編輯:關於Android編程
RxJava的簡單使用基本上也了解了,其實還有一個比較好玩的就是java8才有的lambda了。
下面就來搭建下這個環境了,因為android不支持java8,所以需要用到一個開源庫, retolambda,點這裡。具體怎麼使用基本上都有,這裡簡單地介紹下,首先就是下載java8了:下載java8,點這裡。
下載好安裝好後,需要修改build.gradle:
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:1.5.0'
classpath 'me.tatarka:gradle-retrolambda:3.2.0'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}
這裡添加了me.tatarka:gradle-retrolambda:3.2.0。
接著是 app目錄下的build.gradle:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'me.tatarka.retrolambda'
android {
compileSdkVersion 23
buildToolsVersion "23.0.2"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.jared.emrxandroidstudy"
minSdkVersion 15
targetSdkVersion 23
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.1.1'
compile 'io.reactivex:rxandroid:1.1.0'
compile 'io.reactivex:rxjava:1.1.0'
}
添加完後需要修改編譯的jdk為java8:
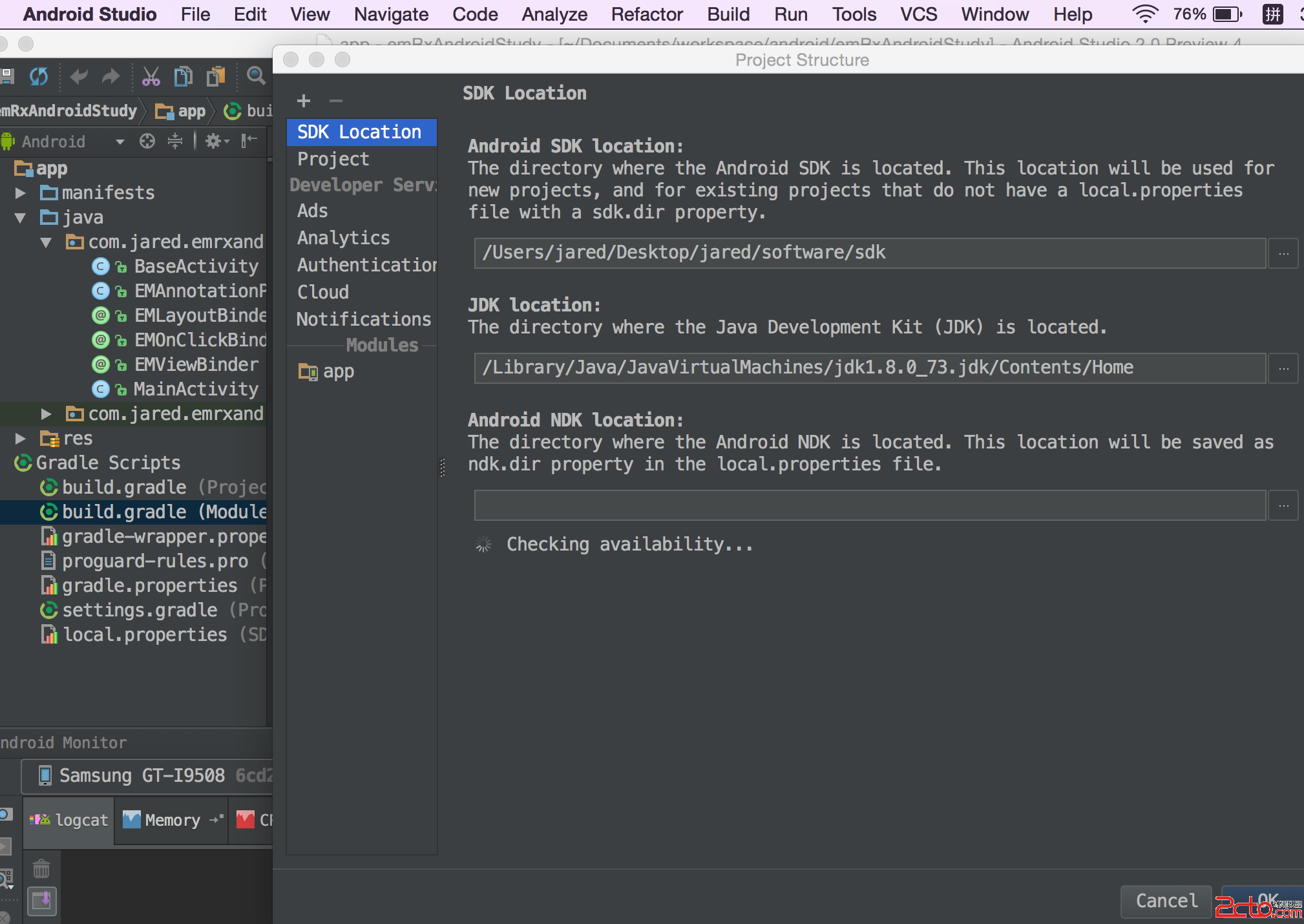
修改完後,重新啟動下工程,然後我們開始基於上一篇的文章繼續了。這裡對上一篇文章的代碼通過lambda簡化:
private void createObservableByMap() {
Log.d(TAG, "createObservableByMap");
Observable.just(getHello()).map(new Func1() {
@Override
public String call(String s) {
return s + " by eastmoon";
}
}).subscribe(onNextAction);
}
onNextAction = new Action1() {
@Override
public void call(String s) {
mHello.setText(s);
}
};
簡化後如下所示:
private void createObservableBylambda() {
Log.d(TAG, "createObservableBylambda");
Observable.just(getHello())
.map(s -> s + " by eastmoon")
.subscribe(s -> mHello.setText(s));
}
是不是非常清晰,非常的簡潔優雅,這裡先不分析。
簡單理解下lambda吧,lambda是一種匿名表達式,關於lambda表達式這篇文章講得不錯:講lambda比較好的文章。這裡還是記錄下當作學習吧,首先lambda的表達式一般是:
(argument) -> (body)
其中argument表示參數,body表示函數體要做的事。常用的表達式如下:
(arg1, arg2...) -> { body }
(type1 arg1, type2 arg2...) -> { body }
具體一些是這樣:
(int a, int b) -> { return a + b; }
() -> System.out.println("Hello World");
(String s) -> { System.out.println(s); }
() -> 42
a -> a + 5
() -> { return 3.1415 };
通過上述例子,基本上也理解了表達式怎麼用了。那麼什麼情況下可以使用lambda表達式呢?這裡有個函數式接口的概念,函數式接口就是指只包含一個抽象方法聲明的接口。Runnable只有一個接口run,所以它可以用lambda表達式實現。普通的方式如下:
Runnable r1 = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d(TAG, "testlambda");
}
};
使用lambda表達式如下:
Runnable r2 = () -> Log.d(TAG, "testlambda");
從六行代碼搞到了一行代碼,是不是超級簡潔優雅。來個例子試試水吧:
private void testlambda() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d(TAG, "test by normal func");
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> Log.d(TAG, "test by lambda func")).start();
}
??這裡通過創建線程在run方法中輸出信息,可以看出兩種效果一模一樣:
03-11 09:18:39.453 27601-28067/? D/MainActivity: test by lambda func
03-11 09:18:39.453 27601-28066/? D/MainActivity: test by normal func
既然需要函數式接口,那麼我們來簡單的實現下函數式接口,新建FunctionLambda接口:
package com.jared.emrxandroidstudy;
/**
* Created by jared on 16/3/11.
*/
public interface FunctionLambda {
public void hello();
}
接著編寫類FunctionLambdaTest:
package com.jared.emrxandroidstudy;
/**
* Created by jared on 16/3/11.
*/
public class FunctionLambdaTest {
public static void helloTest(FunctionLambda functionLambda) {
functionLambda.hello();
}
}
接著我們來實現下這個功能:
private void testFunctionLambda() {
FunctionLambdaTest.helloTest(new FunctionLambda() {
@Override
public void hello() {
Log.d(TAG, "test by normal testFunctionLambda");
}
});
FunctionLambdaTest.helloTest(() -> Log.d(TAG, "test by lambda testFunctionLambda"));
}
輸出信息如下:
03-11 09:30:29.005 28776-28776/? D/MainActivity: test by normal testFunctionLambda
03-11 09:30:29.005 28776-28776/? D/MainActivity: test by lambda testFunctionLambda
效果一模一樣,代碼精簡的不要不要的。
好了,講了這麼多lambda表達式,還是看看rxAndroid用到的那個例子吧。這裡再添下代碼:
private void createObservableBylambda() {
Log.d(TAG, "createObservableBylambda");
Observable.just(getHello())
.map(s -> s + " by eastmoon")
.subscribe(s -> mHello.setText(s));
}
??首先是map方法,因為map方法中重寫了call方法,傳入的參數為s,函數體裡面要做的事情是s+” by eastmoon”,所以就寫成了s -> s+” by eastmoon”,由這可知就是s變為了s+” by eastmoon”。同理subscribe方法也一樣,傳入的需要處理的mHello.setText(s)。
??基本上lambda的簡單使用ok了,接下去繼續學習RxAndroid了。
 安卓自動化測試入門-2-配置項目
安卓自動化測試入門-2-配置項目
本文翻譯自Riggaroo的《Introduction to Automated Android Testing – Part 2 – Setup
 Android學習之AppWidget筆記分享
Android學習之AppWidget筆記分享
什麼是AppWidget?AppWidget就是我們平常在桌面上見到的那種一個個的小窗口,利用這個小窗口可以給用戶提供一些方便快捷的操作。 今天的目標就是怎麼創建一個簡單
 Android 4.4(KitKat)中apk包的安裝過程
Android 4.4(KitKat)中apk包的安裝過程
其實對於apk包的安裝,4.4和之前版本沒大的差別。Android中app安裝主要有以下幾種情況:系統啟動時安裝,adb命令安裝,Google
 Android圓形的Imageview
Android圓形的Imageview
網上找的圓形imageview自定義控件:‘package com.wangll.widget;import android.content.Context;