編輯:關於Android編程
(本文講解了在Android中實現列表下拉刷新的動態效果的過程,文末附有源碼。)
2.自定義Android控件,重寫其ListView
3.ScrollListener滾動監聽
4.Adapter適配器的使用
話不多說,先來看看效果圖:
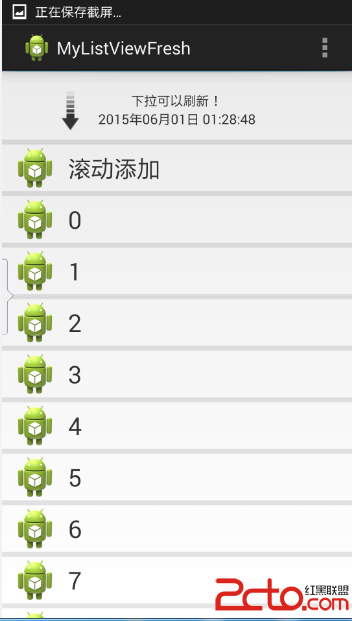
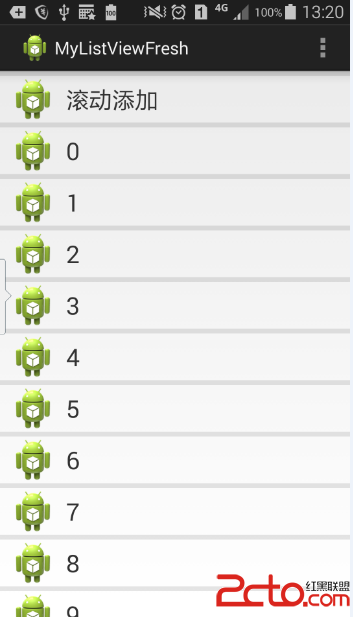
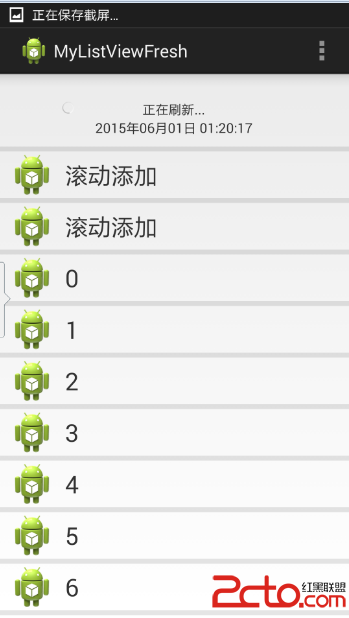
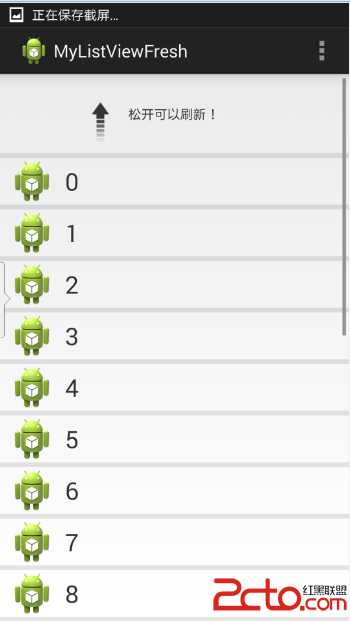
接下來我們一步一步地實現以上的效果。
看一下這一步的效果圖:
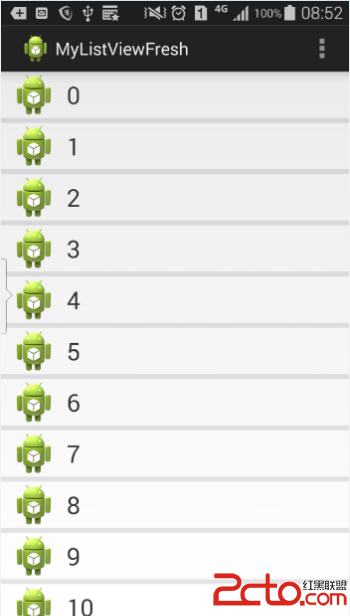
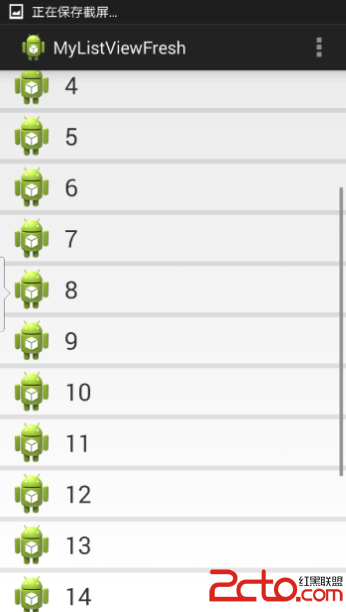
首先,我們要實現的是帶下拉刷新效果的ListView。所以我們選擇自己重寫原生控件ListView。只需要寫一個類繼承它就可以了,先不添加任何的具體實現。
RefreshListView.java:
public class RefreshListView extends ListView {
public RefreshListView(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public RefreshListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public RefreshListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
listview_item.xml:
然後需要我們注意的是,既然我們自己定義了ListView,那我們主界面的布局也要響應地修改了:
activity_main.xml:
可以一眼看出我們修改了它的控件標簽,改為我們自己定義的類的完全路徑。
最後是主角MainActivity.java,裡面的一些代碼我詳細地給了注釋。這裡要注意的是適配器的使用。
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private RefreshListView listView;
private SimpleAdapter simple_adapter;
private List> list;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
listView = (RefreshListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
iniData(); //初始化數據,我們給它加20條Item
// 設置SimpleAdapter監聽器
/**
* SimpleAdapter的五個參數的含義:
* 第一個:context上下文
* 第二個:用於顯示的數據,map的list
* 第三個:Item的布局,即我們自定義的那個文件
* 第四個:與第二個參數緊密聯系,與第五個緊密聯系,是在map中的鍵值
* 第五個:我們看到是id(int類型)的數組,這個數組裡的東西是哪裡來的?是我們自己在布局文件中定義的,忘記的讀者可以回過頭去看一下
* 這幾個參數獨立開來可能不知道是干嗎的,但是我覺得聯合在一起就挺好理解了。
*/
simple_adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this, list,
R.layout.listview_item, new String[] { "image", "text" },
new int[] { R.id.image, R.id.text });
//設置適配器
listView.setAdapter(simple_adapter);
}
// 初始化SimpleAdapter數據集
private List> iniData() {
list = new ArrayList>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Map map = new HashMap();
//解釋下這裡的數據,key對應SimpleAdapter的第三個參數,必須都包含它們。值對應第五個參數,分別是圖片和文字
map.put("text", i);
map.put("image", R.drawable.ic_launcher);
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
到了這一步,應該能夠實現圖片+文字的listview了吧,喝口茶,我們繼續看下去。
這裡我們要說一下下拉刷新的實現思路了:
首先,我們平常用到的下拉刷新,都是在下拉後屏幕上方顯示出一些之前被隱藏的控件,類似下拉的箭頭、progress bar等等。
那我們可以直接把它們設置為不可見嗎?顯然是不可以的。因為這些空間的顯示與否,有一個漸變的過程,不是刷一下就出來的。
所以我們應該這樣做:
加入一個隱藏的布局,放在屏幕上方。根據下拉的范圍來顯示響應的控件。
這一步,我們要實現的是加入隱藏的布局,具體怎樣根據下拉的狀態來實時調整Header的顯示狀態,我們在下文細說。
我們為了需要隱藏的header再自定義個新的布局,header.xml:
這個布局中包含了提示語“下拉可以刷新”、最新更新時間、下拉箭頭的圖片(已經預先放在drawable文件夾中了,讀者可以自己找個圖片放進去,命名為pull_to_refresh_arrow.phg)、一個更新時才顯示的progressbar(現在是隱藏的)。
為了把這個布局加到我們定義的List,我們需要改寫之前自定義的RefreshLIstview控件:
public class RefreshListView extends ListView {
View header;// 頂部布局文件;
int headerHeight;// 頂部布局文件的高度;
public RefreshListView(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
initView(context);
}
public RefreshListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
initView(context);
}
public RefreshListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
initView(context);
}
/**
* 初始化界面,添加頂部布局文件到 listview
*/
private void initView(Context context) {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
header = inflater.inflate(R.layout.header, null);
measureView(header);
headerHeight = header.getMeasuredHeight();
Log.i("tag", "headerHeight = " + headerHeight);
//topPadding(-headerHeight); //這一行被我注釋了,如果你去除注釋,就可以顯示出來了
this.addHeaderView(header);
}
/**
* 通知父布局,占用的寬,高;
*/
private void measureView(View view) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams p = view.getLayoutParams();
if (p == null) {
p = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
int width = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(0, 0, p.width);
int height;
int tempHeight = p.height;
if (tempHeight > 0) {
height = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(tempHeight,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
height = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
}
view.measure(width, height);
}
/**
* 設置header布局 上邊距;
*/
private void topPadding(int topPadding) {
header.setPadding(header.getPaddingLeft(), topPadding,
header.getPaddingRight(), header.getPaddingBottom());
header.invalidate();
}
}
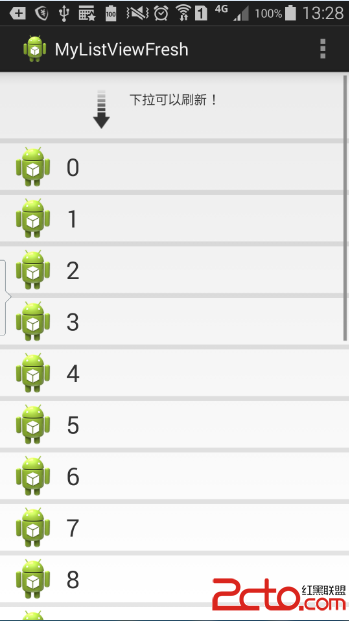
如果去除注釋,header就被隱藏。
思路:
添加屏幕觸摸監聽和屏幕滾動監聽。
觸摸監聽尤其重要:
在觸摸時記錄下觸摸坐標的Y值即startY,然後在移動過程中監聽當前的Y值,根據兩者的插值判斷當前的移動距離,與一些臨界值做比較。
比較之後得出當前的狀態:提示下拉狀態、提示釋放狀態、刷新狀態。根據當前的狀態來刷新header布局的顯示情況。
滾動監聽的作用是判斷當前是否是列表的頂端(通過判斷當前可見的第一個item的position是否為0),以及在之後判斷屏幕的滾動狀態。
另外在自定義的Listview類中定義了一個接口,在mainactivity中實現這個接口,用來對數據進行刷新。我們在刷新的時候用了Handler延遲了兩秒,以清晰地看到刷新的效果。
修改後的MainActivity以及ListView:
ListView: (裡面很多注釋,自己看著應該很好理解)
public class RefreshListView extends ListView implements OnScrollListener {
View header;// 頂部布局文件;
int headerHeight;// 頂部布局文件的高度;
int firstVisibleItem;// 當前第一個可見的item的位置;
int scrollState;// listview 當前滾動狀態;
boolean isRemark;// 標記,當前是在listview最頂端摁下的;
int startY;// 摁下時的Y值;
int state;// 當前的狀態;
final int NONE = 0;// 正常狀態;
final int PULL = 1;// 提示下拉狀態;
final int RELEASE = 2;// 提示釋放狀態;
final int REFRESHING = 3;// 刷新狀態;
IRefreshListener iRefreshListener;//刷新數據的接口
public RefreshListView(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
initView(context);
}
public RefreshListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
initView(context);
}
public RefreshListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
initView(context);
}
/**
* 初始化界面,添加頂部布局文件到 listview
*
* @param context
*/
private void initView(Context context) {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
header = inflater.inflate(R.layout.header, null);
measureView(header);
headerHeight = header.getMeasuredHeight();
Log.i("tag", "headerHeight = " + headerHeight);
topPadding(-headerHeight);
this.addHeaderView(header);
this.setOnScrollListener(this);
}
/**
* 通知父布局,占用的寬,高;
*
* @param view
*/
private void measureView(View view) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams p = view.getLayoutParams();
if (p == null) {
p = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
int width = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(0, 0, p.width);
int height;
int tempHeight = p.height;
if (tempHeight > 0) {
height = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(tempHeight,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
height = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
}
view.measure(width, height);
}
/**
* 設置header 布局 上邊距;
*
* @param topPadding
*/
private void topPadding(int topPadding) {
header.setPadding(header.getPaddingLeft(), topPadding,
header.getPaddingRight(), header.getPaddingBottom());
header.invalidate();
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem,
int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.firstVisibleItem = firstVisibleItem;
}
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.scrollState = scrollState;
}
/**
* 對屏幕觸摸的監控,
* 先判斷當前是否是在頂端。如果是在最頂端,記錄下你開始滑動的Y值
* 然後在滑動過程中(監聽到的是ACTION_MOVE),不斷地判斷當前滑動的范圍是否到達應該刷新的程度。
* (根據當前的Y-之前的startY的值 與我們的控件的高度之間關系來判斷)
* 然後在監聽到手指松開時,根據當前的狀態(我們在onmove()中計算的),做相應的操作。
*/
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch (ev.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (firstVisibleItem == 0) {
isRemark = true;
startY = (int) ev.getY();
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
onMove(ev);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
if (state == RELEASE) {
//即提示松開刷新的狀態,一旦松開,進入到正在刷新;這時候就可以加載數據了!
state = REFRESHING;
// 加載最新數據;
refreshViewByState();
iRefreshListener.onRefresh();
} else if (state == PULL) {
//提示下拉狀態狀態,如果放掉的話,把一切還原,什麼都沒有做
state = NONE;
isRemark = false;
refreshViewByState();
}
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(ev);
}
/**
* 判斷移動過程操作:
* 如果不是頂端,不需要做任何的操作
* 否則就獲取當前的Y值,與開始的Y值做比較。
* 判斷下拉的高度,與我們定義的一些臨界值做判斷(其實這個臨界值你可以自己定義)
*
* @param ev
*/
private void onMove(MotionEvent ev) {
if (!isRemark) {
return;
}
int tempY = (int) ev.getY();
int space = tempY - startY;
int topPadding = space - headerHeight;
switch (state) {
case NONE:
if (space > 0) {
state = PULL; //正在下拉
refreshViewByState();
}
break;
case PULL:
topPadding(topPadding);
//如果大於一定高度,並且滾動狀態是正在滾動時,就到了松開可以刷新的狀態
if (space > headerHeight + 30
&& scrollState == SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL) {
state = RELEASE;
refreshViewByState();
}
break;
case RELEASE:
topPadding(topPadding);
//在提示松開刷新時,如果你往上拖,距離小於一定高度時,提示下拉可以刷新
if (space < headerHeight + 30) {
state = PULL;
refreshViewByState();
}
break;
}
}
/**
* 根據當前狀態,改變界面顯示;
*/
private void refreshViewByState() {
//如果要提高性能,這些應該在oncreate中寫,但是。。那裡面參數太多了,為了大家讀代碼更舒服,就寫在這裡了。
TextView tip = (TextView) header.findViewById(R.id.tip);
ImageView arrow = (ImageView) header.findViewById(R.id.arrow);
ProgressBar progress = (ProgressBar) header.findViewById(R.id.progress);
RotateAnimation anim = new RotateAnimation(0, 180,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f);
anim.setDuration(500);
anim.setFillAfter(true);
RotateAnimation anim1 = new RotateAnimation(180, 0,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f);
anim1.setDuration(500);
anim1.setFillAfter(true);
switch (state) {
case NONE: //正常狀態不顯示
arrow.clearAnimation();
topPadding(-headerHeight);
break;
case PULL: //下拉狀態顯示箭頭,隱藏進度條,以下的狀態也類似。自己根據實際情況去修改。
arrow.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
progress.setVisibility(View.GONE);
tip.setText("下拉可以刷新!");
arrow.clearAnimation();
arrow.setAnimation(anim1);
break;
case RELEASE:
arrow.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
progress.setVisibility(View.GONE);
tip.setText("松開可以刷新!");
arrow.clearAnimation();
arrow.setAnimation(anim);
break;
case REFRESHING:
topPadding(50);
arrow.setVisibility(View.GONE);
progress.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
tip.setText("正在刷新...");
arrow.clearAnimation();
break;
}
}
/**
* 獲取完數據之後
*/
public void refreshComplete() {
state = NONE;
isRemark = false;
refreshViewByState();
TextView lastupdatetime = (TextView) header
.findViewById(R.id.lastupdate_time);
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
String time = format.format(date);
lastupdatetime.setText(time);
}
public void setInterface(IRefreshListener iRefreshListener){
this.iRefreshListener = iRefreshListener;
}
/**
* 刷新數據接口
* @author Administrator
*/
public interface IRefreshListener{
public void onRefresh();
}
}
MainActivity: (添加了接口回調,即在listview中調用main的添加數據的方法)
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements IRefreshListener {
private RefreshListView listView;
private SimpleAdapter simple_adapter;
private List> list;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
listView = (RefreshListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
iniData(); //初始化數據,我們給它加20條Item
// 設置SimpleAdapter監聽器
/**
* SimpleAdapter的五個參數的含義:
* 第一個:context上下文
* 第二個:用於顯示的數據,map的list
* 第三個:Item的布局,即我們自定義的那個文件
* 第四個:與第二個參數緊密聯系,與第五個緊密聯系,是在map中的鍵值
* 第五個:我們看到是id(int類型)的數組,這個數組裡的東西是哪裡來的?是我們自己在布局文件中定義的,忘記的讀者可以回過頭去看一下
* 這幾個參數獨立開來可能不知道是干嗎的,但是我覺得聯合在一起就挺好理解了。
*/
simple_adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this, list,
R.layout.listview_item, new String[] { "image", "text" },
new int[] { R.id.image, R.id.text });
//設置適配器
listView.setAdapter(simple_adapter);
//設置更新數據的接口
listView.setInterface(this);
}
// 初始化SimpleAdapter數據集
private List> iniData() {
list = new ArrayList>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Map map = new HashMap();
//解釋下這裡的數據,key對應SimpleAdapter的第三個參數,必須都包含它們。值對應第五個參數,分別是圖片和文字
map.put("text", i);
map.put("image", R.drawable.ic_launcher);
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
/**
* 接口回調,在RefreshListView中可以調用此方法進行數據添加。
*/
@Override
public void onRefresh() {
// TODO 自動生成的方法存根
Handler handler = new Handler();
handler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("text", "滾動添加 ");
map.put("image", R.drawable.ic_launcher);
list.add(0, map);
listView.setAdapter(simple_adapter);
simple_adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
listView.refreshComplete();
}
}, 2000);
}
}
 Android Content Provider在應用程序之間共享數據的原理分析
Android Content Provider在應用程序之間共享數據的原理分析
本文參考Android應用程序組件Content Provider在應用程序之間共享數據的原理分析http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/ar
 android 手機SD卡讀寫操作(以txt文本為例)實現步驟
android 手機SD卡讀寫操作(以txt文本為例)實現步驟
1、首先對manifest注冊SD卡讀寫權限 要說明一下,我這裡沒有用MainActivity.class作為軟件入口 復制代碼 代碼如下: AndroidManifes
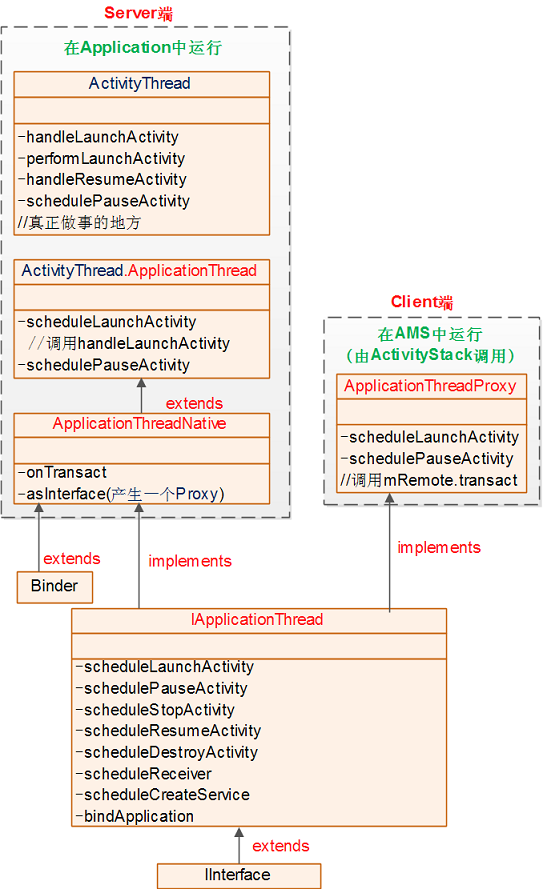 Android 6.0 應用啟動全流程源碼分析
Android 6.0 應用啟動全流程源碼分析
今天是國慶,首先祝大家國慶快樂!漫漫國慶長假,然而我卻只能宅宿捨,但時間總不能這樣白白浪費了,這樣的時候,沒出去浪,那麼,就總結一下前段時間通過Android源碼分析了一
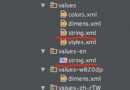 Android app應用多語言切換功能實現
Android app應用多語言切換功能實現
本文實例為大家分享了Android app應用實現多語言切換功能,供大家參考,具體內容如下1.添加多語言文件 在不同的 value 文件夾下(例如 value 、valu