorView = new DecorView(getContext(), st.featureId);
st.gravity = Gravity.CENTER | Gravity.BOTTOM;
st.setStyle(getContext());
return true;
}
WindowManagerImpl保存DecorView到mViews,創建對應的ViewRoot;
ViewRoot用於管理窗口的根View,並和global window manger進行交互。ViewRoot中有一個nested class: W,W是一個Binder子類,用於接收global window manager的各種消息, 如按鍵消息, 觸摸消息等。 ViewRoot有一個W類型的成員mWindow,ViewRoot在Constructor中創建一個W的instance並賦值給mWindow。 ViewRoot是Handler的子類, W會通過Looper把消息傳遞給ViewRoot。 ViewRoot在setView方法中把mWindow傳給sWindowSession。
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (display == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);
}
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Start watching for system property changes.
if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) {
mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
synchronized (mLock) {
for (ViewRootImpl viewRoot : mRoots) {
viewRoot.loadSystemProperties();
}
}
}
};
SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater);
}
int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view
+ " has already been added to the window manager.");
}
// If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being
// attached to for future reference.
if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW &&
wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {
final int count = mViews != null ? mViews.length : 0;
for (int i=0; i= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
}
throw e;
}
}
ViewRoot是GUI管理系統與GUI呈現系統之間的橋梁,需要注意它並不是一個View類型,。
它的主要作用如下:
1、向DecorView分發收到的用戶發起的event事件,如按鍵,觸屏,軌跡球等事件;
2、與WindowManagerService交互,完成整個Activity的GUI的繪制。
這裡先給出Android系統View的繪制流程:依次執行View類裡面的如下三個方法:
measure(int ,int) :測量View的大小
layout(int ,int ,int ,int) :設置子View的位置
draw(Canvas) :繪制View內容到Canvas畫布上
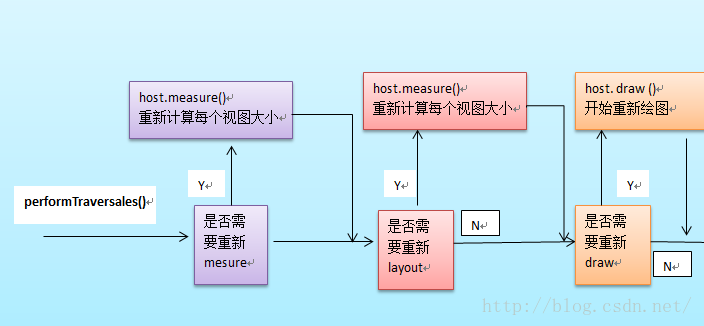
整個View樹的繪圖流程是在ViewRoot.java類的performTraversals()函數展開的,該函數做的執行過程可簡單概況為根據之前設置的狀態,判斷是否需要重新計算視圖大小(measure)、是否重新需要安置視圖的位置(layout)、以及是否需要重繪 (draw)
主要作用:為整個View樹計算實際的大小,即設置實際的高(mMeasuredHeight)和寬(mMeasureWidth),每個View的控件的實際寬高都是由父視圖和本身視圖決定的。
具體的調用如下:
ViewRootImpl 的performTraversals方法中,調用measureHierarchy,然後調用performMeasure
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
ViewRoot根對象地屬性mView(其類型一般為ViewGroup類型)調用measure()方法去計算View樹的大小,回調
2、如果該View對象是個ViewGroup類型,需要重寫onMeasure()方法,對其子視圖進行遍歷的measure()過程。
對每個子視圖的measure()過程,是通過調用父類ViewGroup.java類裡的measureChildWithMargins()方法去實現,該方法內部只是簡單地調用了View對象的measure()方法。
整個measure調用流程就是個樹形的遞歸過程
measure()方法兩個參數都是父View傳遞過來的,也就是代表了父view的規格。他由兩部分組成,高2位表示MODE,定義在MeasureSpec類(View的內部類)中,有三種類型,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY表示確定大小, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST表示最大大小, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED不確定。低30位表示size,也就是父View的大小。對於系統Window類的DecorVIew對象Mode一般都為MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ,而size分別對應屏幕寬高。對於子View來說大小是由父View和子View共同決定的。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
int desiredWindowHeight) {
mLayoutRequested = false;
mScrollMayChange = true;
mInLayout = true;
final View host = mView;
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_LAYOUT) {
Log.v(TAG, "Laying out " + host + " to (" +
host.getMeasuredWidth() + ", " + host.getMeasuredHeight() + ")");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "layout");
try {
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
mInLayout = false;
int numViewsRequestingLayout = mLayoutRequesters.size();
if (numViewsRequestingLayout > 0) {
// requestLayout() was called during layout.
// If no layout-request flags are set on the requesting views, there is no problem.
// If some requests are still pending, then we need to clear those flags and do
// a full request/measure/layout pass to handle this situation.
ArrayList validLayoutRequesters = getValidLayoutRequesters(mLayoutRequesters,
false);
if (validLayoutRequesters != null) {
// Set this flag to indicate that any further requests are happening during
// the second pass, which may result in posting those requests to the next
// frame instead
mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest = true;
// Process fresh layout requests, then measure and layout
int numValidRequests = validLayoutRequesters.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numValidRequests; ++i) {
final View view = validLayoutRequesters.get(i);
Log.w("View", "requestLayout() improperly called by " + view +
" during layout: running second layout pass");
view.requestLayout();
}
measureHierarchy(host, lp, mView.getContext().getResources(),
desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
mInLayout = true;
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest = false;
// Check the valid requests again, this time without checking/clearing the
// layout flags, since requests happening during the second pass get noop'd
validLayoutRequesters = getValidLayoutRequesters(mLayoutRequesters, true);
if (validLayoutRequesters != null) {
final ArrayList finalRequesters = validLayoutRequesters;
// Post second-pass requests to the next frame
getRunQueue().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int numValidRequests = finalRequesters.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numValidRequests; ++i) {
final View view = finalRequesters.get(i);
Log.w("View", "requestLayout() improperly called by " + view +
" during second layout pass: posting in next frame");
view.requestLayout();
}
}
});
}
}
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
mInLayout = false;
}
host.layout()開始View樹的布局,繼而回調給View/ViewGroup類中的layout()方法。具體流程如下
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList listenersCopy =
(ArrayList)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
}
一般引起invalidate()操作的函數如下:
1、直接調用invalidate()方法,請求重新draw(),但只會繪制調用者本身。
2、setSelection()方法 :請求重新draw(),但只會繪制調用者本身。
3、setVisibility()方法 : 當View可視狀態在INVISIBLE轉換VISIBLE時,會間接調用invalidate()方法,繼而繪制該View。
4 、setEnabled()方法 : 請求重新draw(),但不會重新繪制任何視圖包括該調用者本身。
 Android使用DrawerLayout實現仿QQ雙向側滑菜單
Android使用DrawerLayout實現仿QQ雙向側滑菜單
1、概述之前寫了一個Android 高仿 QQ5.0 側滑菜單效果 自定義控件來襲 ,恰逢QQ5.2又加了一個右側菜單,剛好看了下DrawerLayout,一方面官方的東
 android greenDao SQLite數據庫操作工具類使用
android greenDao SQLite數據庫操作工具類使用
上一篇介紹了如何建立類生成工程,現在介紹如何使用。 以下是ExampleDaoGenerator工程代碼,做了一些修改 /* * Copyright (C) 2011
 [Android] 環境配置之Android Studio開發NDK
[Android] 環境配置之Android Studio開發NDK
說到 NDK 開發,其實是為了有些時候為了項目需求需要調用底層的一些 C/C++ 的一些東西;另外就是為了效率更加高些。 但是很多時候能不用就不用;這個是啥
 Android動畫TimeInterpolator(插值器)和TypeEvaluator(估值器)分析
Android動畫TimeInterpolator(插值器)和TypeEvaluator(估值器)分析
這篇文章繼續分析Android動畫的TimeInterpolator(插值器)和TypeEvaluator(估值器)的簡單實現,以及分別去自定義插值器和估值器。一,Tim