編輯:關於Android編程
前兩節我們學了Bitmap和一些基本的繪圖API的屬性以及常用的方法,但心裡總覺得有點
不踏實,總得寫點什麼加深下映像是吧,嗯,本節我們就來寫兩個簡單的例子:
1.簡單畫圖板的實現
2.幫美女擦衣服的簡單實現
嘿嘿,第二個例子是小豬剛學安卓寫的一個小Demo~嘿嘿~
開始本節內容~
這個相信大家都不陌生,很多手機都會自帶一個給用戶塗鴉的畫圖板,這裡我們就來寫個簡單的
例子,首先我們分析下,實現這個東東的一些邏輯:
Q1:這個畫板放在哪裡?
答:View裡,我們自定義一個View,在onDraw()裡完成繪制,另外View還有個onTouchEvent的方法,
我們可以在獲取用戶的手勢操作!
q2.需要准備些什麼?
答:一只畫筆(Paint),一塊畫布(Canvas),一個路徑(Path)記錄用戶繪制路線;
另外劃線的時候,每次都是從上次拖動時間的發生點到本次拖動時間的發生點!那麼之前繪制的
就會丟失,為了保存之前繪制的內容,我們可以引入所謂的“雙緩沖”技術:
其實就是每次不是直接繪制到Canvas上,而是先繪制到Bitmap上,等Bitmap上的繪制完了,
再一次性地繪制到View上而已!
3.具體的實現流程?
答:初始化畫筆,設置顏色等等一些參數;在View的onMeasure()方法中創建一個View大小的Bitmap,
同時創建一個Canvas;onTouchEvent中獲得X,Y坐標,做繪制連線,最後invalidate()重繪,即調用
onDraw方法將bitmap的東東畫到Canvas上!
好了,邏輯知道了,下面就上代碼了:
MyView.java:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/10/15 0015.
*/
public class MyView extends View{
private Paint mPaint; //繪制線條的Path
private Path mPath; //記錄用戶繪制的Path
private Canvas mCanvas; //內存中創建的Canvas
private Bitmap mBitmap; //緩存繪制的內容
private int mLastX;
private int mLastY;
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init(){
mPath = new Path();
mPaint = new Paint(); //初始化畫筆
mPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setDither(true);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND); //結合處為圓角
mPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND); // 設置轉彎處為圓角
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(20); // 設置畫筆寬度
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
// 初始化bitmap,Canvas
mBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
mCanvas = new Canvas(mBitmap);
}
//重寫該方法,在這裡繪圖
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
drawPath();
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, 0, 0, null);
}
//繪制線條
private void drawPath(){
mCanvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (action)
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
mPath.moveTo(mLastX, mLastY);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int dx = Math.abs(x - mLastX);
int dy = Math.abs(y - mLastY);
if (dx > 3 || dy > 3)
mPath.lineTo(x, y);
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
break;
}
invalidate();
return true;
}
}
運行效果圖:

你可以根據自己的需求進行擴展,比如加上修改畫筆大小,修改畫筆顏色,保存自己畫的圖等!
發散思維,自己動手~
核心思路是:
利用幀布局,前後兩個ImageView,前面的顯示未擦掉衣服的情況,後面的顯示擦掉衣服後的情況!
為兩個ImageView設置美女圖片後,接著為前面的ImageView設置OnTouchListener!在這裡對手指
觸碰點附近的20*20個像素點,設置為透明!
運行效果圖:

代碼實現:
Step 1:第一個選妹子的Activity相關的編寫,首先是界面,一個ImageView,Button和Gallery!
activity_main.xml:
接著是我們Gallery的Adapter類,這裡我們重寫下BaseAdapter,而裡面就顯示一個圖片比較簡單,
就不另外寫一個布局了!
MeiziAdapter.java:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/10/16 0016.
*/
public class MeiziAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private Context mContext;
private int[] mData;
public MeiziAdapter() {
}
public MeiziAdapter(Context mContext,int[] mData) {
this.mContext = mContext;
this.mData = mData;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mData.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return mData[position];
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ImageView imgMezi = new ImageView(mContext);
imgMezi.setImageResource(mData[position]); //創建一個ImageView
imgMezi.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY); //設置imgView的縮放類型
imgMezi.setLayoutParams(new Gallery.LayoutParams(250, 250)); //為imgView設置布局參數
TypedArray typedArray = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery);
imgMezi.setBackgroundResource(typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0));
return imgMezi;
}
}
最後到我們的Activity,也很簡單,無非是為gallery設置onSelected事件,點擊按鈕後把,當前選中的
Position傳遞給下一個頁面!
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener,
View.OnClickListener {
private Context mContext;
private ImageView img_choose;
private Button btn_choose;
private Gallery gay_choose;
private int index = 0;
private MeiziAdapter mAdapter = null;
private int[] imageIds = new int[]
{
R.mipmap.pre1, R.mipmap.pre2, R.mipmap.pre3, R.mipmap.pre4,
R.mipmap.pre5, R.mipmap.pre6, R.mipmap.pre7, R.mipmap.pre8,
R.mipmap.pre9, R.mipmap.pre10, R.mipmap.pre11, R.mipmap.pre12,
R.mipmap.pre13, R.mipmap.pre14, R.mipmap.pre15, R.mipmap.pre16,
R.mipmap.pre17, R.mipmap.pre18, R.mipmap.pre19, R.mipmap.pre20,
R.mipmap.pre21
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = MainActivity.this;
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
img_choose = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img_choose);
btn_choose = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_choose);
gay_choose = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.gay_choose);
mAdapter = new MeiziAdapter(mContext, imageIds);
gay_choose.setAdapter(mAdapter);
gay_choose.setOnItemSelectedListener(this);
btn_choose.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView parent, View view, int position, long id) {
img_choose.setImageResource(imageIds[position]);
index = position;
}
@Override
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView parent) {
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent it = new Intent(mContext,CaClothes.class);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putCharSequence(num, Integer.toString(index));
it.putExtras(bundle);
startActivity(it);
}
}
接著是我們擦掉妹子衣服的頁面了,布局比較簡單,FrameLayout + 前後兩個ImageView:
activity_caclothes.xml:
<framelayout android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_width="match_parent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
</framelayout>
接著到就到Java部分的代碼了:
CaClothes.java:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/10/16 0016.
*/
public class CaClothes extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnTouchListener {
private ImageView img_after;
private ImageView img_before;
private Bitmap alterBitmap;
private Canvas canvas;
private Paint paint;
private Bitmap after;
private Bitmap before;
private int position;
int[] imageIds1 = new int[]
{
R.mipmap.pre1, R.mipmap.pre2, R.mipmap.pre3, R.mipmap.pre4,
R.mipmap.pre5, R.mipmap.pre6, R.mipmap.pre7, R.mipmap.pre8,
R.mipmap.pre9, R.mipmap.pre10, R.mipmap.pre11, R.mipmap.pre12,
R.mipmap.pre13, R.mipmap.pre14, R.mipmap.pre15, R.mipmap.pre16,
R.mipmap.pre17, R.mipmap.pre18, R.mipmap.pre19, R.mipmap.pre20,
R.mipmap.pre21
};
int[] imageIds2 = new int[]
{
R.mipmap.after1, R.mipmap.after2, R.mipmap.after3, R.mipmap.after4,
R.mipmap.after5, R.mipmap.after6, R.mipmap.after7, R.mipmap.after8,
R.mipmap.after9, R.mipmap.after10, R.mipmap.after11, R.mipmap.after12,
R.mipmap.after13, R.mipmap.after14, R.mipmap.after15, R.mipmap.after16,
R.mipmap.after17, R.mipmap.after18, R.mipmap.after19, R.mipmap.after20,
R.mipmap.after21
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_caclothes);
Bundle bd = getIntent().getExtras();
position = Integer.parseInt(bd.getString(num));
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
img_after = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img_after);
img_before = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img_before);
BitmapFactory.Options opts = new BitmapFactory.Options();
opts.inSampleSize = 1;
after = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), imageIds2[position], opts);
before = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), imageIds1[position], opts);
//定義出來的是只讀圖片
alterBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(before.getWidth(), before.getHeight(), Bitmap.Config.ARGB_4444);
canvas = new Canvas(alterBitmap);
paint = new Paint();
paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
paint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
paint.setStrokeWidth(5);
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
canvas.drawBitmap(before, new Matrix(), paint);
img_after.setImageBitmap(after);
img_before.setImageBitmap(before);
img_before.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int newX = (int) event.getX();
int newY = (int) event.getY();
//setPixel方法是將某一個像素點設置成一個顏色,而這裡我們把他設置成透明
//另外通過嵌套for循環將手指觸摸區域的20*20個像素點設置為透明
for (int i = -20; i < 20; i++) {
for (int j = -20; j < 20; j++) {
if (i + newX >= 0 && j + newY >= 0 && i + newX < before.getWidth() && j + newY < before.getHeight())
alterBitmap.setPixel(i + newX, j + newY, Color.TRANSPARENT);
}
}
img_before.setImageBitmap(alterBitmap);
break;
}
return true;
}
}
代碼也不算苦澀難懂,還是比較簡單的哈,嗯,效果圖看看就好,別做那麼多右手螺旋定則哈….
 Android中Notification用法實例總結
Android中Notification用法實例總結
本文實例總結了 Android中Notification用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:我們在用手機的時候,如果來了短信,而我們沒有點擊查看的話,是不是在手機的最上
 Android觸摸及手勢操作GestureDetector
Android觸摸及手勢操作GestureDetector
現在的智能手機不敢說百分百的都是觸摸屏,也應該是百分之九九以上為觸摸屏了,觸摸屏為我們操作無鍵盤、無鼠標的手機系統帶來了很多的便利。當用戶觸摸屏幕時會產生很多的觸摸事件,
 android 4.0 USB Camera實例(二)應用層
android 4.0 USB Camera實例(二)應用層
上一篇說了HAL層 這一篇具體應用HAL層 實例預覽與拍照的功能 首先貼上兩個主文件的源碼 Fimcgzsd.java package com.dao.usbcam;
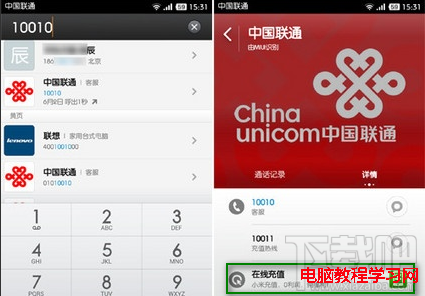 小米手機(MIUI系統)怎麼在撥號界面直接充值話費
小米手機(MIUI系統)怎麼在撥號界面直接充值話費
如果你是小米手機或小米MIUI系統的用戶,充值話費可以很簡單,你知道嗎?還在打開電腦、登陸淘寶,搜索充值話費的店嗎?看看小米MIUI系統是怎麼在撥號界面輕松