編輯:關於Android編程
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor可以添加定時任務的線程池,包括添加周期性定時任務。在前一篇文章Android Java 線程池 ThreadPoolExecutor源碼篇基礎上來看這篇文件應該更加的方便一點。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor構造函數
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
我們先關注兩個東西DelayedWorkQueue 和DelayedWorkQueue 隊列裡面放的RunnableScheduledFuture(ScheduledFutureTask)
先說DelayedWorkQueue 我們關心裡面的offer, poll,take三個方法,DelayedWorkQueue 是以數組的形式存放RunnableScheduledFuture(這個類我們稍後分析)這個類實現了Comparable接口,在每次offer的時候會調用siftUp函數根據compareTo的比較值插入到隊列中並且保證隊列中的順序是從小到大的順序。數組下標低位的小,高位的大。poll的時候也是先從低位取出然後siftDown調整數組下標。其實compareTo比較的依據就是計算之後任務要跑的時間點下面會提到。
在一個就是RunnableScheduledFuture(ScheduledFutureTask) 一步一步的來看吧 那我們就直接看ScheduledFutureTask類圖
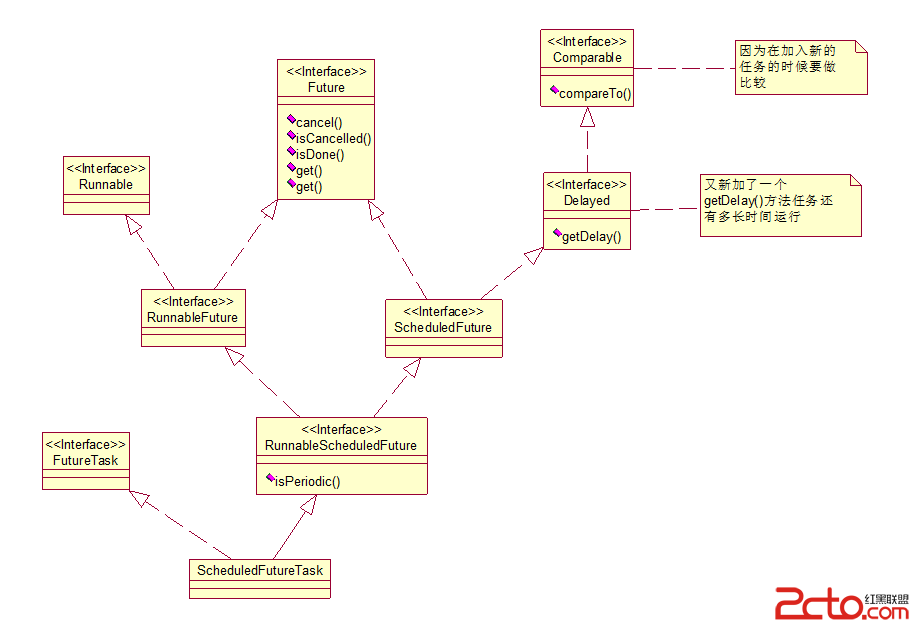 vc/C0ru49sjOzvG/qsq8tcTKsbzkKHNjaGVkdWxlV2l0aEZpeGVkRGVsYXkpoaM8L3A+DQo8cD5TY2hlZHVsZWRGdXR1cmVUYXNrubnU7Lqvyv3I/bj2INPQtcS0q8jrtcTKx1J1bm5hYmxlINPQtcS0q8jrtcTKx0NhbGxhYmxlo6y+zcvjtKvI67XEysdSdW5uYWJsZdKyu+G5ub2os/bSu7j2Q2FsbGFibGW1xLbUz/OjrNTaQ2FsbGFibGW1xGNhbGy3vbeo1tC199PDUnVubmFibGW1xHJ1bre9t6iho9fuuvO2vMrHQ2FsbGFibGWho8TH1eLI/bj2ubnU7Lqvyv2+zcO7yrLDtL+0tcTBy6GjPC9wPg0KPHByZSBjbGFzcz0="brush:java;">
vc/C0ru49sjOzvG/qsq8tcTKsbzkKHNjaGVkdWxlV2l0aEZpeGVkRGVsYXkpoaM8L3A+DQo8cD5TY2hlZHVsZWRGdXR1cmVUYXNrubnU7Lqvyv3I/bj2INPQtcS0q8jrtcTKx1J1bm5hYmxlINPQtcS0q8jrtcTKx0NhbGxhYmxlo6y+zcvjtKvI67XEysdSdW5uYWJsZdKyu+G5ub2os/bSu7j2Q2FsbGFibGW1xLbUz/OjrNTaQ2FsbGFibGW1xGNhbGy3vbeo1tC199PDUnVubmFibGW1xHJ1bre9t6iho9fuuvO2vMrHQ2FsbGFibGWho8TH1eLI/bj2ubnU7Lqvyv2+zcO7yrLDtL+0tcTBy6GjPC9wPg0KPHByZSBjbGFzcz0="brush:java;">
...
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long triggerTime) {
super(r, result);
this.time = triggerTime;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long triggerTime,
long period) {
super(r, result);
this.time = triggerTime;
this.period = period;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
ScheduledFutureTask(Callable
再關注ScheduledFutureTask裡面的getDelay,compareTo,isPeriodic,setNextRunTime幾個方法。
getDelay 方法簡單,就是time減去當前時間。用來判斷任務是不是該執行了。
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(time - now(), NANOSECONDS);
}
compareTo 方法比較的就是time。在任務加入的時候用來找到新的任務在隊列中的位置。
public int compareTo(Delayed other) {
if (other == this) // compare zero if same object
return 0;
if (other instanceof ScheduledFutureTask) {
ScheduledFutureTask x = (ScheduledFutureTask)other;
long diff = time - x.time;
if (diff < 0)
return -1;
else if (diff > 0)
return 1;
else if (sequenceNumber < x.sequenceNumber)
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
long diff = getDelay(NANOSECONDS) - other.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
return (diff < 0) ? -1 : (diff > 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
isPeriodic 任務是不是周期任務
public boolean isPeriodic() {
return period != 0;
}
setNextRunTime 如果是周期性的任務算出任務的下次執行時間,當周期性任務執行了第一次之後要算第二次的執行時間,依次類推。period > 0 上一個任務開始時間到下一個任務結束時間 time+=p(scheduleAtFixedRate), perid<0上一個任務結束時間到下一個任務開始時間那肯定是當前時間+ (-p)(scheduleWithFixedDelay) 這個函數是會在周期性任務執行完之後調用。
private void setNextRunTime() {
long p = period;
if (p > 0)
time += p;
else
time = triggerTime(-p);
}
總結下RunnableScheduledFuture(ScheduledFutureTask) 和DelayedWorkQueue 部分為接下的的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor做些准備哦。
1. 入隊offer的時候會按照任務RunnableScheduledFuture(ScheduledFutureTask)的time(任務的運行時間)來排序。從小到大來排序。
2. 出隊poll的時候先取出index 0位置上的任務(因為0位置的任務時間小最先執行)。然後再調整隊列。
3. ScheduledFutureTask 裡面getDelay() 方法可以得到當前任務還有多長時間執行。
4. ScheduledFutureTask 裡面setNextRunTime()如果周期性任務執行完了一次通過他得到下一次的執行時間,計算完之後再重新放到隊列裡面去(稍後講)
5. ScheduledFutureTask 裡面isPeriodic 當前任務是不是周期任務,和第四點配合使用。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的隊列和隊列裡面的任務我都清楚了一點。接下來就是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor源碼分析了
和分析Android Java 線程池 ThreadPoolExecutor源碼篇時候一樣。構造函數我們就不看了 看submit函數,不管是哪個submit函數 最後走的都是schedule函數。我們直接看schedule函數。
...
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(command,
new ScheduledFutureTask(command, null,
triggerTime(delay, unit)));
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (callable == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(callable,
new ScheduledFutureTask(callable,
triggerTime(delay, unit)));
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
public ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (delay <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(-delay));
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
...
上面四個方法不管是哪個做的事情都差不多,都是先構造出RunnableScheduledFureture(ScheduledFutureTask)對象然後調用delayedExecutef(t)函數。我們就看下ScheduledFutureTask的構造過程。看到每個都調用了triggerTime(initialDelay, unit) 這個函數的就是通過delay的時間去計算出任務要執行的時間。
scheduleAtFixedRate scheduleWithFixedDelay兩個函數的區別主要看第三個參數的區別,scheduleAtFixedRate 表示上一個任務開始到下一個任務開始的時間。scheduleWithFixedDelay 則表示上一個任務結束到下一個任務開始的時間。從這裡的代碼裡面我們就看到scheduleAtFixedRate 給ScheduledFutureTask裡的period 是大於0的,scheduleWithFixedDelay 則是小於0的。 正好映射到ScheduledFutureTask 裡面setNextRunTime()方法。
繼續往下走了delayedExecute 函數
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture task) {
if (isShutdown())
reject(task);
else {
super.getQueue().add(task);
if (isShutdown() &&
!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&
remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
ensurePrestart();
}
}
第5行 super.getQueue().add(task); 接著會調用DelayedWorkQueue 的offer方法 前面也有說到入隊offer的時候會按照任務RunnableScheduledFuture(ScheduledFutureTask)的time(任務的運行時間)來排序。從小到大來排序。
第11行 ensurePrestart函數調用了addWorker()函數 addWorker和前一篇文章Android Java 線程池 ThreadPoolExecutor源碼篇裡面的addWorker是一樣。
void ensurePrestart() {
int wc = workerCountOf(ctl.get());
if (wc < corePoolSize)
addWorker(null, true);
else if (wc == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
接下來我們就該關心怎麼從隊列裡面拿任務了(根據前文Android Java 線程池 ThreadPoolExecutor源碼篇的分析),分析到上面線程已經啟動起來了。從隊列裡面拿任務關心隊列的take 和 poll方法,也就是DelayedWorkQueue 的take 和 poll方法。
先看DelayedWorkQueue take方法
public RunnableScheduledFuture take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture first = queue[0];
if (first == null)
available.await();
else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
具體干的事情就是拿到index=0的任務。得到delay 如果delay<=0 這個任務就應該運行了 前面有說getDelay的作用(ScheduledFutureTask 裡面getDelay() 方法可以得到當前任務還有多長時間執行。),其他情況就得available.await();阻塞等待了。finishPoll是拿出一個任務之後做相應的調整。
接著是poll方法了 至於什麼時候會調用poll方法什麼時候會調用take方法可以參考Android Java 線程池 ThreadPoolExecutor源碼篇
public RunnableScheduledFuture poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture first = queue[0];
if (first == null) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
else
nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos);
} else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
if (nanos < delay || leader != null)
nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos);
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
long timeLeft = available.awaitNanos(delay);
nanos -= delay - timeLeft;
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
和take差不多,只是這個不會一直阻塞住有timeout時間的。這樣一次任務的調用時間跑完了吧,結合上一篇文章Android Java 線程池 ThreadPoolExecutor源碼篇的分析。
就剩下周期性的任務了。接著看下周期性的任務是怎麼周期性執行的。看ScheduledFutureTask的run方法。
public void run() {
boolean periodic = isPeriodic();
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic))
cancel(false);
else if (!periodic)
ScheduledFutureTask.super.run();
else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
setNextRunTime();
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}
不是周期性任務的時候直接調用run方法,這個好說,理解。不是周期性任務的時候先調用了runAndReset() 調用了ScheduledFutureTask 裡面Callable的call方法 執行了任務的邏輯,又把任務的狀態恢復了。
第8行,setNextRunTime 前面有說吧目的是計算下次任務執行的時間。
第9行,reExecutePeriodic 有把這個任務加入到隊列裡面去了。
周期性任務也到此為止。
總結
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 的隊列是DelayedWorkQueue 在offer的時候會按照delay從小到大的順序插入到隊列當中去。poll 或者take的時候都是先拿的index=0的任務,然後看是否任務的getDelay方法是不是小於等於0,任務是否到了該執行的時間了。 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 隊列裡面的任務是ScheduledFutureTask 實現了Comparable接口,在任務入隊offer的時候用到。關鍵方法getDelay,compareTo,isPeriodic,setNextRunTime。 周期性任務的執行都是每次任務執行完之後再計算出下一次的運行時間,然後再重新插入到隊列中。在ScheduledFutureTask 的run方法中完成。Executors 裡面一些常用方法的介紹
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)Executors 的其他的一些static方法可能是多傳入了一個ThreadFactory或者RejectedExecutionHandler就沒有列出來了。
 Java4Android開發教程(三)java基本概念
Java4Android開發教程(三)java基本概念
什麼是環境變量?環境變量通常是指在操作系統當中,用來指定操作系統運行時需要的一些參數。通常為一系列的鍵值對。path環境變量的作用path環境變量是操作系統外部命令搜索路
 GeekBand第十一周筆記
GeekBand第十一周筆記
本周的主要內容介紹Gradle,NDK,管理依賴和Git等一、GradleGradle是一個基於Apache Ant和Apache Maven概念的項目自動化建構工具。它
 Android 實現藍牙客戶端與服務器端通信
Android 實現藍牙客戶端與服務器端通信
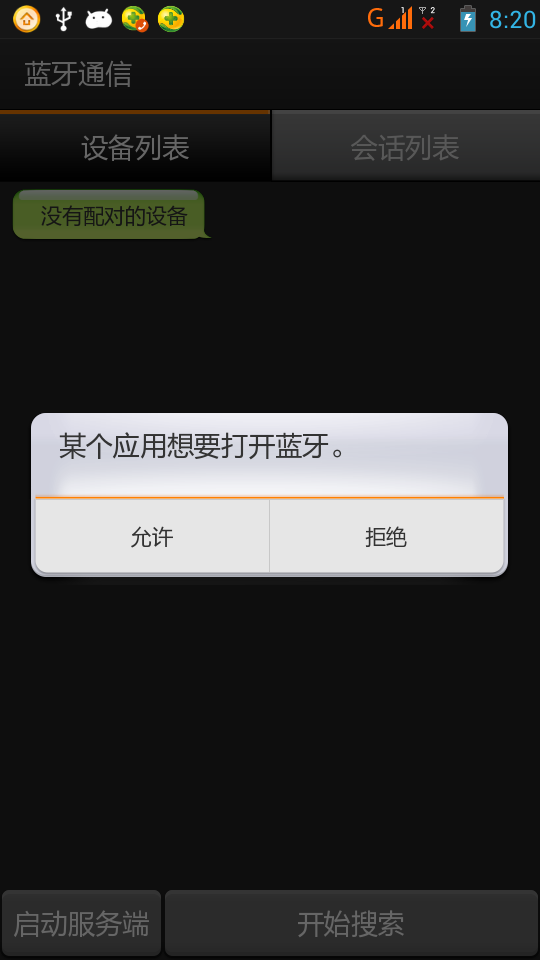
一、首先說明:藍牙通信必須用手機測試,因為avd裡沒有相關的硬件,會報錯!好了,看看最後的效果圖:二、概述:1.判斷是否支持BluetoothBluetoothAdapt
 Android加載對話框同時異步執行實現方法
Android加載對話框同時異步執行實現方法
Android中通過子線程連接網絡獲取資料,同時顯示加載進度對話框給用戶的操作,需要Thread和Handler來完成,在Thread中執行比較耗時的代碼,完成後再通過H