編輯:關於Android編程
IOS現成的API裡的json解析速度非常快,這裡就不說了,今天對比一下Android裡面json的解析庫。
首先第一個是Android API裡面自帶的json解析,其次是谷歌提供的Gson解析庫(開源),其次是在網上看到的解析很快速的阿裡巴巴分享的Fastjson包。Android自帶的json解析大家一定都很熟悉了,這裡不介紹了,這裡詳細說說谷歌提供的另一套解析庫Gson:
gson的使用方法非常的簡單。只需要將需要解析的json字符串和對應的Bean類xing型傳遞給GSON類的from方法既可:
Gson gson = new Gson();
List so = gson.fromJson(mJsonString, new TypeToken>() {
}.getType());
這裡的beanlei類中的字段的命名要和json中的字段相同,其次實現get和set方法(稍後講原因)。
標准的bean:
import java.util.List;
public class Geo {
private String type;
private List coordinates;
public Geo() {}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public List getCoordinates() {
return coordinates;
}
public void setCoordinates(List coordinates) {
this.coordinates = coordinates;
}
}
我曾經擔心復雜的json結構會不會解析出現問題,但是試驗了以後嵌套了其他的bean類,照樣迭代賦值了。
阿裡巴巴提供的fastjson庫使用方法和gson一樣,只是底層的原理不同。這裡不詳細介紹了。
下面看一下三個庫解析相同的json字段的對比:(使用了25條非常復雜的Json數據)
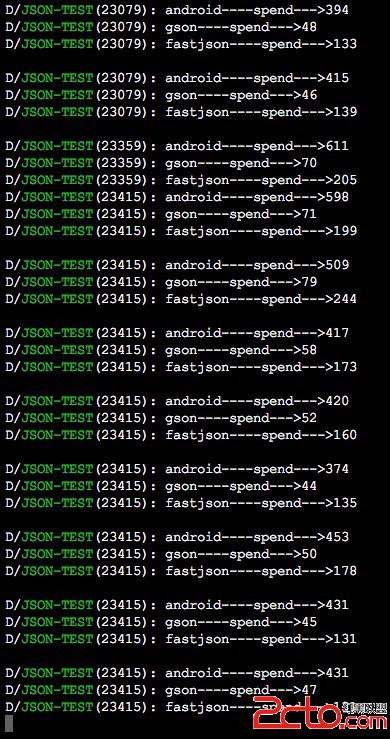
大家可以看到谷歌提供的gson有非常大的速度優勢。這裡我們走進它的代碼浏覽一下。
找到了關鍵的類:JsonObject.java
package com.google.gson;
import com.google.gson.internal.LinkedTreeMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public final class JsonObject extends JsonElement
{
private final LinkedTreeMap members = new LinkedTreeMap();
JsonObject deepCopy()
{
JsonObject result = new JsonObject();
for (Map.Entry entry : this.members.entrySet()) {
result.add((String)entry.getKey(), ((JsonElement)entry.getValue()).deepCopy());
}
return result;
}
public void add(String property, JsonElement value)
{
if (value == null) {
value = JsonNull.INSTANCE;
}
this.members.put(property, value);
}
public JsonElement remove(String property)
{
return (JsonElement)this.members.remove(property);
}
public void addProperty(String property, String value)
{
add(property, createJsonElement(value));
}
public void addProperty(String property, Number value)
{
add(property, createJsonElement(value));
}
public void addProperty(String property, Boolean value)
{
add(property, createJsonElement(value));
}
public void addProperty(String property, Character value)
{
add(property, createJsonElement(value));
}
private JsonElement createJsonElement(Object value)
{
return value == null ? JsonNull.INSTANCE : new JsonPrimitive(value);
}
public Set> entrySet()
{
return this.members.entrySet();
}
public boolean has(String memberName)
{
return this.members.containsKey(memberName);
}
public JsonElement get(String memberName)
{
return (JsonElement)this.members.get(memberName);
}
public JsonPrimitive getAsJsonPrimitive(String memberName)
{
return (JsonPrimitive)this.members.get(memberName);
}
public JsonArray getAsJsonArray(String memberName)
{
return (JsonArray)this.members.get(memberName);
}
public JsonObject getAsJsonObject(String memberName)
{
return (JsonObject)this.members.get(memberName);
}
public boolean equals(Object o)
{
return (o == this) || (((o instanceof JsonObject)) && (((JsonObject)o).members.equals(this.members)));
}
public int hashCode()
{
return this.members.hashCode();
}
}
可以看到其中使用了一個LinkedTreeMap來緩存字段與值。這裡要比我們直接使用API中的方法尋找要快,其次在類ProtoTypeAdapter.java中我們找到了賦值方法:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public GeneratedMessage deserialize(JsonElement json, Type typeOfT,
JsonDeserializationContext context) throws JsonParseException {
try {
JsonObject jsonObject = json.getAsJsonObject();
Class protoClass =
(Class) typeOfT;
try {
// Invoke the ProtoClass.newBuilder() method
Object protoBuilder = getCachedMethod(protoClass, "newBuilder")
.invoke(null);
Class builderClass = protoBuilder.getClass();
Descriptor protoDescriptor = (Descriptor) getCachedMethod(
protoClass, "getDescriptor").invoke(null);
// Call setters on all of the available fields
for (FieldDescriptor fieldDescriptor : protoDescriptor.getFields()) {
String name = fieldDescriptor.getName();
if (jsonObject.has(name)) {
JsonElement jsonElement = jsonObject.get(name);
String fieldName = name + "_";
Field field = protoClass.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
Type fieldType = field.getGenericType();
Object fieldValue = context.deserialize(jsonElement, fieldType);
Method method = getCachedMethod(
builderClass, "setField", FieldDescriptor.class, Object.class);
method.invoke(protoBuilder, fieldDescriptor, fieldValue);
}
}
// Invoke the build method to return the final proto
return (GeneratedMessage) getCachedMethod(builderClass, "build")
.invoke(protoBuilder);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new JsonParseException("Error while parsing proto: ", e);
}
}
這裡通過反射類的set方法來給變量賦值,因此bean類中的變量要加上get和set方法。
 Android 自定義View 實現刮刮卡效果
Android 自定義View 實現刮刮卡效果
主要思想:將一個view設計成多層:背景層,含中獎信息等;遮蓋層,用於刮獎,使用關聯一個Bitmap的Canvas在該Bitmap上,使用它的canvas.drawPat
 Fragment(碎片)(1)
Fragment(碎片)(1)
Fragment碎片(Fragment)是一種可以嵌入在活動當中的UI片段,它能讓程序更加合理和充分地利用大屏幕的空間,因而在平板上應用的非常廣泛。碎片是什麼這是《第一行
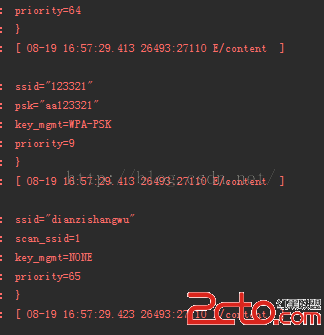 android 讀取系統文件 wpa_supplicant
android 讀取系統文件 wpa_supplicant
1,需要權限 2,下載 RootTools.jar包。3,兩個關鍵方法。主要是獲取shell,並執行命令行。方法如下: private
 Android Application Fundamentals——Android應用程序基礎知識
Android Application Fundamentals——Android應用程序基礎知識
Application Fundamentals——應用程序基礎知識Key classes——關鍵類Activ