編輯:關於Android編程
在Android手機的桌面上,我們經常可以看到如下小控件
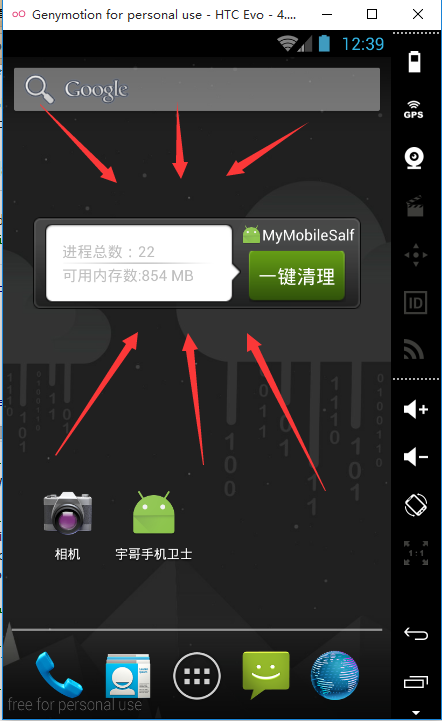
在這些控件上,可以顯示我們APP的一些重要的交互信息,以我最近開發的手機衛士為例,在widget上可以顯示進程總數,可用內存數,應用名稱Logo,以及一鍵清理快捷鍵。接下來這篇文章就簡單的記錄下如何在自己的應用中創建widget。
國內Android API鏡像
如下所示:
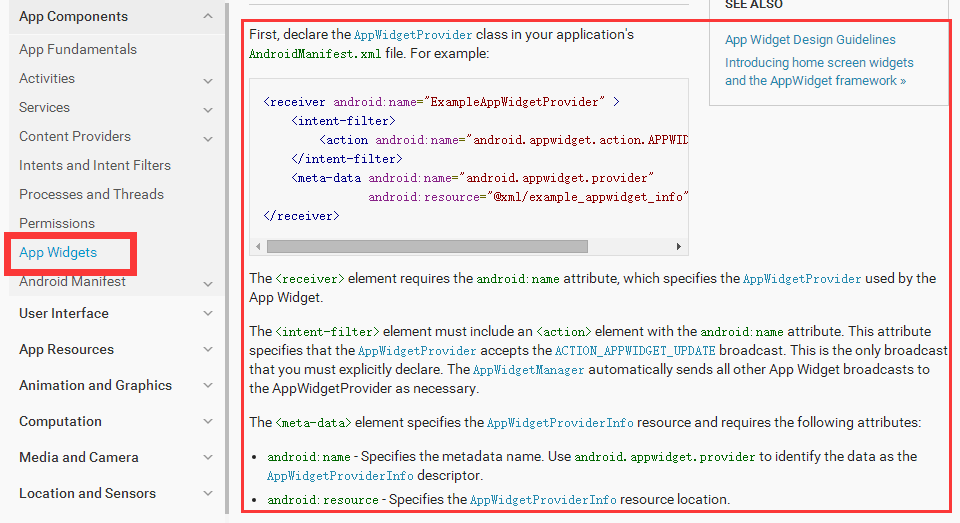


長篇大論一整面,我把最重要的幾點扣了出來,英語比較好的看了這篇文檔就應該知道怎麼給自己的APP創建widget了,下面結合我結合實例,翻譯並且記錄一下用法
1. 在AndroidManifest文件中配置如下節點
此處創建了一個XML文件(process_widget_provider),一個繼承了Broadcast的類的子類。下面詳細說一下這兩個。
2.官方文檔中給出的XML文件解釋如下
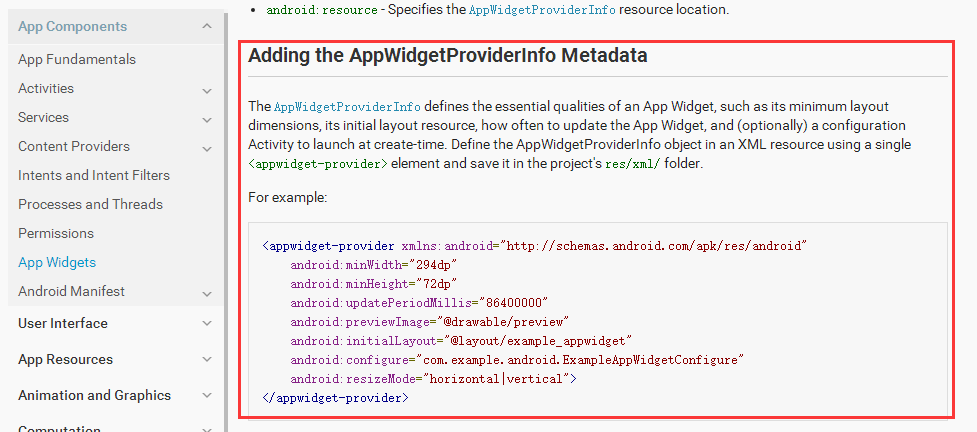
其中
android:initialLayout="@layout/example_appwidget"
這一條屬性設置的layout文件就是最終顯示在桌面上的widget的樣式布局
不是所有的屬性都需要配置,按需配置。下面貼出我應用中的widget的XML文件:
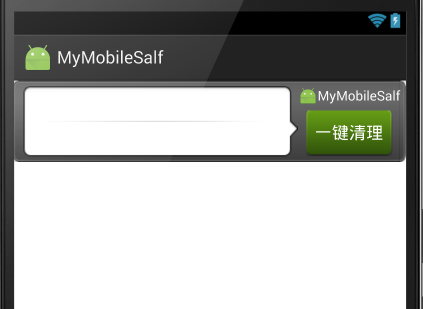
其中initialLayout文件process_widget如下:
這個layout文件決定了我應用的widget長下面這個樣子(使用到的圖片資源就不貼出來了):
3.myAppWidgetProvider
public class myAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider {
private static final String tag = "------>";
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Log.i(tag, "onReceive............");
super.onReceive(context, intent);
}
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
//創建第一個窗口小部件的方法
Log.i(tag, "onEnabled 創建第一個窗體小部件調用方法");
//開啟服務
context.startService(new Intent(context, updateWidgetService.class));
super.onEnabled(context);
}
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) {
Log.i(tag, "onUpdate 創建多一個窗體小部件調用方法");
context.startService(new Intent(context, updateWidgetService.class));
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
}
@Override
public void onAppWidgetOptionsChanged(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int appWidgetId, Bundle newOptions) {
//當窗體小部件寬高發生改變的時候調用方法,創建小部件的時候,也調用此方法
context.startService(new Intent(context,updateWidgetService.class));
Log.i(tag, "onAppWidgetOptionsChanged 創建多一個窗體小部件調用方法");
super.onAppWidgetOptionsChanged(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId, newOptions);
}
@Override
public void onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds) {
Log.i(tag, "onDeleted 刪除一個窗體小部件調用方法");
super.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
}
@Override
public void onDisabled(Context context) {
Log.i(tag, "onDisabled 刪除最後一個窗體小部件調用方法");
context.stopService(new Intent(context, updateWidgetService.class));
super.onDisabled(context);
}
}
這個類和widget的生命周期相關聯,重寫的每個方法的回調情景已經在代碼注釋中給出,寫到這裡我們就可以在手機中調出這個widget了,但是這個widget還沒有具體的功能,只是可以起到一個展示的作用。
widget的功能業務邏輯要結合具體的應用。下面我記錄下我自己最近的應用中widget的業務邏輯。
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
//創建第一個窗口小部件的方法
Log.i(tag, "onEnabled 創建第一個窗體小部件調用方法");
//開啟服務
context.startService(new Intent(context, updateWidgetService.class));
super.onEnabled(context);
}
在widget被拖拽到桌面上時候,上述方法會被調用,我們在該方法中開啟一個Service,因為widget的使用脫離了Activity,所以在服務中書寫業務邏輯可以讓widget脫離activity也可以完成某些功能。
public class updateWidgetService extends Service {
private Timer mTimer;
private InnerReceiver mInnerReceiver;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
//管理進程總數和可用內存數更新(定時器)
startTimer();
//注冊開鎖解鎖廣播接收者
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SCREEN_OFF);
intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SCREEN_ON);
mInnerReceiver = new InnerReceiver();
registerReceiver(mInnerReceiver, intentFilter);
super.onCreate();
}
private class InnerReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (intent.getAction().equals(Intent.ACTION_SCREEN_ON)) {
//開啟定時更新任務
startTimer();
} else {
//關閉定時更新任務
cancelTimerTask();
}
}
}
private void startTimer() {
//1.創建Timer對象
mTimer = new Timer();
mTimer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
//UI定時刷新
updateAppWidget();
Log.i("------>", "5秒一次的定時任務正在運行");
}
}, 0, 5000);
}
private void updateAppWidget() {
//1.獲取APPWidget對象 單例模式
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(this);
//2.獲取窗體小部件對應的布局轉換成的對象(定位應用的包名,當前應用中的那個布局文件)
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), R.layout.process_widget);
//3.給窗體小部件對應的View對象remoteViews 內部的控件賦值
remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.tv_process_count, "進程總數:" + processInfoProvider.getProcessCount(this));
//顯示可使用內存大小
String strAvailRAM = Formatter.formatFileSize(this, processInfoProvider.getAvailRAM(this));
remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.tv_process_memory, "可用內存數:" + strAvailRAM);
//點擊窗口小部件進入應用 (1.在哪個控件上響應點擊事件 2.延遲意圖)
Intent intent = new Intent("android.intent.action.HOME");
intent.addCategory("android.intent.category.DEFAULT");
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.ll_root, pi);
//通過延遲意圖發送廣播,在廣播接收者中殺死進程
Intent broadcastIntent = new Intent("android.intent.action.KILL_BACKGROUND_PROCESS");
PendingIntent broadcast = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, broadcastIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btn_clear, broadcast);
//4.通知Manager更新
//上下文環境 窗體小部件對應廣播接收者的字節碼文件
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(this, myAppWidgetProvider.class);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(componentName, remoteViews);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
private void cancelTimerTask() {
if (mTimer != null) {
mTimer.cancel();
mTimer = null;
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
if (mInnerReceiver != null) {
unregisterReceiver(mInnerReceiver);
}
//onDestroy()方法被調用時,服務關閉,最後一個窗體小部件被移除,所以定時任務也關閉
cancelTimerTask();
super.onDestroy();
}
}
updateWidgetService這個類完成的功能如下:
將進程總數和剩余內存顯示在widget上。 通過定時器對顯示的數據進行刷新,5秒刷新一次。 點擊widget進入應用的HomeAcitvity界面。 鎖屏時停止對widget的刷新操作。 點擊一鍵清除按鈕,清楚後台運行的程序。接收到指定的廣播"android.intent.action.KILL_BACKGROUND_PROCESS" 之後,下面拿到類中的onReceive()方法會被調用:
public class killProcessReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
//殺死進程
processInfoProvider.killAll(context);
}
}
其中殺死空閒進程的方法如下:
public static void killAll(Context context){
//1.拿刀
ActivityManager activityManager =
(ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
//2.通過拿ActivityManager拿到正在運行的進程的信息列表
List runningAppProcesses =
activityManager.getRunningAppProcesses();
//3.循環遍歷所有進程,然後殺!!
for (ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo info:runningAppProcesses){
//4除了手機衛士以外,其他的都殺!
if (info.processName.equals(context.getPackageName())){
continue;
}
activityManager.killBackgroundProcesses(info.processName);
}
}
感覺現在做的這個項目,都不能稱之為項目,准確的來說應該大型的Demo,它將Android中四大組件:Activity,Service,Content Provider,Broascast Receiver以及資源文件,Animation,等等都結合起來了,算是對Android基礎的一個很好的復習。最主要的是提高了自己對知識點的索引能力(好吧,不吹牛逼了。。說通俗點就是怎麼使用百度來解決問題)。
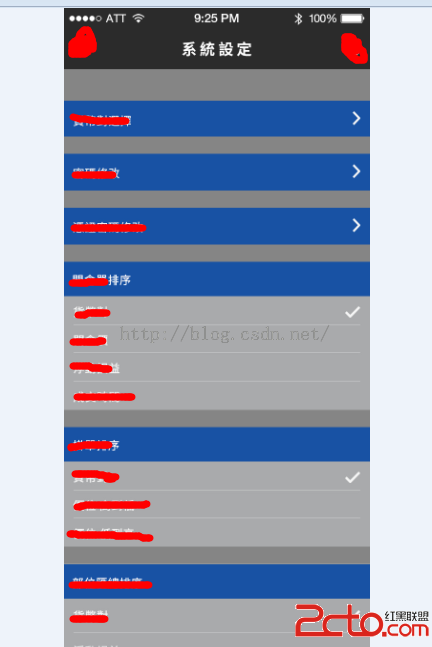 Android app系統設置界面 數據的保存與讀取 SharedPreferences 的正確使用
Android app系統設置界面 數據的保存與讀取 SharedPreferences 的正確使用
很開心的是經歷過兩個多月的努力,項目在11月份即將要交付使用,基礎功能已經完成,剩下的是系統設定界面沒有開發完畢,如下圖:很顯然要實現的功能是幾個界面要顯示很多數據,要依
 Android中的數據存取和IO (第一篇)
Android中的數據存取和IO (第一篇)
應用程序都會涉及到數據的輸入、輸出,android應用也不例外。Android中應用程序存儲數據通常有兩種模式:1,數據量少,格式簡單(例如,字符串、標量)
 Android圓形旋轉菜單
Android圓形旋轉菜單
【點擊下載】
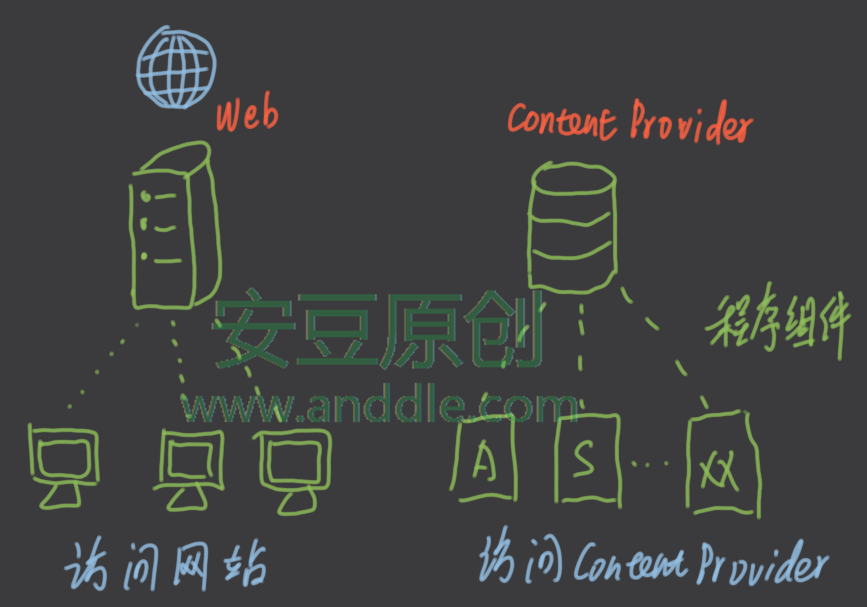 四大組件之ContentProvider(一)-使用系統提供的ContentProvider
四大組件之ContentProvider(一)-使用系統提供的ContentProvider
第1節 ContentProvider介紹ContentProvider是安卓系統的四大組件之一,可以向其他組件提供數據訪問的能力。它就像是一個網站,其他組件(或者其他應