編輯:關於Android編程
適配:即當前應用在相同的手機上面顯示相同的效果。適配前需要首先確定當前手機所屬像素密度類型(如:xhdpi、hdpi、mdpi等),然後計算其像素密度,按一定比例給出界面元素的布局位置和大小。
案例一:
手機型號:G700
手機分辨率:1280*720 (注:手機兩個直角邊上分別放置了1280及720個像素點)
手機尺寸大小:5英寸(手機斜邊長度)
假設a,b分別為兩個直角邊,c為斜邊,由勾股定理可得出計算方式:sqrt(a*a+b*b)/c
計算結果:sqrt(1280*1280+720*720)/5 ≈ 293.72dpi
根據google官方文檔說明得出,當前手機最接近320dpi,則將其歸納在xhdpi手機范圍內,即1dp=2px;
案例二:
手機型號:模擬器
手機分辨率:800*480(注:手機兩個直角邊上分別放置了800及480個像素點)
手機尺寸大小:3.7英寸(手機斜邊大小)
計算結果:sqrt(800*800+480*480)/3.7 ≈ 252.15dpi
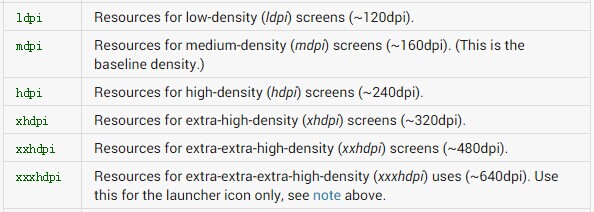
根據google官方文檔(圖1-1)得出,當前手機接近240dpi,則將其歸納在hdpi手機范圍內,即1dp=1.5px。
參照以上方式可將市場上大多數手機劃分為5個像素密度等級,分別為:
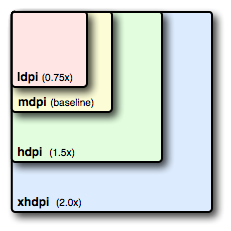
ldpi:120dpi,像素密度與dp轉換關系為:1dp = 0.75px
mdpi:160dpi ,像素密度與dp轉換關系為:1dp = 1px
hdpi:240dpi,像素密度與dp轉換關系為:1dp = 1.5px
xhdpi:320dpi,像素密度與dp轉換關系為:1dp = 2px
xxhdpi:480dpi,像素密度與dp轉換關系為:1dp = 3px
(注:以下案例就當前兩款手機進行屏幕適配測試)
不同像素密度的手機加載工程資源文件(res)中不同資源圖片,以上述兩款手機為例。布局代碼如下:
<code><relativelayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<imageview android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@drawable/a">
</imageview></relativelayout>
</code>
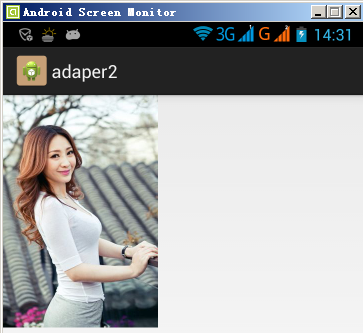
G700(xhdpi):加載a.jpg資源文件,位於res/drawable-xhdpi文件夾下,顯示效果如下:
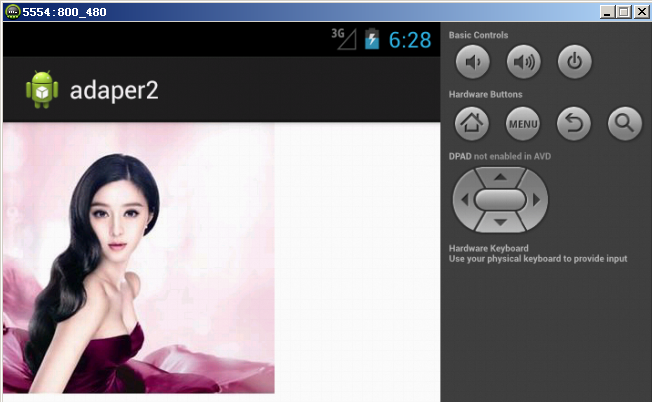
模擬器(hdpi):加載a.jpg資源文件,位於res/drawable-hdpi文件夾下,顯示效果如下:
dimens.xml存在於工程資源(res)文件夾中不同values(如:value-1280x720、value-800x480)文件夾下,可用於指定控件大小,不同像素密度手機加載不同values文件夾下的dimens.xml文件,使用方式如下:
<code><linearlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<textview android:background="#987654" android:layout_width="@dimen/width" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world">
</textview></linearlayout>
</code>
模擬器(hdpi):加載dimens.xml資源文件,位於res/value-800x480文件夾下
160dp
根據上述hdpi dp和px的轉換關系1dp = 1.5px,則160dp = 240px,當前控件寬度應該位於屏幕中間位置。
G700(xhdpi):加載dimens.xml資源文件,位於res/value-1280x720文件夾下
180dp
根據上述xhdpi dp和px的轉換關系1dp = 2px,則180dp = 360px,當前控件寬度應該位於屏幕中間位置。
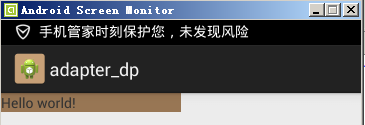
G700(xhdpi)顯示效果如下:
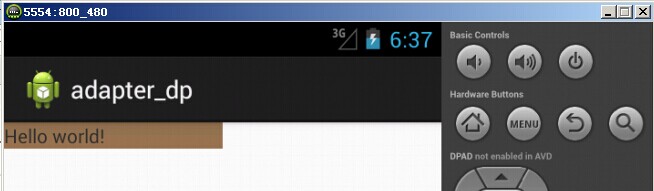
模擬器(hdpi)顯示效果如下:
不同分辨率的手機,加載不同的布局文件已達到適配效果。創建多個layout(如:layout-1280x720、layout-800x480)文件夾用於存放不同像素密度手機所需布局文件。
模擬器(hdpi):加載activity_main.xml布局文件,位於res/layout-800x480文件夾下:
<code> <relativelayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<textview android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="800*480手機會去加載的布局文件">
</textview></relativelayout>
</code>
G700(xhdpi):加載activity_main.xml布局文件,位於res/layout-1280x720文件夾下:
<code> <relativelayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<textview android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="1280*720手機會去加載的布局文件">
</textview></relativelayout>
</code>
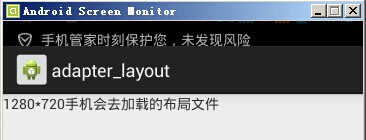
G700(xhdpi)顯示效果如下:
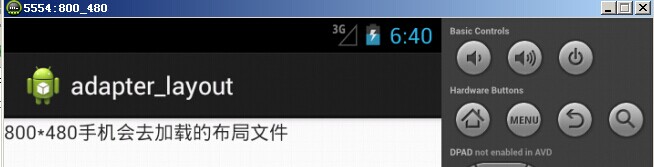
模擬器(hdpi)顯示效果如下:
通過android相應api獲取當前手機的寬高像素值,按比例分配屏幕中控件的寬高以達到適配效果。核心代碼如下:
<code>布局文件
<relativelayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<textview android:id="@+id/tv" android:background="#000000" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world">
</textview></relativelayout>
activity中oncreate核心代碼:
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
//獲取封裝當前手機屏幕信息對象,用於存放寬高值
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
//給當前屏幕設置寬高
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
//獲取高度
Constant.srceenHeight = metrics.heightPixels;
//獲取寬度
Constant.srceenWidth = metrics.widthPixels;
Log.i(tag, "Constant.srceenHeight = "+Constant.srceenHeight);
Log.i(tag, "Constant.srceenWidth = "+Constant.srceenWidth);
//寬高各占50%
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
(int)(Constant.srceenWidth*0.5+0.5),
(int)(Constant.srceenHeight*0.5+0.5));
tv.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
</code>
G700(xhdpi)顯示效果如下:
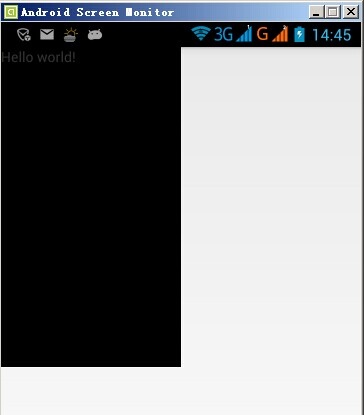
模擬器(hdpi)顯示效果如下:
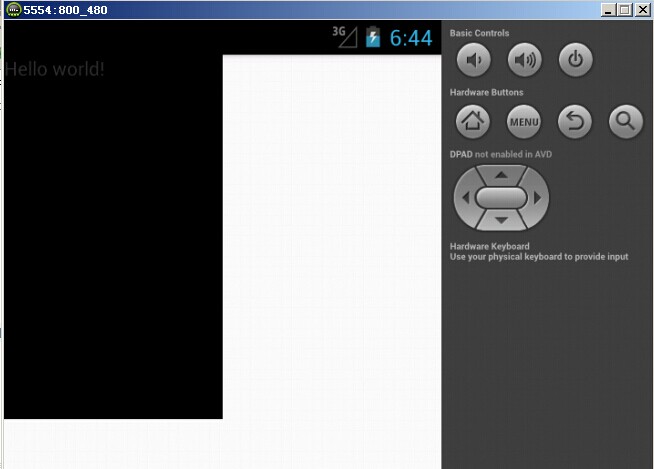
通過android提供的(權重)剩余空間分配,已達到適配效果。顯示界面加載布局文件如下:
<code><linearlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<textview android:background="#000000" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<textview android:background="#123456" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="match_parent">
</textview></textview></linearlayout>
</code>
G700(xhdpi)顯示效果如下:
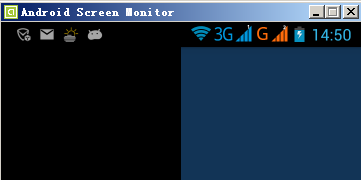
模擬器(hdpi)顯示效果如下:
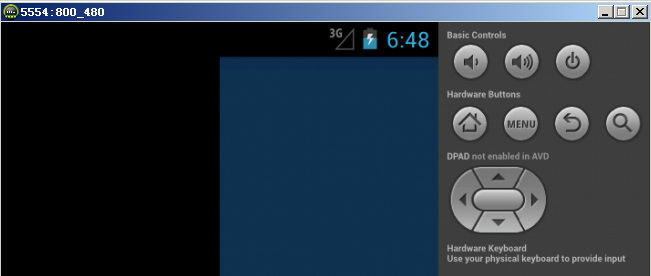
 Andriod下完全自定義控件和在自定義控件中使用自定義屬性
Andriod下完全自定義控件和在自定義控件中使用自定義屬性
首先,自定義控件分為三類:自定義的組合控件繼承View的自定義控件繼承ViewGroup的自定義控件在這裡,我要寫的是第二種,也就是繼承自View的自定義控件,第一種自定
 Android高仿2048小游戲實現代碼
Android高仿2048小游戲實現代碼
剛開始進入Splash界面:1.SplashActivity.Java(兩秒後進入開始界面,Splash界面的布局只有一個圖片,在博客後,會展示給大家看)public c
 Android安全專項測試之反編譯
Android安全專項測試之反編譯
apktool反編譯APK使用apktool d ,默認會生成和APK文件名同名的文件夾,裡面會存放反編譯後的文件:localhost:apk wuxian$ apkt
 Android 6.0 Runtime permission
Android 6.0 Runtime permission
Android版本升級到6.0之後,為了一改往日安全受人诟病的形象,將權限授權的安裝時授予的基礎上,對於一部分危險的權限采用動態控制授權的方式。類似國內手機安全助手權限控